
1.
Pass necessary journal entries to record the transactions.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Journal entry is a set of economic events which can be measured in monetary terms. These are recorded chronologically and systematically.
Accounting rules for Journal entries:
- To record increase balance of account: Debit assets, expenses, losses and credit liabilities, capital, revenue and gains.
- To record decrease balance of account: Credit assets, expenses, losses and debit liabilities, capital, revenue and gains.
Pass necessary journal entries to record the transactions.
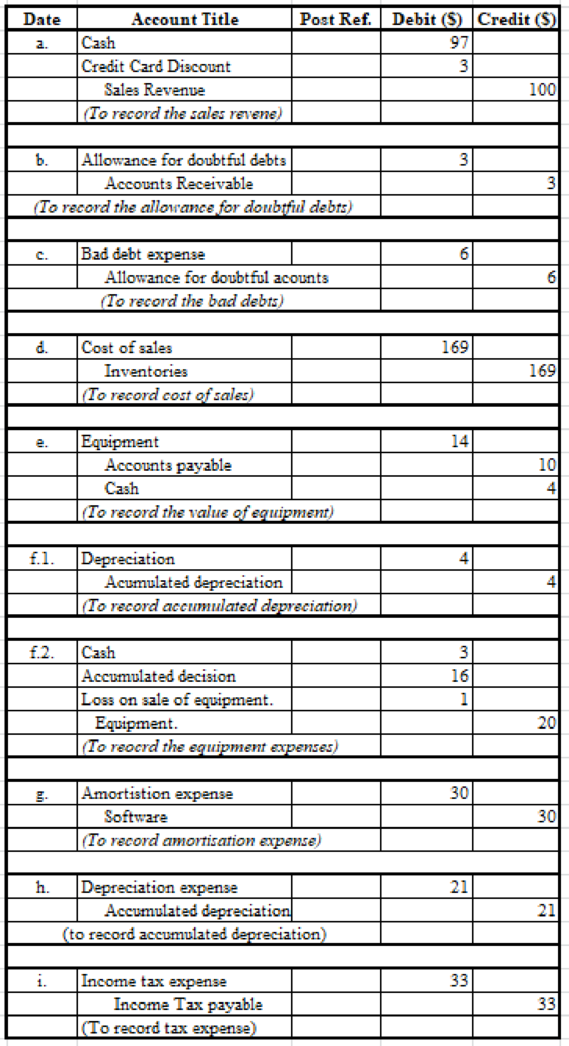
Table (2)
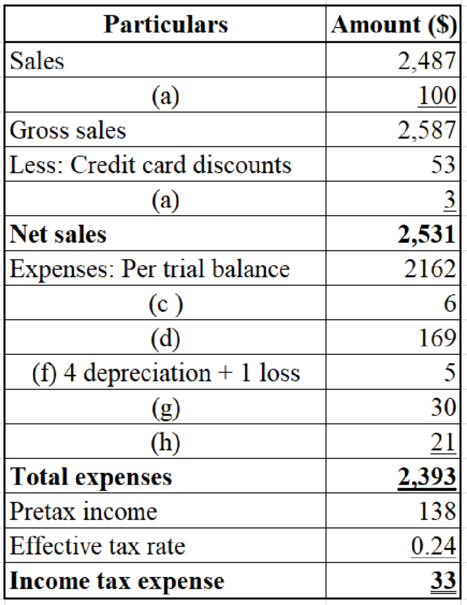
Table (2)
2.
Prepare T accounts using the
2.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare T accounts using the trial balance information and an adjusted trial balance.
