
1.
Record the journal entries for given transactions.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Rules of Debit and Credit:
Following rules are followed for debiting and crediting different accounts while they occur in business transactions:
- Debit, all increase in assets, expenses and dividends, all decrease in liabilities, revenues and stockholders’ equities.
- Credit, all increase in liabilities, revenues, and stockholders’ equities, all decrease in assets, and expenses.
The journal entries for given transactions of Company ACME are as follows:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Debit($) | Credit($) | |
| 2021 | Cash | 8,000 | ||
| January 2 | Deferred Revenue | 8,000 | ||
| (To record the sale of gift cards for cash) | ||||
| 2021 | Inventory | 147,000 | ||
| January, 6 | Accounts payable | 147,000 | ||
| (To record purchase of inventory on account) | ||||
| 2021 | 135,000 | |||
| January 15 | Sales Revenue | 135,000 | ||
| (To record sales of inventory on account) | ||||
| Cost of goods sold | 73,800 | |||
| Inventory | 73,800 | |||
| (To record the cost of inventory sold) | ||||
| 2021 | ||||
|
January 23 | Cash | 125,400 | ||
| Accounts Receivable | 125,400 | |||
| (To record cash on account) | ||||
| 2021 | Accounts Payable | 90,000 | ||
| January 25 | Cash | 90,000 | ||
| (To record pay of cash ) | ||||
| 2021 | Allowance for uncollectible accounts | 4,800 | ||
| January 28 | Accounts Receivable | 4,800 | ||
| (To record the written off of uncollectible accounts) | ||||
| 2021 | Cash | 11,000 | ||
| January 30 | Accounts Receivable | 132,000 | ||
| Sales Revenue | 143,000 | |||
| ( To record sale of inventory for cash) | ||||
| Cost of goods sold | 79,500 | |||
| Inventory | 79,500 | |||
| (To record cost of inventory sold during the year) | ||||
| 2021 | Salaries Expense | 52,000 | ||
| January 31 | Cash | 52,000 | ||
| (To record payment of salaries) | ||||
Table (1)
2.
Record the given
2.
Explanation of Solution
Adjusting entries: Adjusting entries are those entries which are recorded at the end of the year, to update the income statement accounts (revenue and expenses) and
Adjusting entries of Company ACME are as follows:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Debit($) | Credit($) | |
| 2021 | a. | 500 | ||
| January 31 | 500 | |||
| (To record the depreciation for January) | ||||
| 2021 | b. | 12,500 | ||
| January 31 | Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts | 12,500 | ||
| (To record adjusting entry for uncollectible accounts) | ||||
| 2021 | c. Interest Expense (5) | 250 | ||
| January 31 | Interest Payable | 250 | ||
| (To record the adjusting entry for interest expense) | ||||
| 2021 | d. Income Tax Expense | 13,000 | ||
| January 31 | Income Tax Payable | 13,000 | ||
| (To record the adjusting entry for income taxes) | ||||
| 2021 | e. Deferred Revenue | 3,000 | ||
| January 31 | Sales Revenue | 3,000 | ||
| (To record the deferred revenue for the gift cards redeemed) | ||||
Table (2)
Working Notes:
Calculate the depreciation on the equipment.
Calculate the ending balance of uncollectible accounts.
(2)
Calculate the closing balance of accounts receivable account
Calculate the bad debt expense
Calculate the Interest expense.
3.
Prepare the adjusted trial balance for the month January 31, 2021.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Trial balance: Trial balance is a summary of all the ledger accounts balances presented in a tabular form with two column, debit and credit. It checks the mathematical accuracy of the ledger postings and helps preparing the final accounts.
Prepare the adjusted trial balance for the month January 31, 2021 as follows:
| Company ACME | ||
| Adjusted Trial Balance | ||
| January 31, 2021 | ||
| Accounts (Refer table 4) | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | 27,500 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 183,000 | |
| Inventory | 13,700 | |
| Land | 46,000 | |
| Equipment | 15,000 | |
| Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts | 11,900 | |
| Accumulated Depreciation | 2,000 | |
| Accounts Payable | 85,500 | |
| Deferred Revenue | 5,000 | |
| Interest Payable | 250 | |
| Income Tax Payable | 13,000 | |
| Notes Payable | 50,000 | |
| Common Stock | 35,000 | |
| Retained Earnings | 33,100 | |
| Sales Revenue | 281,000 | |
| Cost of Goods Sold | 153,300 | |
| Salaries Expense | 52,000 | |
| Bad Debt Expense | 12,500 | |
| Depreciation Expense | 500 | |
| Interest Expense | 250 | |
| Income Tax Expense | 13,000 | |
| Totals | $516,750 | $516,750 |
Table (3)
Calculation of adjusted trial balance of Company ACME for the month January:
| Accounts | Ending Balance | = | |
| Cash | $27,500 | = | |
| Accounts Receivable | 183,000 | = | |
| Inventory | 13,700 | = | |
| Land | 46,000 | = | 46,000 |
| Equipment | 15,000 | = | 15,000 |
| Allow for Uncollectible Accounts | 11,900 | = | |
| Accumulated Depreciation | 2,000 | = | |
| Accounts Payable | 85,500 | = | |
| Deferred Revenue | 5,000 | = | |
| Interest Payable | 250 | = | 250 |
| Income Tax Payable | 13,000 | = | 13,000 |
| Notes Payable | 50,000 | = | 50,000 |
| Common Stock | 35,000 | = | 35,000 |
| Retained Earnings | 33,100 | = | 33,100 |
| Sales Revenue | 281,000 | = | |
| Cost of Goods Sold | 153,300 | = | |
| Salaries Expense | 52,000 | = | 52,000 |
| Bad Debt Expense | 12,500 | = | 12,500 |
| Depreciation Expense | 500 | = | 500 |
| Interest Expense | 250 | = | 250 |
| Income Tax Expense | 13,000 | = | 13,000 |
Table (4)
4.
