
The power output produced from the turbine, and the overall isentropic efficiency of turbine.
Answer to Problem 197RP
The power output produced from the turbine is
The overall isentropic efficiency of turbine is
Explanation of Solution
Write the formula to calculate the specific entropy of steam from tables
Here, specific entropy of saturated liquid is
Write the formula to calculate the specific enthalpy of steam from tables
Here, specific entropy of saturated liquid is
Draw the
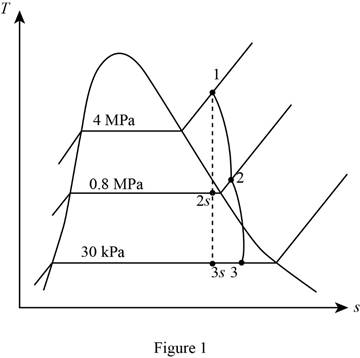
Write the formula for isentropic efficiency of the turbine
Here, specific enthalpy at the turbine inlet is
Write the formula for isentropic efficiency of the turbine
Here, specific enthalpy at the actual turbine exit is
Write the expression for the energy balance Equation for a closed system.
Here, net energy rate transfer into the control volume is
Write the general expression to calculate the isentropic efficiency of turbine
Here, actual work output is
Conclusion:
The rate of change in energy of the system is zero at steady state.
Substitute
Substitute
Re-write the Equation (VIII) for the isentropic work output
Here, mass flow rate of steam at inlet is
From the Table A-6 “Superheated water”, obtain the specific enthalpy
From the Table A-5 “Saturated water - Pressure”, obtain the following properties of water at pressure of
Substitute
Substitute
Equation (II).
Substitute 0.97 for
Equation (III).
Substitute
Substitute
From the Table A-5 “Saturated water - Pressure”, obtain the following properties of water at pressure of
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the power output produced from the turbine is
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the overall isentropic efficiency of turbine is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
THERMODYNAMICS LLF W/ CONNECT ACCESS
- 3. Water enters the constant 125-mm inside-diameter tubes of a boiler at 7.5 MPa and 60°C and leaves the tubes at 6 MPa and 500°C with a velocity of 75 m/s. Calculate the velocity of the water at the tube inlet and the inlet volume flow rate.arrow_forward2. A piston-cylinder device contains 2.4 kg of nitrogen initially at 120 kPa and 27°C. The nitrogen is now compressed slowly in a polytropic process during which PV1.3 = constant until the volume is reduced by one-half. Determine the work done and the heat transfer for this process.arrow_forward1. 1.25 m³ of saturated liquid water at 225°C is expanded isothermally in a closed system until its quality is 75 percent. Determine the total work produced by this expansion, in kJ.arrow_forward
- An undamped single-degree-of-freedom system is subjected to dynamic excitation as shown in Figure 1.• System properties: m = 1, c = 0, k = (6π)2.• Force excitation: p(t) = posin(ωt) where po = 9 and ω = 2π.• Initial conditions: u(t = 0) = 0 and ̇u(t = 0) = 0.Please, complete Parts (a) through (d) using any computational tool of your preference. The preferred toolis MATLAB. Print and turn in a single pdf file that will include your code/calculations and your plots.(a) Generate the solution using a linear interpolation of the load over each time step (note that hereyou can use the undamped coefficients). Plot the displacement response for the first 4 seconds andcompare to the exact closed form solution. Repeat using the following time step sizes, ∆t = 0.01,0.05, 0.15, 0.20 seconds. Include the closed form solution and the solutions for different ∆t values in asingle plot. Please, provide your observations by comparing the closed form solution with the solutionsderived using the four…arrow_forwardAssume multiple single degree of freedom systems with natural periods T ∈ [0.05, 2.00] seconds with in-crement of period dT = 0.05 seconds. Assume three cases of damping ratio: Case (A) ξ = 0%; Case (B)ξ = 2%; Case (C) ξ = 5%. The systems are initially at rest. Thus, the initial conditions are u(t = 0) = 0 anḋu(t = 0) = 0. The systems are subjected to the base acceleration that was provided in the ElCentro.txt file(i.e., first column). For the systems in Case (A), Case (B), and Case (C) and for each natural period computethe peak acceleration, peak velocity, and peak displacement responses to the given base excitation. Please,use the Newmark method for β = 1/4 (average acceleration) to compute the responses. Create threeplots with three lines in each plot. The first plot will have the peak accelerations in y-axis and the naturalperiod of the system in x-axis. The second plot will have the peak velocities in y-axis and the natural periodof the system in x-axis. The third plot will have…arrow_forwardBoth portions of the rod ABC are made of an aluminum for which E = 70 GPa. Based on the given information find: 1- deformation at A 2- stress in BC 3- Total strain 4- If v (Poisson ratio is 0.25, find the lateral deformation of AB Last 3 student ID+ 300 mm=L2 724 A P=Last 2 student ID+ 300 KN 24 24 Diameter Last 2 student ID+ 15 mm Last 3 student ID+ 500 mm=L1 724 C B 24 Q=Last 2 student ID+ 100 KN 24 Diameter Last 2 student ID+ 40 mmarrow_forward
- Q2Two wooden members of uniform cross section are joined by the simple scarf splice shown. Knowing that the maximum allowable tensile stress in the glued splice is 75 psi, determine (a) the largest load P that can be safely supported, (b) the corresponding shearing stress in the splice. น Last 1 student ID+5 inch=W =9 4 L=Last 1 student ID+8 inch =12 60° P'arrow_forwardQ4 The two solid shafts are connected by gears as shown and are made of a steel for which the allowable shearing stress is 7000 psi. Knowing the diameters of the two shafts are, respectively, dBC determine the largest torque Tc that can be applied at C. 4 and dEF dBC=Last 1 student ID+3 inch dEF=Last 1 student ID+1 inch 7 R=Last 1 Student ID+5 inch 9 R B Tc 2.5 in. E TF Harrow_forwardExperiment تكنولوجيا السيارات - Internal Forced convenction Heat transfer Air Flow through Rectangular Duct. objective: Study the convection heat transfer of air flow through rectangular duct. Valve Th Top Dead Centre Exhaust Valve Class CP. N; ~ RIVavg Ti K 2.11 Te To 18.8 21.3 45.8 Nath Ne Pre Calculations:. Q = m cp (Te-Ti) m: Varg Ac Acca*b Q=hexp As (Ts-Tm) 2 2.61 18.5 20.846.3 Tm = Te-Ti = 25 AS-PL = (a+b)*2*L Nu exp= Re-Vavy D heep Dh k 2ab a+b Nu Dh the- (TS-Tm) Ts. Tmy Name / Nu exp Naxe بب ارتدان العشريarrow_forward
- Procedure:1- Cartesian system, 2D3D,type of support2- Free body diagram3 - Find the support reactions4- If you find a negativenumber then flip the force5- Find the internal force3D∑Fx=0∑Fy=0∑Fz=0∑Mx=0∑My=0\Sigma Mz=02D\Sigma Fx=0\Sigma Fy=0\Sigma Mz=05- Use method of sectionand cut the elementwhere you want to findarrow_forwardProcedure:1- Cartesian system, 2D3D,type of support2- Free body diagram3 - Find the support reactions4- If you find a negativenumber then flip the force5- Find the internal force3D∑Fx=0∑Fy=0∑Fz=0∑Mx=0∑My=0\Sigma Mz=02D\Sigma Fx=0\Sigma Fy=0\Sigma Mz=05- Use method of sectionand cut the elementwhere you want to findthe internal force andkeep either side of thearrow_forwardProcedure: 1- Cartesian system, 2D3D, type of support 2- Free body diagram 3 - Find the support reactions 4- If you find a negative number then flip the force 5- Find the internal force 3D ∑Fx=0 ∑Fy=0 ∑Fz=0 ∑Mx=0 ∑My=0 ΣMz=0 2D ΣFx=0 ΣFy=0 ΣMz=0 5- Use method of section and cut the element where you want to find the internal force and keep either side of thearrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