| Cash | ||
| Beginning balance 570 | ||
| ||
| f.2 3 | e. 4 | |
| Ending balance 666 | ||
Table (3)
| Beginning balance 373 |
| |
| Ending balance 370 | ||
Table (3)
| Allowance for doubtful accounts | ||
| Balance 570 | ||
| b 3 | c 6 | |
| Balance 21 | ||
Table (3)
| Inventories | ||
| Beginning balance 539 |
| |
| Ending balance 370 | ||
Table (4)
| Prepaid Expenses | ||
| Beginning balance 59 | ||
| Ending balance 59 | ||
Table (5)
| Land | ||
| Beginning balance 22 | ||
| Ending balance 22 | ||
Table (6)
| Building | ||
| Beginning balance 189 | ||
| Ending balance 189 | ||
Table (7)
| Equipment | ||
|
Beginning balance 360
| f.2. 20 | |
| Ending balance 354 | ||
Table (8)
| Balance 222 | ||
| f.1. 4 | ||
| f.2 16 | h. 21 | |
| Balance 231 | ||
Table (9)
| Software | ||
| Beginning balance 90 |
| |
| Ending balance 60 | ||
Table (10)
| Patents | ||
| Beginning balance 1 | ||
| Ending balance 1 | ||
Table (11)
| Beginning balance 161 | ||
| Ending balance 161 | ||
Table (12)
| Accounts Payable | ||
| Balance 252 | ||
| e. 10 | ||
| Balance 262 | ||
Table (13)
| Accrued Liabilities | ||
| Balance 182 | ||
| Balance 182 | ||
Table (14)
| Income Tax Payable | ||
| Balance 16 | ||
| i. 33 | ||
| Balance 49 | ||
Table (15)
| Long term Debt | ||
| Balance 49 | ||
| Balance 49 | ||
Table (16)
| Common Stock | ||
| Balance 3 | ||
| Balance 3 | ||
Table (17)
| Additional paid in capital | ||
| Balance 243 | ||
| Balance 243 | ||
Table (18)
| Balance 1,107 | ||
| Balance 1,107 | ||
Table (19)
| Sales Revenue | ||
|
Balance 2,847 a. 100 | ||
| Balance 2,587 | ||
Table (20)
| Credit Card Discounts | ||
|
Beginning balance 53
| ||
| Ending balance 56 | ||
Table (21)
| Cost of sales | ||
|
Beginning balance 1,306 d. 169 | ||
| Ending balance 1,475 | ||
Table (22)
| Advertising Expense | ||
| Beginning balance 145 | ||
| Ending balance 145 | ||
Table (23)
| Utilities Expense | ||
| Beginning balance 85 | ||
| Ending balance 85 | ||
Table (24)
| Wages Expense | ||
| Beginning balance 625 | ||
| Ending balance 625 | ||
Table (25)
| Depreciation Expense | ||
|
Beginning balance 0 f.1. 4 h. 21 | ||
| Ending balance 25 | ||
Table (26)
| Amortisation Expense | ||
|
Beginning balance 0 g. 30 | ||
| Ending balance 30 | ||
Table (27)
| Interest Expense | ||
| Beginning balance 1 | ||
| Ending balance 1 | ||
Table (28)
|
Beginning balance 0 C 6 | ||
| Ending balance 6 | ||
Table (28)
| Loss of sale of equipment | ||
|
Beginning balance 0 f.2. 1 | ||
| Ending balance 1 | ||
Table (29)
| Income Tax Expense | ||
|
Beginning balance 0 f.2. 33 | ||
| Ending balance 33 | ||
Table (30)
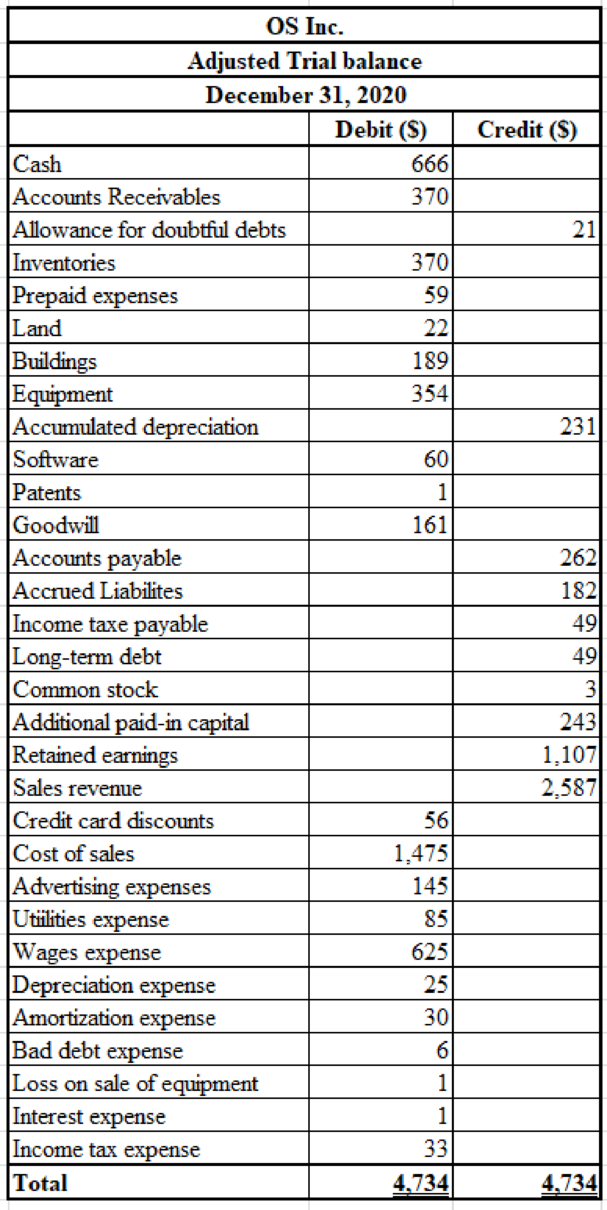
Table (31)
3.
Prepare an income statement, statement of
3.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare an income statement for OS Inc.
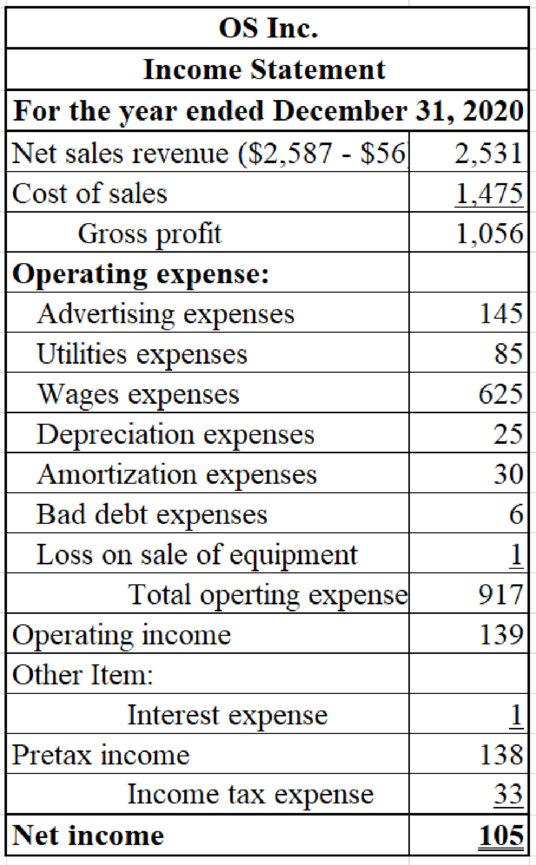
Table (32)
Prepare a statement of stockholders’ equity for OS Inc.
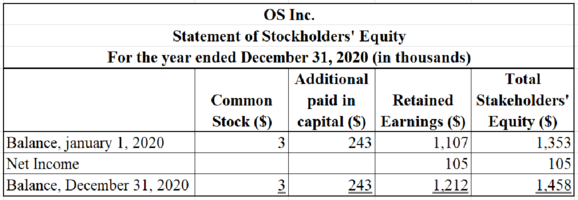
Table (33)
Prepare a balance sheet for OS Inc.
