
1.
Prepare a table to allocate the costs incurred by Company M.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Lump-Sum purchase:
If a company purchases a group of assets collectively and a lump sum amount is paid for such purchase, then it is referred to as basket purchase. The accounting term for this type of acquisition is the lump-sum purchase.
Compute the total cost of the assets as follows:
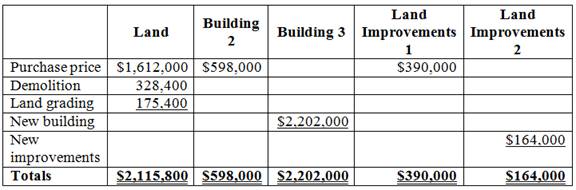
Table (1)
Prepare a table to allocate the costs incurred by Company M as follows:
| Assets | Fair Market Value (in $) | Percent of total= | Allocation of the purchase price based on the percentage of total |
| Land | 1,736,000 | 1,612,000 | |
| Building 2 | 644,000 | 598,000 | |
| Land Improvements 1 | 420,000 | 390,000 | |
| Total | $2,80,000 | $2,600,000 |
Table (2)
2.
Prepare a single
2.
Explanation of Solution
Depreciation expense is a non-cash expense, which is recorded on the income statement reflecting the consumption of economic benefits of long-term asset on account of its wear and tear or obsolescence.
Prepare journal entry to record the purchase as follows:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| January 1, 2015 | Land | 2,115,800 | |
| Land improvements 1 | 390,000 | ||
| Land Improvements 2 | 164,000 | ||
| Building 2 | 598,000 | ||
| Building 3 | 2,202,000 | ||
| Cash | 5,469,800 | ||
| (To record the costs of lump-sum purchase) |
Table (3)
- Land is an asset account and it is increased. Therefore, debit land account.
- Land Improvements are the asset account and they are increased. Therefore, debit land improvements account.
- Building is an asset account and it is increased. Therefore debit building account.
- Cash is an asset account and it is decreased. Therefore credit cash account.
3.
Prepare the December 31
3.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the December 31 adjusting entries to record depreciation of the assets for the year 2015 as follows:
Adjusting entry to record the depreciation of Building 2 for the year 2015:
| Date | Account title and Explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit (In $) |
Credit (In $) |
| December 31, 2015 | Depreciation expense | 26,900 | ||
| | 26,900 | |||
| (To record the depreciation expense) |
Table (4)
Working Note:
Calculate the depreciation expense.
- Depreciation expense is a component of
retained earnings . It decreases the retained earnings. Thus, depreciation expense is debited. - Accumulated depreciation is a contra asset which decreases the value of the asset. Increase in accumulated depreciation decreases the asset’s value. Thus, accumulated depreciation on equipment is credited.
Adjusting entry to record the depreciation of Building 3 for the year 2015:
| Date | Account title and Explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit (In $) |
Credit (In $) |
| December 31, 2015 | Depreciation expense | 72,400 | ||
| Accumulated depreciation | 72,400 | |||
| (To record the depreciation expense) |
Table (5)
Working Note:
Calculate the depreciation expense.
- Depreciation expense is a component of retained earnings. It decreases the retained earnings. Thus, depreciation expense is debited.
- Accumulated depreciation is a contra asset which decreases the value of the asset. Increase in accumulated depreciation decreases the asset’s value. Thus, accumulated depreciation on equipment is credited.
Adjusting entry to record the depreciation of Land Improvements 1 for the year 2015:
| Date | Account title and Explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit (In $) |
Credit (In $) |
| December 31, 2015 | Depreciation expense | 32,500 | ||
| Accumulated depreciation | 32,500 | |||
| (To record the depreciation expense) |
Table (6)
Working Note:
Calculate the depreciation expense.
- Depreciation expense is a component of retained earnings. It decreases the retained earnings. Thus, depreciation expense is debited.
- Accumulated depreciation is a contra asset which decreases the value of the asset. Increase in accumulated depreciation decreases the asset’s value. Thus, accumulated depreciation on equipment is credited.
Adjusting entry to record the depreciation of Land Improvements 2 for the year 2015:
| Date | Account title and Explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit (In $) |
Credit (In $) |
| December 31, 2015 | Depreciation expense | 8,200 | ||
| Accumulated depreciation | 8,200 | |||
| (To record the depreciation expense) |
Table (7)
Working Note:
Calculate the depreciation expense.
- Depreciation expense is a component of retained earnings. It decreases the retained earnings. Thus, depreciation expense is debited.
- Accumulated depreciation is a contra asset which decreases the value of the asset. Increase in accumulated depreciation decreases the asset’s value. Thus, accumulated depreciation on equipment is credited.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING FUND. W/CONNECT
- DC Co. exchanged equipment and $25,000 cash for similar equipment. The book value and fair value of the old equipment were $120,000 and $135,000, respectively. Assuming that the exchange has commercial substance, DC would record a gain/(loss) of __.arrow_forwardPlease show me the valid approach to solving this financial accounting problem with correct methods.arrow_forwardHelp with accounting questionarrow_forward
- Which accounting principle requires that expenses be recorded in the same period as the revenues they help generate?A. Cost PrincipleB. Revenue Recognition PrincipleC. Matching PrincipleD. Full Disclosure Principlearrow_forwardI need guidance with this financial accounting problem using the right financial principles.arrow_forwardWhat is the formula for calculating the weighted average cost of capital (WACC)?A) WACC = (Cost of Debt × Proportion of Debt) + (Cost of Equity × Proportion of Equity)B) WACC = (Cost of Debt + Cost of Equity) / 2C) WACC = Cost of Debt + Cost of EquityD) WACC = Proportion of Debt + Proportion of Equityarrow_forward
- If a company has annual sales of $840,000 with a gross profit margin of 35%, what is the cost of goods sold?arrow_forwardKindly help me with general accounting questionarrow_forwardA business purchased a machine for $120,000 with an estimated useful life of 8 years and salvage value of $24,000. What is the annual straight-line depreciation amount? Helparrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





