
a.
Prepare the journal entries to record cost of goods sold under (1) specific identification method, (2) average-cost method, (3) FIFO method, and (4) LIFO method, and discuss the financial reporting differences that may arise from choosing the FIFO method over the LIFO method.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Journal entry is a set of economic events which can be measured in monetary terms. These are recorded chronologically and systematically.
Rules of Debit and Credit:
Following rules are followed for debiting and crediting different accounts while they occur in business transactions:
- Debit, all increase in assets, expenses and dividends, all decrease in liabilities, revenues and stockholders’ equities.
- Credit, all increase in liabilities, revenues, and stockholders’ equities, all decrease in assets, and expenses.
Perpetual inventory system: The method or system of maintaining, recording, and adjusting the inventory perpetually throughout the year, is referred to as perpetual inventory system.
First-in-First-Out (FIFO): In this method, items purchased initially are sold first. So, the value of the ending inventory consist the recent cost for the remaining unsold items.
Last-in-First-Out (LIFO): In this method, items purchased recently are sold first. So, the value of the ending inventory consist the initial cost for the remaining unsold items.
Average Cost method: In this method, the inventories are priced at the average rate of goods available for sales.
Prepare the journal entries to record cost of goods sold under specific identification method as follows:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit | Credit |
| Cost of goods sold (1) | $30,500 | |||
| Inventory | $30,500 | |||
| (To record the cost of goods sold incurred) |
Table (1)
- Cost of goods sold is an operating expense account and decreases the
stockholders’ equity account by $30,500. Therefore, debit cost of goods account with $30,500. - Inventory is an asset account, and it decreases the value of assets by $30,500. Therefore, credit inventory account with $30,500.
Working note:
Calculate the value of cost of goods sold under separate identification method
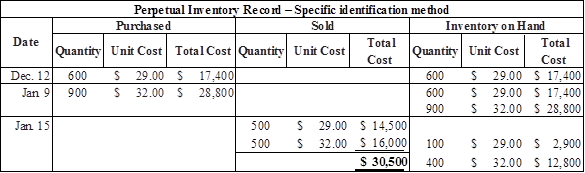
Table (2)
(1)
Prepare the journal entries to record cost of goods sold under average cost method as follows:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit | Credit |
| Cost of goods sold (3) | $30,800 | |||
| Inventory | $30,800 | |||
| (To record the cost of goods sold incurred) |
Table (3)
- Cost of goods sold is an operating expense account and decreases the stockholders’ equity account by $30,800. Therefore, debit cost of goods account with $30,800.
- Inventory is an asset account, and it decreases the value of assets by $30,800. Therefore, credit inventory account with $30,800.
Working note:
Calculate average cost per unit
Calculate the value of cost of goods sold under average cost method
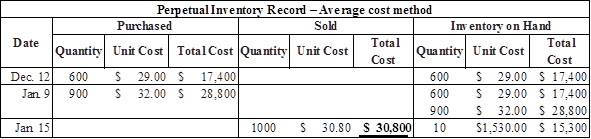
Table (4)
(3)
Prepare the journal entries to record cost of goods sold under FIFO method as follows:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit | Credit |
| Cost of goods sold (4) | $30,200 | |||
| Inventory | $30,200 | |||
| (To record the cost of goods sold incurred) |
Table (5)
- Cost of goods sold is an operating expense account and decreases the stockholders’ equity account by $30,200. Therefore, debit cost of goods account with $30,200.
- Inventory is an asset account, and it decreases the value of assets by $30,200. Therefore, credit inventory account with $30,200.
Working note:
Calculate the value of cost of goods sold under FIFO assets
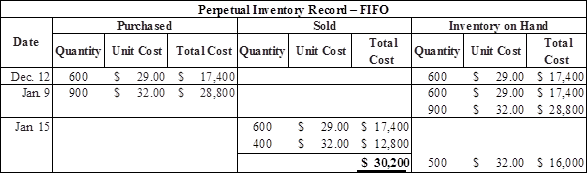
Table (6)
(4)
Prepare the journal entries to record cost of goods sold under LIFO method as follows:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit | Credit |
| Cost of goods sold (5) | $31,700 | |||
| Inventory | $31,700 | |||
| (To record the cost of goods sold incurred) |
Table (7)
- Cost of goods sold is an operating expense account and decreases the stockholders’ equity account by $31,700. Therefore, debit cost of goods account with $31,700.
- Inventory is an asset account, and it decreases the value of assets by $31,700. Therefore, credit inventory account with $31,700.
Working note:
Calculate the value of cost of goods sold under LIFO assets
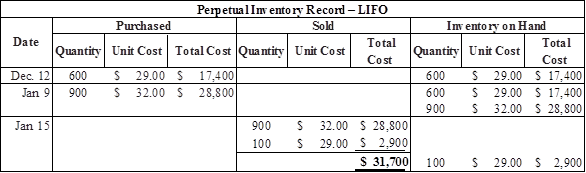
Table (8)
(5)
b.
Prepare the subsidiary ledger record for Company under the four inventory method valuation.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Subsidiary ledger:
Subsidiary ledger refers to the ledger that provides the detailed information of the account already recorded in the general ledger such as
Prepare the subsidiary ledger record for Company under the four inventory method valuation as follows:
(1) Specific identification method:
| PURCHASED | SOLD | BALANCE | |||||||
| Date | Units | Unit Cost | Total | Units | Unit Cost | Cost of Goods Sold | Units | Unit Cost | Balance |
| Dec 12 | 600 | 29 | 17,400 | 600 | 29 | 17,400 | |||
| Jan 09 | 900 | 32 | 28,800 | 600 | 29 | ||||
| 900 | 32 | 46,200 | |||||||
| Jan 15 | 500 | 29 | 100 | 29 | |||||
| 500 | 32 | 30,500 | 400 | 32 | 15,700 | ||||
Table (9)
(2) Average-cost method:
| PURCHASED | SOLD | BALANCE | |||||||
| Date | Units | Cost | Total | Units | Cost | Cost of Goods Sold | Units | Cost | Balance |
| Dec 12 | 600 | 29 | 17,400 | 600 | 29 | 17,400 | |||
| Jan 09 | 900 | 32 | 28,800 | 1,500 | 31 | 46,200 | |||
| Jan 15 | 1,000 | 31 | 30,800 | 500 | 31 | 15,400 | |||
Table (10)
(3) First-in, first-out (FIFO) method:
| PURCHASED | SOLD | BALANCE | |||||||
| Date | Units | Unit Cost | Total | Units | Unit Cost | Cost of Goods Sold | Units | Unit Cost | Balance |
| Dec 12 | 600 | 29 | 17,400 | 600 | 29 | 17,400 | |||
| Jan 09 | 900 | 32 | 28,800 | 600 | 29 | ||||
| 900 | 32 | 46,200 | |||||||
| Jan 15 | 600 | 29 | |||||||
| 400 | 32 | 30,200 | 500 | 32 | 16,000 | ||||
Table (11)
(4) Last-in, first-out (LIFO) method:
| PURCHASED | SOLD | BALANCE | |||||||
| Date | Units | Unit Cost | Total | Units | Unit Cost | Cost of Goods Sold | Units | Unit Cost | Balance |
| Dec 12 | 600 | 29 | 17,400 | 600 | 29 | 17,400 | |||
| Jan 09 | 900 | 32 | 28,800 | 600 | 29 | ||||
| 900 | 32 | 46,200 | |||||||
| Jan 15 | 900 | 32 | |||||||
| 100 | 29 | 31,700 | 500 | 29 | 14,500 | ||||
Table (12)
c.
Explain whether the
c.
Explanation of Solution
Explain whether the inventory valuation method gives lowest cost of goods sold or not, and the valuation method that gives highest cost of goods sold for the tax purposes as follows:
In this case, the cost of goods sold under FIFO and LIFO is $30,200, and $31,700 respectively. Hence, the LIFO method has highest cost of goods sold whereas the FIFO method has the lowest cost of goods sold.
