
For the digraph shown in Fig. 8-25, find
a. the indegree and outdegree of A.
b. the indegree and outdegree of B.
c. the indegree and outdegree of D.
d. the sum of the indegrees of all the vertices.
e. the sum of the outdegrees of all the vertices.
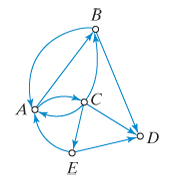
Figure 8-25
(a)
To find:
The in degree and out degree of A in the given digraph.
Answer to Problem 1E
Solution:
The in degree of A is 3 and out degree of A is 2.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given digraph is shown in figure (1).
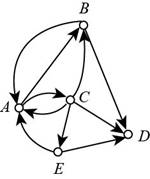
Figure (1)
Definitions:
Arc:
An arc
Indegree:
For a vertex Y, the number of arcs having Y as their ending vertex is called indegree.
Outdegree:
For a vertex X, the number of arcs having X as their starting vertex is called outdegree.
Calculation:
From figure (1) it can be noticed that there are 3 arcs having their ending vertex as A and 2 arcs having their starting vertex as A.
So, the indegree of A is 3 and outdegree of A is 2.
Conclusion:
Thus, the indegree of A is 3 and outdegree of A is 2.
(b)
To find:
The in degree and out degree of B in the given digraph.
Answer to Problem 1E
Solution:
The in degree of B is 2 and out degree of B is 2.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given digraph is shown in figure (2).
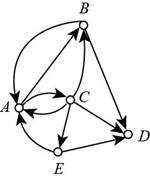
Figure (2)
Definitions:
Arc:
An arc
Indegree:
For a vertex Y, the number of arcs having Y as their ending vertex is called indegree.
Outdegree:
For a vertex X, the number of arcs having X as their starting vertex is called outdegree.
Calculation:
From figure (2) it can be noticed that there are 2 arcs having their ending vertex as B and 2 arcs having their starting vertex as B.
So, the indegree of B is 2 and outdegree of A is 2.
Conclusion:
Thus, the indegree of B is 2 and outdegree of B is 2.
(c)
To find:
The in degree and out degree of D in the given digraph.
Answer to Problem 1E
Solution:
The in degree of D is 3 and out degree of D is 0.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given digraph is shown in figure (3).
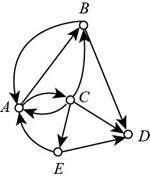
Figure (3)
Definitions:
Arc:
An arc
Indegree:
For a vertex Y, the number of arcs having Y as their ending vertex is called indegree.
Outdegree:
For a vertex X, the number of arcs having X as their starting vertex is called outdegree.
Calculation:
From figure (3) it can be noticed that there are 3 arcs having their ending vertex as D and no arc having their starting vertex as D.
So, the indegree of D is 3 and outdegree of D is 0.
Conclusion:
Thus, the indegree of D is 3 and outdegree of D is 0.
(d)
To find:
The sum of the in degrees of all the vertices.
Answer to Problem 1E
Solution:
The sum of all the indegrees is 10.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given digraph is shown in figure (4).

Figure (4)
Definitions:
Arc:
An arc
Indegree:
For a vertex Y, the number of arcs having Y as their ending vertex is called indegree.
Outdegree:
For a vertex X, the number of arcs having X as their starting vertex is called outdegree.
Calculation:
From figure (4) it can be noticed that there total 10 arcs, so there will be total 10 indegrees for all the vertices.
Conclusion:
Thus, the sum of all the indegrees is 10.
(e)
To find:
The sum of the out degrees of all the vertices.
Answer to Problem 1E
Solution:
The sum of all the outdegrees is 10.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given digraph is shown in figure (5).

Figure (5)
Definitions:
Arc:
An arc
Indegree:
For a vertex Y, the number of arcs having Y as their ending vertex is called indegree.
Outdegree:
For a vertex X, the number of arcs having X as their starting vertex is called outdegree.
Calculation:
From figure (5) it can be noticed that there total 10 arcs, so there will be total 10 outdegrees for all the vertices.
Conclusion:
Thus, the sum of all the outdegrees is 10.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Excursions in Modern Mathematics, Books a la carte edition (9th Edition)
- Consider a body of mass m dropped from rest at t = 0. The body falls under the influence of gravity, and the air resistance FD opposing the motion is assumed to be proportional to the square of the velocity, so that FD = kV2. Call x the vertical distance and take the positive direction of the x-axis downward, with origin at the initial position of the body. Obtain relationships for the velocity and position of the body as a function of time t.arrow_forwardAssuming that the rate of change of the price P of a certain commodity is proportional to the difference between demand D and supply S at any time t, the differential equations describing the price fluctuations with respect to time can be expressed as: dP/dt = k(D - s) where k is the proportionality constant whose value depends on the specific commodity. Solve the above differential equation by expressing supply and demand as simply linear functions of price in the form S = aP - b and D = e - fParrow_forwardFind the area of the surface obtained by rotating the circle x² + y² = r² about the line y = r.arrow_forward
- 3) Recall that the power set of a set A is the set of all subsets of A: PA = {S: SC A}. Prove the following proposition. АСВ РАСРВarrow_forwardA sequence X = (xn) is said to be a contractive sequence if there is a constant 0 < C < 1 so that for all n = N. - |Xn+1 − xn| ≤ C|Xn — Xn−1| -arrow_forward3) Find the surface area of z -1≤ y ≤1 = 1 + x + y + x2 over the rectangle −2 ≤ x ≤ 1 and - Solution: TYPE YOUR SOLUTION HERE! ALSO: Generate a plot of the surface in Mathematica and include that plot in your solution!arrow_forward
- 7. Walkabout. Does this graph have an Euler circuit? If so, find one. If not, explain why not.arrow_forwardBelow, let A, B, and C be sets. 1) Prove (AUB) nC = (ANC) U (BNC).arrow_forwardQ1: find the Reliability of component in the system in fig(1) by minimal cut method. Q2: A component A with constant failure rate 1.5 per 1000 h, B per to 2 in 1000h, A and B in parallel, find the Reliability system? [ by exponential distribution]. Q3: Give an example to find the minimal path and estimate the reliability of this block diagram. Q4: By Tie set method find the Reliability of fig (2) FUZarrow_forward
- A sequence X = (xn) is said to be a contractive sequence if there is a constant 0 < C < 1 so that for all n = N. - |Xn+1 − xn| ≤ C|Xn — Xn−1| -arrow_forward1) Suppose continuous random variable X has sample space S = [1, ∞) and a pdf of the form f(x) = Ce-(2-1)/2. What is the expected value of X?arrow_forwardA sequence X = (xn) is said to be a contractive sequence if there is a constant 0 < C < 1 so that for all n = N. - |Xn+1 − xn| ≤ C|Xn — Xn−1| -arrow_forward

 College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781285195728Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. SchwittersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781285195728Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. SchwittersPublisher:Cengage Learning Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell





