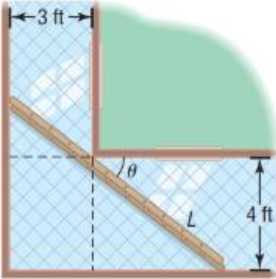
Problem 1AYU: Solve: 3x5=x+1 Problem 2AYU: sin( 4 )= ______; cos( 8 3 )= ______. Problem 3AYU: Find the real solutions of 4 x 2 x5=0 . Problem 4AYU: Find the real solutions of x 2 x1=0 . Problem 5AYU: Find the real solutions of ( 2x1 ) 2 3( 2x1 )4=0 . Problem 6AYU Problem 7AYU: True or False Most trigonometric equations have unique solutions. Problem 8AYU: True or False Two solutions of the equation sin= 1 2 are 6 and 5 6 . Problem 9AYU: True or False The set of all solutions of the equation tan=1 is given by { |= 4 +k,kisanyinteger } Problem 10AYU: True or False The equation sin=2 has a real solution that can be found using a calculator. Problem 11AYU: If all solutions of a trigonometric equation are given by the general formula = 6 +2k or = 11 6 +2k... Problem 12AYU: Suppose = 2 is the only solution of a trigonometric equation in the interval 02 . Assuming a period... Problem 13AYU: In Problems 13-36, solve each equation on the interval 02 . 2sin+3=2 Problem 14AYU: In Problems 13-36, solve each equation on the interval 02 . 1cos= 1 2 Problem 15AYU: In Problems 13-36, solve each equation on the interval 02 . 2sin+1=0 Problem 16AYU: In Problems 13-36, solve each equation on the interval 02 . cos+1=0 Problem 17AYU: In Problems 13-36, solve each equation on the interval 02 . tan+1=0 Problem 18AYU: In Problems 13-36, solve each equation on the interval 02 . 3 cot+1=0 Problem 19AYU: In Problems 13-36, solve each equation on the interval 02 . 4sec+6=2 Problem 20AYU: In Problems 13-36, solve each equation on the interval 02 . 5csc3=2 Problem 21AYU: In Problems 13-36, solve each equation on the interval 02 . 3 2 cos+2=1 Problem 22AYU: In Problems 13-36, solve each equation on the interval 02 . 4sin+3 3 = 3 Problem 23AYU: In Problems 13-36, solve each equation on the interval 02 . 4 cos 2 =1 Problem 24AYU: In Problems 13-36, solve each equation on the interval 02 . tan 2 = 1 3 Problem 25AYU: In Problems 13-36, solve each equation on the interval 02 . 2 sin 2 1=0 Problem 26AYU: In Problems 13-36, solve each equation on the interval 02 . 4 cos 2 3=0 Problem 27AYU: In Problems 13-36, solve each equation on the interval 02 . sin( 3 )=1 Problem 28AYU: In Problems 13-36, solve each equation on the interval 02 . tan 2 = 3 Problem 29AYU: In Problems 13-36, solve each equation on the interval 02 . cos( 2 )= 1 2 Problem 30AYU: In Problems 13-36, solve each equation on the interval 02 . tan( 2 )=1 Problem 31AYU: In Problems 13-36, solve each equation on the interval 02 . sec 3 2 =2 Problem 32AYU: In Problems 13-36, solve each equation on the interval 02 . cot 2 3 = 3 Problem 33AYU: In Problems 13-36, solve each equation on the interval 02 . cos( 2 2 )=1 Problem 36AYU: In Problems 13-36, solve each equation on the interval 02 . cos( 3 4 )= 1 2 Problem 37AYU: In Problems 37-46, solve each equation. Give a general formula for all the solutions. List six... Problem 38AYU: In Problems 37-46, solve each equation. Give a general formula for all the solutions. List six... Problem 39AYU: In Problems 37-46, solve each equation. Give a general formula for all the solutions. List six... Problem 40AYU: In Problems 37-46, solve each equation. Give a general formula for all the solutions. List six... Problem 41AYU: In Problems 37-46, solve each equation. Give a general formula for all the solutions. List six... Problem 42AYU: In Problems 37-46, solve each equation. Give a general formula for all the solutions. List six... Problem 43AYU: In Problems 37-46, solve each equation. Give a general formula for all the solutions. List six... Problem 44AYU: In Problems 37-46, solve each equation. Give a general formula for all the solutions. List six... Problem 45AYU: In Problems 37-46, solve each equation. Give a general formula for all the solutions. List six... Problem 46AYU: In Problems 37-46, solve each equation. Give a general formula for all the solutions. List six... Problem 47AYU: In Problems use a calculator to solve each equation on the interval Round answers to two decimal... Problem 48AYU: In Problems use a calculator to solve each equation on the interval Round answers to two decimal... Problem 49AYU: In Problems use a calculator to solve each equation on the interval Round answers to two decimal... Problem 50AYU: In Problems use a calculator to solve each equation on the interval Round answers to two decimal... Problem 51AYU: In Problems use a calculator to solve each equation on the interval Round answers to two decimal... Problem 52AYU: In Problems use a calculator to solve each equation on the interval Round answers to two decimal... Problem 53AYU: In Problems use a calculator to solve each equation on the interval Round answers to two decimal... Problem 54AYU: In Problems use a calculator to solve each equation on the interval Round answers to two decimal... Problem 55AYU: In Problems 4758, use a calculator to solve each equation on the interval 02 Round answers to two... Problem 56AYU: In Problems 4758, use a calculator to solve each equation on the interval 02 Round answers to two... Problem 57AYU: In Problems 4758, use a calculator to solve each equation on the interval 02 Round answers to two... Problem 58AYU: In Problems 4758, use a calculator to solve each equation on the interval 02 Round answers to two... Problem 59AYU: In Problems 59-82, solve each equation on the interval 02 . 2 cos 2 +cos=0 Problem 60AYU: In Problems 59-82, solve each equation on the interval 02 . sin 2 1=0 Problem 61AYU: In Problems 59-82, solve each equation on the interval 02 . 2 sin 2 sin1=0 Problem 62AYU: In Problems 59-82, solve each equation on the interval 02 . 2 cos 2 +cos1=0 Problem 63AYU: In Problems 59-82, solve each equation on the interval 02 . ( tan1 )( sec1 )=0 Problem 64AYU: In Problems 59-82, solve each equation on the interval 02 . ( cot+1 )( csc 1 2 )=0 Problem 65AYU: In Problems 59-82, solve each equation on the interval 02 . sin 2 cos 2 =1+cos Problem 66AYU: In Problems 59-82, solve each equation on the interval 02 . cos 2 sin 2 +sin=0 Problem 67AYU: In Problems 59-82, solve each equation on the interval 02 . sin 2 =6( cos( )+1 ) Problem 68AYU: In Problems 59-82, solve each equation on the interval 02 . 2 sin 2 =3( 1cos( ) ) Problem 69AYU: In Problems 59-82, solve each equation on the interval 02 . cos=sin( ) Problem 70AYU: In Problems 59-82, solve each equation on the interval 02 . cossin( )=0 Problem 71AYU: In Problems 59-82, solve each equation on the interval 02 . tan=2sin Problem 72AYU: In Problems 59-82, solve each equation on the interval 02 . tan=cot Problem 73AYU: In Problems 59-82, solve each equation on the interval 02 . 1+sin=2 cos 2 Problem 74AYU: In Problems 59-82, solve each equation on the interval 02 . sin 2 =2cos+2 Problem 75AYU: In Problems 59-82, solve each equation on the interval 02 . 2 sin 2 5sin+3=0 Problem 76AYU: In Problems 59-82, solve each equation on the interval 02 . 2 cos 2 7cos4=0 Problem 77AYU: In Problems 59-82, solve each equation on the interval 02 . 