The inventory method that would be preferable for financial statements is FIFO, because FIFO method would produce higher net income, lower cost of goods sold, and higher ending inventory (total assets). At the same time, the higher amount of net income produces the more income tax expense, so LIFO method is preferred for income tax reporting. When a company uses LIFO method it would produce lower amount of tax obligation and higher amount of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Financial Accounting
- Martin Hughes earns net self-employment income of $157,100. He works a second job from which he receives FICA taxable earnings of $127,600.Self-Employment tax =arrow_forwardQuestion 2 U. Richards does not keep his books on the double entry system. His bank summary amount for 2010 is as follows: Balance 1.1.2010 1890 Receipts from $44656 debtors Creditors Loan from U. Miller $2.000 Rates Rent Drawings Cash withdrawn from bank $540 0 Payment to Trade $316 95 2750 1316 3095 1642 Sundry Expense Records of cash paid were sundry $122, trade creditors $642. Cash sales amounted to cash drawings were $5289. The following information is also available: 31.12.201 31.12.2 0 011 Cash in hand $48 $93 Trade creditors $4896 $5091 Accounts Receivables 60 $71 13 32 Rent Owing $250 Rates in Advance $282 $312 Motor van (at valuation) 2800 2400 Stock 11163 13021 Required: A. Statement of Affairs. (to find opening capital as at 31.12.2010) B. Cash Account & Bank Account. C. Accounts Receivables & Accounts Payables Control A/Cs. D. Income Statement for the year ended 31 December 2011.arrow_forward2: Martin Hughes earns net self-employment income of $157,100. He works a second job from which he receives FICA taxable earnings of $127,600. Self-Employment tax = $ 6,440.70 3: Elisa Grant earns net self-employment income of $198,000. She works a second job from which she receives FICA taxable earnings of $100,400. Self-Employment tax = $ 30,294.00arrow_forward
- Cash Accounts Receivable Supplies Prepaid Insurance Equipment Notes Payable Accounts Payable The Lexington Group Unadjusted Trial Balance May 31, 2016 Debit Balances Credit Balances 20,350 37,000 1,100 200 171,175 36,000 26,000 Common Stock 50,000 Retained Earnings 94,150 Dividends 15,000 Fees Earned 429,850 Wages Expense 270,000 Rent Expense 63,000 Advertising Expense 25,200 Miscellaneous Expense 5,100 608,125 636,000arrow_forwardTrial Balance Rocky Mountain Tours Co. is a travel agency. The nine transactions recorded by Rocky Mountain Tours during June 20Y2, its first month of operations, are indicated in the following T accounts: Cash (1) 40,000 (2) 4,000 (7) 13,100 (3) 5,000 (4) 6,175 (6) 6,000 (9) 1,500 Equipment (3) 15,000 Dividends (9) 1,500 Accounts Receivable Accounts Payable Service Revenue (5) 20,500 (7) 13,100 (6) 6,000 (3) 10,000 (5) 20,500 Supplies (2) 4,000 (8) 2,200 Common Stock Operating Expenses (1) 40,000 (4) 6,175 (8) 2,200arrow_forwardQ1: Wyatt Company had three intangible assets at the end of 2024 (end of the fiscal year): Computer software and Web development technology purchased on January 1, 2024, for $70,000. The technology is expected to have a useful life of four years. A patent purchased from R. Jay on January 1, 2024 for a cash cost of $6,000. Jay had registered the patent with the Canadian Intellectual Property Office seven years earlier on January 1, 2017. The cost of the patent is amortized over its legal life. A trademark that was internally developed and registered with the Canadian government for $13,000 on November 1, 2023. Management decided that the trademark has an indefinite life. Required: 1. What is the acquisition cost of each intangible asset? tech 70k patent 6k trademark 13k 2. Compute the amortization of each intangible asset at December 31, 2024. The company does not use contra accounts. (Round the final answers to the nearest whole dollar.) tech 17.5k patent: ???? 3-a.…arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





