
Concept explainers
a)
To determine: The standard time for the operation.
Introduction: The amount of the dependency on human effort by an organization in terms of achieving its goals is given by the work design. It is directly linked to the productivity of an organization where good work design helps in achieving high productivity.
a)
Answer to Problem 9P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Performance rating | Observations (minutes per cycles) | Allowance | ||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 0.9 | 1.4 | 1.42 | 1.39 | 1.38 | 1.41 | 0.10 |
| 1.2 | 2.1 | 2.05 | 2 | 1.85 | 1.8 | 0.10 |
| 1.11 | 1.6 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 1.45 | 1.55 | 0.10 |
Formula:
| Element | Performance rating | Observations (minutes per cycles) | Allowance | Observed time | Normal time | Afjob | Standard time | ||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||||||
| A | 0.9 | 1.4 | 1.42 | 1.39 | 1.38 | 1.4 | 0.10 | 1.4 | 1.26 | 1.10 | 1.39 |
| B | 1.2 | 2.1 | 2.05 | 2 | 1.85 | 1.8 | 0.10 | 1.96 | 2.352 | 1.10 | 2.59 |
| C | 1.11 | 1.6 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 1.45 | 1.6 | 0.10 | 1.5 | 1.665 | 1.10 | 1.83 |
| Standard time for operation | 5.80 | ||||||||||
Calculation of standard time of operation:
Excel Worksheet:
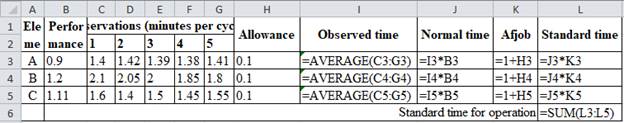
Element A:
Normal time is calculated by multiplying observed timing, 1.4 and performance rating, 0.9 which yields 1.26 minutes.
Allowance factor is calculated by adding 1 with the allowance factor 0.10 to give 1.10.
Standard time for element A is calculated by multiplying normal time of 1.26 minutes with allowance factor of 1.10 which gives 1.39 minutes.
Same process applies for element B and C which yields the standard times as 2.59 and 1.83. The standard time for operation is obtained by adding 1.39, 2.59 and 1.83 minutes which gives 5.80 minutes.
Hence, the standard time for the operation is 5.80 minutes.
b)
To determine: The number of observations for element A
Introduction: The amount of the dependency on human effort by an organization in terms of achieving its goals is given by the work design. It is directly linked to the productivity of an organization where good work design helps in achieving high productivity.
b)
Answer to Problem 9P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Performance rating | Observations (minutes per cycles) | Allowance | ||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 0.9 | 1.4 | 1.42 | 1.39 | 1.38 | 1.41 | 0.10 |
| 1.2 | 2.1 | 2.05 | 2 | 1.85 | 1.8 | 0.10 |
| 1.11 | 1.6 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 1.45 | 1.55 | 0.10 |
Confidence= 98%
4% of true value
Formula:
Calculation of number of observations for element A:
In the above formula the sample standard deviation is calculated by,
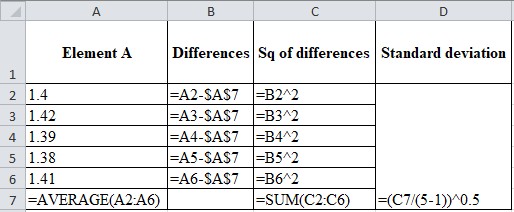
Calculation of standard deviation:
| Element A | Differences | Square of differences | Standard deviation |
| 1.4 | 0 | 0 | 0.015811 |
| 1.42 | 0.02 | 0.0004 | |
| 1.39 | -0.01 | 0.0001 | |
| 1.38 | -0.02 | 0.0004 | |
| 1.41 | 0.01 | 0.0001 | |
| Mean=1.4 | SSQ=0.001 |
Excel worksheet:
Z value for confidence interval of 98% is 2.33.
The confidence interval
Using z = 2.33:
The number of observations from the standard z table for confidence level of 98% is calculated by dividing the product of 2.33 and 0.0158 with product of 0.04 and 1.40 and squaring the resultant which gives 0.4322. Rounding off the value it gives the number of observation as 1.
Hence, the number of observation is 1.
c)
To determine: The number of observations for element C.
