
(a)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Addition of halides to
Halogens like chlorine and bromine adds to the alkyne compounds. The general form of the reaction is given below.
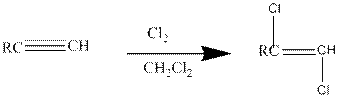
If excess halides are present, a second addition reaction also occurs.
(b)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Addition of halides to alkynes:
Halogens like chlorine and bromine adds to the alkyne compounds. The general form of the reaction is given below.

If excess halides are present, a second addition reaction also occurs.
(c)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Addition of halides to alkynes:
Halogens like chlorine and bromine adds to the alkyne compounds. The general form of the reaction is given below.

If excess halides are present, a second addition reaction also occurs.
(d)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Addition of halides to alkynes:
Halogens like chlorine and bromine adds to the alkyne compounds. The general form of the reaction is given below.

If excess halides are present, a second addition reaction also occurs.
(e)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Addition of halides to alkynes:
Halogens like chlorine and bromine adds to the alkyne compounds. The general form of the reaction is given below.

If excess halides are present, a second addition reaction also occurs.
(f)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Addition of halides to alkynes:
Halogens like chlorine and bromine adds to the alkyne compounds. The general form of the reaction is given below.

If excess halides are present, a second addition reaction also occurs.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
CHEM 262 ORG CHEM EBOOK DIGITAL DELIVERY
- In the drawing area below, draw the major products of this organic reaction: If there are no major products, because nothing much will happen to the reactant under these reaction conditions, check the box under the drawing area instead. 1. NaH 2. CH3Br ? Click and drag to start drawing a structure. No reaction. : ☐ Narrow_forward+ Predict the major product of the following reaction. : ☐ + ☑ ค OH H₂SO4 Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardConsider this organic reaction: ... OH CI Draw the major products of the reaction in the drawing area below. If there won't be any major products, because this reaction won't happen at a significant rate, check the box under the drawing area instead. ☐ No Reaction. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : аarrow_forward
- Consider the following reactants: Br Would elimination take place at a significant rate between these reactants? Note for advanced students: by significant, we mean that the rate of elimination would be greater than the rate of competing substitution reactions. yes O no If you said elimination would take place, draw the major products in the upper drawing area. If you said elimination would take place, also draw the complete mechanism for one of the major products in the lower drawing area. If there is more than one major product, you may draw the mechanism that leads to any of them. Major Products:arrow_forwardDraw one product of an elimination reaction between the molecules below. Note: There may be several correct answers. You only need to draw one of them. You do not need to draw any of the side products of the reaction. OH + ! : ☐ + Х Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardFind one pertinent analytical procedure for each of following questions relating to food safety analysis. Question 1: The presence of lead, mercury and cadmium in canned tuna Question 2: Correct use of food labellingarrow_forward
- Formulate TWO key questions that are are specifically in relation to food safety. In addition to this, convert these questions into a requirement for chemical analysis.arrow_forwardWhat are the retrosynthesis and forward synthesis of these reactions?arrow_forwardWhich of the given reactions would form meso product? H₂O, H2SO4 III m CH3 CH₂ONa CH3OH || H₂O, H2SO4 CH3 1. LiAlH4, THF 2. H₂O CH3 IVarrow_forward
- What is the major product of the following reaction? O IV III HCI D = III ა IVarrow_forwardThe reaction of what nucleophile and substrate is represented by the following transition state? CH3 CH3O -Br อ δ CH3 Methanol with 2-bromopropane Methanol with 1-bromopropane Methoxide with 1-bromopropane Methoxide with 2-bromopropanearrow_forwardWhat is the stepwise mechanism for this reaction?arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
