
a.
Prepare the journal entries to record cost of goods sold under (1) specific identification method, (2) average-cost method, (3) FIFO method, and (4) LIFO method, and discuss the financial reporting differences that may arise from choosing the FIFO method over the LIFO method.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Journal entry is a set of economic events which can be measured in monetary terms. These are recorded chronologically and systematically.
Rules of Debit and Credit:
Following rules are followed for debiting and crediting different accounts while they occur in business transactions:
- Debit, all increase in assets, expenses and dividends, all decrease in liabilities, revenues and stockholders’ equities.
- Credit, all increase in liabilities, revenues, and stockholders’ equities, all decrease in assets, and expenses.
Perpetual inventory system: The method or system of maintaining, recording, and adjusting the inventory perpetually throughout the year, is referred to as perpetual inventory system.
First-in-First-Out (FIFO): In this method, items purchased initially are sold first. So, the value of the ending inventory consist the recent cost for the remaining unsold items.
Last-in-First-Out (LIFO): In this method, items purchased recently are sold first. So, the value of the ending inventory consist the initial cost for the remaining unsold items.
Average Cost method: In this method, the inventories are priced at the average rate of goods available for sales.
Prepare the journal entries to record cost of goods sold under specific identification method as follows:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit | Credit |
| Cost of goods sold (1) | $14,800 | |||
| Inventory | $14,800 | |||
| (To record the cost of goods sold incurred) |
Table (1)
- Cost of goods sold is an operating expense account and decreases the
stockholders’ equity account by $14,800. Therefore, debit cost of goods account with $14,800. - Inventory is an asset account, and it decreases the value of assets by $14,800. Therefore, credit inventory account with $14,800.
Working note:
Calculate the value of cost of goods sold under separate identification method
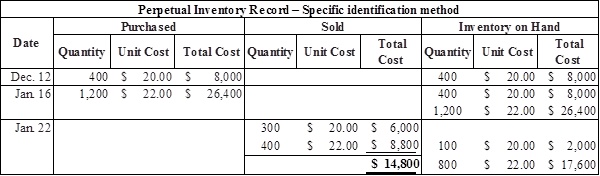
Table (2)
(1)
Prepare the journal entries to record cost of goods sold under average cost method as follows:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit | Credit |
| Cost of goods sold (3) | $15,050 | |||
| Inventory | $15,050 | |||
| (To record the cost of goods sold incurred) |
Table (3)
- Cost of goods sold is an operating expense account and decreases the stockholders’ equity account by $15,050. Therefore, debit cost of goods account with $15,050.
- Inventory is an asset account, and it decreases the value of assets by $15,050. Therefore, credit inventory account with $15,050.
Working note:
Calculate average cost per unit
Calculate the value of cost of goods sold under average cost method
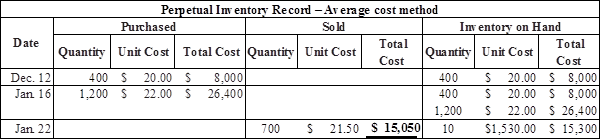
Table (4)
(3)
Prepare the journal entries to record cost of goods sold under FIFO method as follows:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit | Credit |
| Cost of goods sold (4) | $14,600 | |||
| Inventory | $14,600 | |||
| (To record the cost of goods sold incurred) |
Table (5)
- Cost of goods sold is an operating expense account and decreases the stockholders’ equity account by $14,600. Therefore, debit cost of goods account with $14,600.
- Inventory is an asset account, and it decreases the value of assets by $14,600. Therefore, credit inventory account with $14,600.
Working note:
Calculate the value of cost of goods sold under FIFO assets
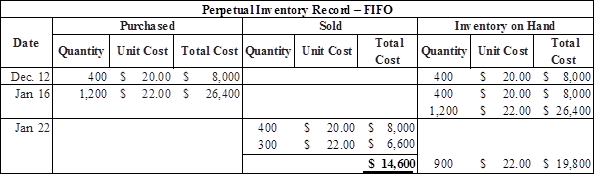
Table (6)
(4)
Prepare the journal entries to record cost of goods sold under LIFO method as follows:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit | Credit |
| Cost of goods sold (5) | $15,400 | |||
| Inventory | $15,400 | |||
| (To record the cost of goods sold incurred) |
Table (7)
- Cost of goods sold is an operating expense account and decreases the stockholders’ equity account by $15,400. Therefore, debit cost of goods account with $15,400.
- Inventory is an asset account, and it decreases the value of assets by $15,400. Therefore, credit inventory account with $15,400.
Working note:
Calculate the value of cost of goods sold under LIFO assets
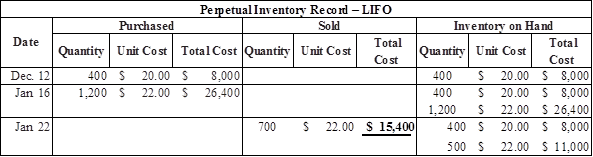
Table (8)
(5)
b.
Prepare the subsidiary ledger record for Company under the four inventory method valuation.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Subsidiary ledger:
Subsidiary ledger refers to the ledger that provides the detailed information of the account already recorded in the general ledger such as
Prepare the subsidiary ledger record for Company under the four inventory method valuation as follows:
(1) Specific identification method:
| PURCHASED | SOLD | BALANCE | |||||||
| Date | Units | Unit Cost | Total | Units | Unit Cost | Cost of Goods Sold | Units | Unit Cost | Balance |
| Dec 12 | 400 | 20 | 8,000 | 400 | 20 | 8,000 | |||
| Jan 16 | 1,200 | 22 | 26,400 | 400 | 20 | ||||
| 1,200 | 22 | 34,400 | |||||||
| Jan 22 | 300 | 20 | 100 | 20 | |||||
| 400 | 22 | 14,800 | 800 | 22 | 19,600 | ||||
Table (9)
(2) Average-cost method:
| PURCHASED | SOLD | BALANCE | |||||||
| Date | Units | Cost | Total | Units | Cost | Cost of Goods Sold | Units | Cost | Balance |
| Dec 12 | 400 | 20 | 8,000 | 400 | 20.00 | 8,000 | |||
| Jan 16 | 1,200 | 22 | 26,400 | 1,600 | 21.50 | 34,400 | |||
| Jan 22 | 700 | $ 21.50 | $ 15,050 | 900 | 21.50 | 19,350 | |||
Table (10)
(3) First-in, first-out (FIFO) method:
| PURCHASED | SOLD | BALANCE | |||||||
| Date | Units | Unit Cost | Total | Units | Unit Cost | Cost of Goods Sold | Units | Unit Cost | Balance |
| Dec 12 | 400 | 20 | 8,000 | 400 | 20 | $ 8,000 | |||
| Jan 16 | 1,200 | 22 | 26,400 | 400 | 20 | ||||
| 1,200 | 22 | 34,400 | |||||||
| Jan 22 | 400 | 20 | |||||||
| 300 | 22 | 14,600 | 900 | 22 | 19,800 | ||||
Table (11)
(4) Last-in, first-out (LIFO) method:
| PURCHASED | SOLD | BALANCE | |||||||
| Date | Units | Unit Cost | Total | Units | Unit Cost | Cost of Goods Sold | Units | Unit Cost | Balance |
| Dec 12 | 400 | 20 | 8,000 | 400 | 20 | 8,000 | |||
| Jan 16 | 1,200 | 22 | 26,400 | 400 | 20 | ||||
| 1,200 | 22 | 34,400 | |||||||
| Jan 22 | 700 | 22 | 15,400 | 400 | 20 | ||||
| 500 | 22 | 19,000 | |||||||
Table (12)
c.
Explain whether the
c.
Explanation of Solution
Explain whether the inventory valuation method gives lowest cost of goods sold or not, and the valuation method that gives highest cost of goods sold for the tax purposes as follows:
In this case, the cost of goods sold under FIFO and LIFO is $14,600, and $15,400 respectively. Hence, the LIFO method has highest cost of goods sold whereas the FIFO method has the lowest cost of goods sold.
The inventory method that would be preferable for financial statements is FIFO, because FIFO method would produce higher net income, lower cost of goods sold, and higher ending inventory (total assets). At the same time, the higher amount of net income produces the more income tax expense, so LIFO method is preferred for income tax reporting. When a company uses LIFO method it would produce lower amount of tax obligation and higher amount of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Financial Accounting
- C&L Estates is developing a lakeside community that includes 300 homelots; 140 lots are lakefront lots and will sell for $110,000 each; 160 are interior lots and will sell for $70,000 each. The developer acquired the landfor $2,100,000 and spent another $1,800,000 on road and utility improvements. Compute the amount of joint cost to be allocated to the lakefront lots using a value basis.arrow_forwardCan you help me with General accounting question?arrow_forwardNeed helparrow_forward
- ABC Company has December unit sales of 12,000 units. Assuming a 5 percent growth, what is the projected unit sales? Helparrow_forwardI need help with this problem and accounting questionarrow_forwardMason Enterprises reported its highest total cost as $ ninety-two thousandin August. Its lowest total cost was $ seventy-four thousand in February. The company produces a single product. Production volumes in August and Februarywere 20,000 units and 11,000 units, respectively. What is the fixed cost per month?arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