3( 1cos )= sin 2 Problem 78AYU Problem 79AYU Problem 80AYU Problem 81AYU: In Problems 59-82, solve each equation on the interval 02 . sec 2 +tan=0 Problem 82AYU: In Problems 59-82, solve each equation on the interval 02 . sec=tan+cot Problem 83AYU: In Problems 83-94, use a graphing utility to solve each equation. Express the solution(s) rounded to... Problem 84AYU: In Problems 83-94, use a graphing utility to solve each equation. Express the solution(s) rounded to... Problem 85AYU Problem 86AYU Problem 87AYU Problem 88AYU Problem 89AYU: In Problems 83-94, use a graphing utility to solve each equation. Express the solution(s) rounded to... Problem 90AYU Problem 91AYU: In Problems 83-94, use a graphing utility to solve each equation. Express the solution(s) rounded to... Problem 92AYU Problem 93AYU Problem 94AYU: In Problems 83-94, use a graphing utility to solve each equation. Express the solution(s) rounded to... Problem 95AYU: What are the zeros of f( x )=4 sin 2 x3 on the interval [ 0,2 ] ? Problem 96AYU Problem 97AYU: f(x)=3sinx a. Find the zeros of f on the interval [ 2,4 ] . b. Graph f(x)=3sinx on the interval [... Problem 98AYU: f( x )=2cosx a. Find the zeros of f on the interval [ 2,4 ] . b. Graph f( x )=2cosx on the interval... Problem 99AYU: f( x )=4tanx a. Solve f( x )=4 . b. For what values of x is f( x )4 on the interval ( 2 , 2 ) ? Problem 100AYU Problem 101AYU Problem 102AYU Problem 103AYU: a. Graph f( x )=4cosx and g( x )=2cosx+3 on the same Cartesian plane for the interval [ 0,2 ] . b.... Problem 104AYU Problem 105AYU Problem 106AYU: The Ferris Wheel In 1893, George Ferris engineered the Ferris wheel. It was 250 feet in diameter. If... Problem 107AYU: Holding Pattern An airplane is asked to slay within a holding pattern near Chicago’s O'Hare... Problem 108AYU: Projectile Motion A golfer hits a golf ball with an initial velocity of 100 miles per hour. The... Problem 109AYU: Heat Transfer In the study of heat transfer, the equation x+tanx=0 occurs. Graph Y 1 =x and Y 2... Problem 110AYU: Carrying a Ladder around a Corner Two hallways, one of width 3 feet, the other of width 4 feet, meet... Problem 111AYU: Projectile Motion The horizontal distance that a projectile will travel in the air (ignoring air... Problem 112AYU: Projectile Motion Refer to Problem 111. a. If you can throw a baseball with an initial speed of 40... Problem 113AYU: sin 1 sin 2 = v 1 v 2 The ratio v 1 v 2 is called the index of refraction. Some values are given... Problem 114AYU: The index of refraction of light in passing from a vacuum into dense flint glass is 1.66 . If the... Problem 115AYU: Ptolemy, who lived in the city of Alexandria in Egypt during the second century AD, gave the... Problem 116AYU: Bending Light The speed of yellow sodium light (wavelength, 589 nanometers) in a certain liquid is... Problem 117AYU: Bending Light A beam of light with a wavelength of 589 nanometers traveling in air makes an angle of... Problem 118AYU: Bending Light A light ray with a wavelength of 589 nanometers (produced by a sodium lamp) traveling... Problem 119AYU: Challenge Problem A light beam passes through a thick slab of material whose index of refraction is... Problem 120AYU: Brewsters Law If the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction are complementary angles, the... Problem 121AYU: Explain in your own words how you would use your calculator to solve the equation cosx=0.6 , 0x2 .... Problem 122AYU: Explain why no further points of intersection (and therefore no further solutions) exist in Figure... Problem 123AYU: Convert 6 x =y to an equivalent statement involving a logarithm. Problem 124AYU: Find the zeros of f( x )=2 x 2 9x+8 . Problem 125AYU Problem 126AYU format_list_bulleted


 Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning