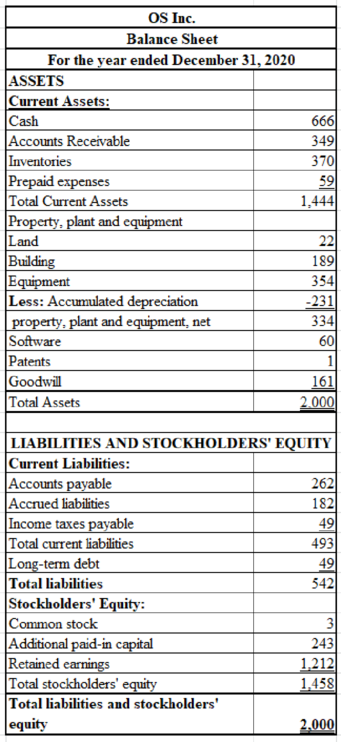
Table (34)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING (LL)-W/CONNECT
- A trial balance will balance even if A. a journal entry to record the purchase of equipment for cash of $52100 is not posted. B. a $13100 cash dividend is debited to dividends for $13100 and credited to cash for $1310. C. a $510 collection on accounts receivable is credited to accounts receivable for $510 without a corresponding debit. D. a purchase of supplies for $595 on account is debited to supplies for $595 and credited to accounts payable for $559.arrow_forwardEquipment costing $15200 is purchased by paying $3800 cash and signing a note payable for the remainder. The journal entry to record this transaction should include a credit to Notes Payable. credit to Notes Receivable. credit to Equipment. debit to Cash.arrow_forwardAt December 1, 2025, a company's Accounts Receivable balance was $20160. During December, the company had credit sales of $54000 and collected accounts receivable of $43200. At December 31, 2025, the Accounts Receivable balance is A. $30960 debit. B. $30960 credit. C. $74160 debit. D. $20160 debit.arrow_forward
- Whispering Winds Corp.'s trial balance at the end of its first month of operations reported the following accounts and amounts with normal balances: Cash $14720 Prepaid insurance 460 Accounts receivable 2300 Accounts payable 1840 Notes payable 2760 Common stock 4600 Dividends 460 Revenues 20240 Expenses 11500 Total credits on Whispering Winds Corp's trial balance are A. $28980. B. $30360. C. $29900. D. $29440arrow_forwardSwifty Corporation's trial balance reported the following normal balances at the end of its first year: Cash $14440 Prepaid insurance 530 Accounts receivable 2660 Accounts payable 2130 Notes payable 3190 Common stock 4100 Dividends 530 Revenues 22040 Expenses 13300 What amount did Swifty Corporation's trial balance show as total credits? A. $31460 B. $32520 C. $30930 D. $31990arrow_forwardMonty Inc., a major retailer of high-end office furniture, operates several stores and is a publicly traded company. The company is currently preparing its statement of cash flows. The comparative statement of financial position and income statement for Monty as at May 31, 2020, are as The following is additional information about transactions during the year ended May 31, 2020 for Monty Inc., which follows IFRS. Plant assets costing $69,000 were purchased by paying $47,000 in cash and issuing 5,000 common shares. In order to supplement its cash, Monty issued 4,000 additional common shares. Cash dividends of $35,000 were declered and paid at the end of the fiscal year. create direct method cash flow statement, show your workarrow_forward
- Following is additional information about transactiona during the year ended May 31, 2020 for Monty Inc., which follows IFRS. Plant assets costing $69,000 were purchased by paying $47,000 in cash and issuing 5,000 common shares. In order to supplement iRs cash, Monty Issued 4,000 additional common shares. Cash dividends of $35,000 were declared and paid at the end of the fiscal year. PRepare a direct Method Cash FLow using the format.arrow_forwardmake a trail balancearrow_forwardOn July 31, 2025, the general ledger of Cullumber Legal Services Inc. showed the following balances: Cash $4,960, Accounts Receivable $1,860, Supplies $620, Equipment $6,200, Accounts Payable $5,080, Common Stock $4,340, and Retained Earnings $4,220. During August, the following transactions occurred. Aug. 3 5 Collected $1,490 of accounts receivable due from customers. Received $1,610 cash for issuing common stock to new investors. 6 Paid $3,350 cash on accounts payable. 7 Performed legal services of $8,060, of which $3,720 was collected in cash and the remainder was due on account. 2 2 2 2 2 12 Purchased additional equipment for $1,490, paying $500 in cash and the balance on account. 14 Paid salaries $4,340, rent $1,120, and advertising expenses $340 for the month of August. 18 20 24 26 27 Collected the balance for the services performed on August 7. Paid cash dividend of $620 to stockholders. Billed a client $1,240 for legal services performed. Received $2,480 from Laurentian Bank;…arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