Introduction: The amount of the dependency on human effort by an organization in terms of achieving its goals is given by the work design. It is directly linked to the productivity of an organization where good work design helps in achieving high productivity.
c)
Answer to Problem 9P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Performance rating | Observations (minutes per cycles) | Allowance | ||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 0.9 | 1.4 | 1.42 | 1.39 | 1.38 | 1.41 | 0.10 |
| 1.2 | 2.1 | 2.05 | 2 | 1.85 | 1.8 | 0.10 |
| 1.11 | 1.6 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 1.45 | 1.55 | 0.10 |
Confidence= 90%
0.10 minute of actual value.
Formula:
Calculation of number of observations for element C:
In the above formula the sample standard deviation is calculated by,
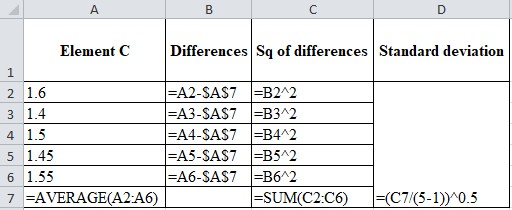
Calculation of standard deviation:
| Element C | Differences | Square of differences | Standard deviation |
| 1.6 | 0.1 | 0.01 | 0.0791 |
| 1.4 | -0.1 | 0.01 | |
| 1.5 | 0 | 0 | |
| 1.45 | -0.05 | 0.0025 | |
| 1.55 | 0.05 | 0.0025 | |
| Mean=1.5 | SSQ=0.025 |
Excel worksheet:
Z value for confidence interval of 90% is 1.65.
The confidence interval
- Using z = 1.64:
The number of observations from the standard z table for confidence level of 90 is calculated by dividing the product of 1.64 and 0.0791 with 0.10 and squaring the resultant which gives 1.6828.
- Using z = 1.65:
The number of observations from the standard z table for confidence level of 90 is calculated by dividing the product of 1.65 and 0.0791 with 0.10 and squaring the resultant which gives 1.7034.
Hence, the number of observations for element C is 2
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Operations Management (The Mcgraw-hill Series in Operations and Decision Sciences)
- The Donald Fertilizer Company produces industrial chemical fertilizers. The projected manufacturing requirements (in gallons) for the next four quarters are 60,000, 90,000, 90,000, and 140,000 respectively. A level workforce is desired, relying only on anticipation inventory as a supply option. Stockouts and backorders are to be avoided, as are overtime and undertime. a. Determine the quarterly production rate required to meet total demand for the year, and minimize the anticipation inventory that would be left over at the end of the year. Beginning inventory is 0. The quarterly production rate is ☐ gallons. (Enter your response as an integer.)arrow_forwardHow would you design an operations plan and schedule for a new product/service? What factors would you consider and what challenges would you anticipate? Why are these factors and challenges relevant and how would you address them?arrow_forwardYou are the newly appointed CEO of TechSouth, a South African multinational technology company based in Cape Town. TechSouth specialises in manufacturing smartphones, laptops, and smart home devices. The company has a significant presence in the African market and has recently expanded into Europe and Asia. However, TechSouth is facing several critical challenges:· Declining Market Share - Over the past three years, TechSouth has lost considerable market share to both localcompetitors and international giants like Samsung and Apple. The company's products are perceived as outdated and lacking innovation.· Employee Engagement Issues - Recent employee surveys indicate low morale and engagement levels, particularly among the younger workforce, leading to high turnover rates. Many employees feel disconnected from the company's vision and mission.· Siloed Departments - The organizational structure at TechSouth is highly siloed, with departments operatingindependently rather than…arrow_forward
- What is the best way to manage emotions and thoughts? How to work through Emotions and thoughts?arrow_forwardWhat are the emotions or stressful thoughts? What are the differences between them? How can we work through the emotions or stressful thoughts? How can we avoid or prevent emotions or stressful thoughts from happening or occurring? What are the obstacles?arrow_forwardMain Challenges at TechInnovateStrategic DirectionTechInnovate's board of directors is pushing for a more aggressive expansion into emerging markets, particularly in Africaand Southeast Asia. However, there's internal disagreement about whether to focus on these new markets or consolidatetheir position in existing ones. Sarah Chen favors rapid expansion, while some senior executives advocate for a morecautious approach.Ethical ConcernsThe company's AI algorithms have come under scrutiny for potential biases, particularly in facial recognition technology.There are concerns that these biases disproportionately affect minority groups. Some employees have voiced ethicalconcerns about selling this technology to law enforcement agencies without addressing these issues.Team Leadership and DiversityTechInnovate's leadership team is predominantly male and Western, despite its global presence. There's growing pressurefrom employees and some board members to diversify the leadership team to…arrow_forward
- Sarah Anderson, the Marketing Manager at Exeter Township's Cultural Center, is conducting research on the attendance history for cultural events in the area over the past ten years. The following data has been collected on the number of attendees who registered for events at the cultural center. Year Number of Attendees 1 700 2 248 3 633 4 458 5 1410 6 1588 7 1629 8 1301 9 1455 10 1989 You have been hired as a consultant to assist in implementing a forecasting system that utilizes various forecasting techniques to predict attendance for Year 11. a) Calculate the Three-Period Simple Moving Average b) Calculate the Three-Period Weighted Moving Average (weights: 50%, 30%, and 20%; use 50% for the most recent period, 30% for the next most recent, and 20% for the oldest) c) Apply Exponential Smoothing with the smoothing constant alpha = 0.2. d) Perform a Simple Linear Regression analysis and provide the adjusted…arrow_forwardRuby-Star Incorporated is considering two different vendors for one of its top-selling products which has an average weekly demand of 70 units and is valued at $90 per unit. Inbound shipments from vendor 1 will average 390 units with an average lead time (including ordering delays and transit time) of 4 weeks. Inbound shipments from vendor 2 will average 490 units with an average lead time of 2 weeksweeks. Ruby-Star operates 52 weeks per year; it carries a 4-week supply of inventory as safety stock and no anticipation inventory. Part 2 a. The average aggregate inventory value of the product if Ruby-Star used vendor 1 exclusively is $enter your response here.arrow_forwardSam's Pet Hotel operates 50 weeks per year, 6 days per week, and uses a continuous review inventory system. It purchases kitty litter for $13.00 per bag. The following information is available about these bags: > Demand 75 bags/week > Order cost = $52.00/order > Annual holding cost = 20 percent of cost > Desired cycle-service level = 80 percent >Lead time = 5 weeks (30 working days) > Standard deviation of weekly demand = 15 bags > Current on-hand inventory is 320 bags, with no open orders or backorders. a. Suppose that the weekly demand forecast of 75 bags is incorrect and actual demand averages only 50 bags per week. How much higher will total costs be, owing to the distorted EOQ caused by this forecast error? The costs will be $higher owing to the error in EOQ. (Enter your response rounded to two decimal places.)arrow_forward
- Yellow Press, Inc., buys paper in 1,500-pound rolls for printing. Annual demand is 2,250 rolls. The cost per roll is $625, and the annual holding cost is 20 percent of the cost. Each order costs $75. a. How many rolls should Yellow Press order at a time? Yellow Press should order rolls at a time. (Enter your response rounded to the nearest whole number.)arrow_forwardPlease help with only the one I circled! I solved the others :)arrow_forwardOsprey Sports stocks everything that a musky fisherman could want in the Great North Woods. A particular musky lure has been very popular with local fishermen as well as those who buy lures on the Internet from Osprey Sports. The cost to place orders with the supplier is $40/order; the demand averages 3 lures per day, with a standard deviation of 1 lure; and the inventory holding cost is $1.00/lure/year. The lead time form the supplier is 10 days, with a standard deviation of 2 days. It is important to maintain a 97 percent cycle-service level to properly balance service with inventory holding costs. Osprey Sports is open 350 days a year to allow the owners the opportunity to fish for muskies during the prime season. The owners want to use a continuous review inventory system for this item. Refer to the standard normal table for z-values. a. What order quantity should be used? lures. (Enter your response rounded to the nearest whole number.)arrow_forward
 Management, Loose-Leaf VersionManagementISBN:9781305969308Author:Richard L. DaftPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Management, Loose-Leaf VersionManagementISBN:9781305969308Author:Richard L. DaftPublisher:South-Western College Pub Understanding Management (MindTap Course List)ManagementISBN:9781305502215Author:Richard L. Daft, Dorothy MarcicPublisher:Cengage Learning
Understanding Management (MindTap Course List)ManagementISBN:9781305502215Author:Richard L. Daft, Dorothy MarcicPublisher:Cengage Learning