Prepare the multiple income statement for the period ended January 31, 2021.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Multi-step income statement: The income statement represented in multi-steps with several subtotals, to report the income from principal operations, and separate the other expenses and revenues which affect net income, is referred to as multi-step income statement.
Prepare the multiple income statement for the period ended January 31, 2021 as follows:
| Company ACME | ||
| Multiple-Step Income Statement | ||
| For the year ended January 31, 2021 | ||
| Particulars | $ | $ |
| Sales revenue | $281,000 | |
| Cost of goods sold | 153,300 | |
| Gross profit | $127,700 | |
| Less: Salaries expense | 52,000 | |
| Bad debt expense | 12,500 | |
| Depreciation expense | 500 | |
| Total operating expenses | 65,000 | |
| Operating income | 62,700 | |
| Less: Interest expense | 250 | |
| Income before taxes | 62,450 | |
| Less: Income tax expense | 13,000 | |
| Net income | $49,450 | |
Table (5)
5.
Prepare the classified balance sheet as on January 31, 2021.
5.
Explanation of Solution
Classified balance sheet: The main elements of balance sheet assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity are categorized or classified further into sections, and sub-sections in a classified balance sheet. Assets are further classified as current assets, long-term investments, property, plant, and equipment (PPE), and intangible assets. Liabilities are classified into two sections current and long-term. Stockholders’ equity comprises of common stock and retained earnings. Thus, the classified balance sheet includes all the elements under different sections.
Prepare the classified balance sheet as on January 31, 2021 as follows:
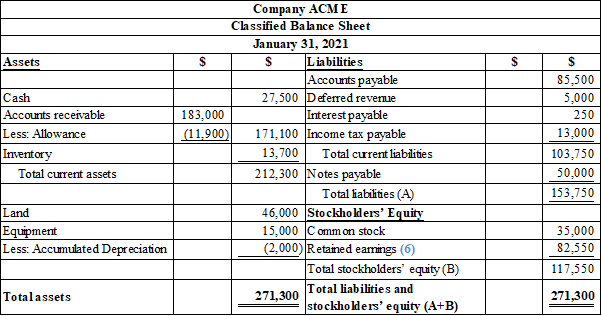
Table (6)
Working Notes:
Calculate the closing amount of retained earnings.
(6)
6.
Record the closing entries of Company ACME.
6.
Explanation of Solution
Closing entries: The journal entries prepared to close the temporary accounts to Retained Earnings account are referred to as closing entries. The revenue, expense, and dividends accounts are referred to as temporary accounts because the information and figures in these accounts is held temporarily and consequently transferred to permanent account at the end of accounting year.
Record the closing entries of Company ACME as follows:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Debit($) | Credit($) | |
| 2021 | Sales Revenue | 281,000 | ||
| January 31 | Retained Earnings | 281,000 | ||
| (To record the closing revenue accounts) | ||||
| Retained Earnings | 231,550 | |||
| Cost of goods sold | 153,300 | |||
| Salaries Expense | 52,000 | |||
| Bad debt Expense | 12,500 | |||
| Depreciation Expense | 500 | |||
| Interest Expense | 250 | |||
| Income Tax Expense | 13,000 | |||
| (To close the expense accounts) | ||||
Table (7)
Closing entry for revenue account:
In this closing entry, the sales revenue account is closed by transferring the amount of sales revenue to retained earnings in order to bring the revenue account balance to zero. Hence, debit the sales revenue account for $281,000, and credit the retained account for $281,000.
Closing entry for expenses account:
In this closing entry, all expenses accounts are closed by transferring the amount all expenses to the retained earnings in order to bring the expense account balance to zero. Hence, debit the retained earnings for $231,550 and credit all expense accounts with respective amount.
7. a
Calculate the current ratio at the end of January.
7. a
Explanation of Solution
Current ratio: The financial ratio which evaluates the ability of a company to pay off the debt obligations which mature within one year or within completion of operating cycle is referred to as current ratio. This ratio assesses the liquidity of a company.
Calculate the current ratio at the end of January as follows:
Company ACME has more liquidity than the average level required by the industry. Company ACME has a high portion of current assets to meet out the current liabilities, which is comparatively higher than the industry average of 1.8.
7. b.
Calculate the acid-test ratio at the end of January.
7. b.
Explanation of Solution
Acid-test ratio: The financial ratio which evaluates the ability of a company to pay off the instant debt obligations is referred to as quick ratio. Quick assets are cash, marketable securities, and accounts receivables. This ratio assesses the short-term liquidity of a company.
Calculate the acid-test ratio at the end of January as follows:
Company ACME has less difficulty to pay its currently matured debts. Company ACME has high portion of quick assets to meet the current liabilities, which is comparatively higher than the industry average of 1.5.
7. c.
Indicate whether the revised ratio would increase, decrease or remain unchanged compared to the requirement (a).
7. c.
Explanation of Solution
Indicate whether the revised ratio would increase, decrease or remain unchanged compared to the requirement (a) as follows:
Calculate current ratio assuming notes payable as current liabilities.
The amount of notes payable increases the value of current liabilities by $153,750. This would decrease the value of the current assets and increase the value of current liabilities because ratio gets reduced when they are divided by larger number.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Financial Accounting
- Accurate Answerarrow_forwardA project will increase sales by $250,000 and cash expenses by $60,000. The project will cost $400,000 and be depreciated using the straight-line method to a zero book value over the 4-year life of the project. The company has a marginal tax rate of 35%. What is the yearly value of the depreciation tax shield?arrow_forwardHi expert please help me this question general accountingarrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





