
Concept explainers
BIO Microraptor gui: The Biplane Dinosaur
The evolution of flight is a subject of intense interest in paleontology. Some subscribe to the “cursorial” (or ground-up) hypothesis, in which flight began with ground-dwelling animals running and jumping after prey Others favor the “arboreal” (or trees-down) hypothesis, in which tree-dwelling animals, like modern-day flying squirrels, developed flight as an extension of gliding from tree to tree.
A recently discovered fossil from the Cretaceous period in China supports the arboreal hypothesis and adds a new element—it suggests that feathers on both the wings and the lower legs and feet allowed this dinosaur, Microraptor gui, to glide much like a biplane, as shown in Figure 7-31 (a). Researchers have produced a detailed computer simulation of Microraptor, and with its help have obtained the power-versus-speed plot presented in Figure 7-31 (b). This curve shows how much power is required for flight at speeds between 0 and 30 m/s. Notice that the power increases at high speeds, as expected, but it is also high for low speeds, where the dinosaur is almost hovering. A minimum of 8.1 W is needed for flight at 10 m/s. The lower horizontal line shows the estimated 9.8-W power output of Microraptor, indicating the small range of speeds for which flight would be possible. The upper horizontal line shows the wider range of flight speeds that would be available if Microraptor were able to produce 20 W of power.
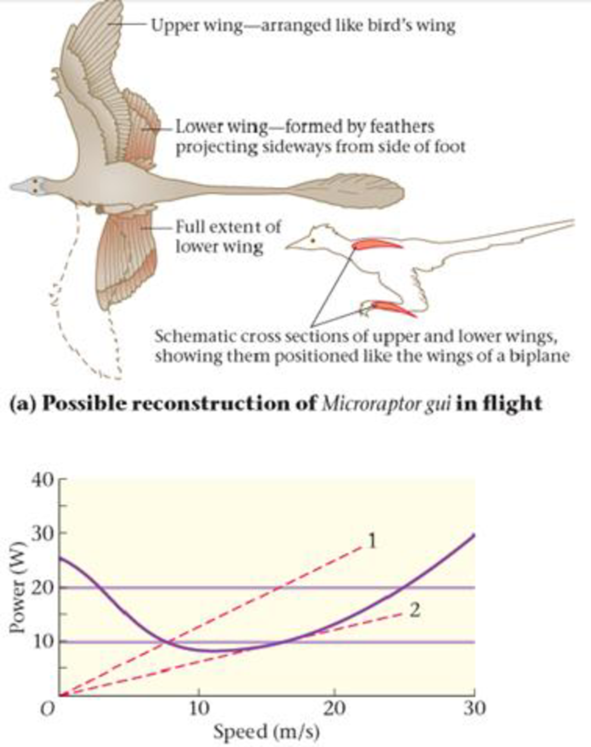
Also of interest are the two dashed, straight lines labeled 1 and 2. These lines represent constant ratios of power to speed—that is, a constant value for P/U Referring to Equation 7-13, we see that
P/v = Fv/v = F
, so lines 1 and 2 correspond to lines of constant force. Line 2 is interesting in that it has the smallest slope that still touches the power-versus-speed curve.
84. Estimate the range of flight speeds for Microraptor gui if its power output is 9.8 W.
- A. A. 0-7.7 m/s
- B. B. 7.7-15 m/s
- C. C. 15-30 m/s
- D. D. 0-15 m/s
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
Physics (5th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Microbiology: An Introduction
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
- 8. With the aid of a diagram draw the following electric circuit and use the resistor as the load, (a) Closed circuit (b) Open circuitarrow_forwardLab 8 Part 3 PHET Wave Interface simulation. I am having trouble with this part of the lab.arrow_forwardMick and Rick are twins born on Earth in the year 2175. Rick grows up to be an Earth-bound robotics technician while Mick becomes an intergalactic astronaut. Mick leaves the Earth on his first space mission in the year 2200 and travels, according to his clock, for 10 years at a speed of 0.75c. Unfortunately, at this point in his journey, the structure of his ship undergoes mechanical breakdown and the ship explodes. How old is Rick when his brother dies?arrow_forward

 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University





