
Answer each of the following:
- The _____ operator returns the location in memory where its operand is stored.
- The _____ operator returns the value of the object to which its operand points.
- To accomplish pass-by-reference when passing a nonarray variable to a function, it’s necessary to pass the _____ of the variable to the function.
(a)
To find the name of the operator that returns the memory location of an operand.
& operator.
Explanation of Solution
In C programming, language and symbol are used to get the address of an operand. The symbol (&) is also known as the ‘Address of’ operator.
Sample Program:
//include essential header files
#include <stdio.h>
//main function
intmain()
{
//declare an operand
int sample;
//Print the address of operand named sample
printf("%p",&sample);
return0;
}
Sample output:
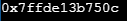
(b)
To find the name of the operator that returns the value of an object who points to other operands.
* operator.
Explanation of Solution
In C programming language, * symbol is used to get the value of other operands that address it points.
Sample Program:
//include essential header files
#include <stdio.h>
//main function
intmain()
{
//declare a operand
int sample =10;
//declare a pointer type operand
int*point;
point =&sample;
//Print the value
printf("%d",*point);
return0;
}
Sample output:
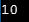
(c)
To find the component of a variable that should be passed to a function to accomplish pass by reference.
address.
Explanation of Solution
In pass by reference, any changes that a function performs on the passed variable always gets reflected in the actual variable. For this to accomplish, the address of the variable must be passed to function.
Sample Program:
//include essential header files
#include <stdio.h>
//function defination
void passRef(int*a,int*b)
{
//declare a temp variable
int temp;
//assign variable a value to temp variable
temp =*a;
//assign variable b value to variable a
*a =*b;
//assign variable temp value to variable b
*b = temp;
//return the value
return;
}
//main function
intmain()
{
//declare variable
int sample1 =10;
int sample2 =15;
//calling function using address of sample1 and sample2
passRef(&sample1,&sample2);
//Print the values after swapping
printf("sample1 = %d sample2 = %d", sample1, sample2);
return0;
}
Sample output:
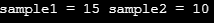
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
C How To Program Plus Mylab Programming With Pearson Etext -- Access Card Package (8th Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science: An Overview (13th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Modern Database Management
- "Do not use AI tools. Solve the problem by hand on paper only and upload a photo of your handwritten solution."arrow_forward"Do not use AI tools. Solve the problem by hand on paper only and upload a photo of your handwritten solution."arrow_forward"Do not use AI tools. Solve the problem by hand on paper only and upload a photo of your handwritten solution."arrow_forward
- "Do not use AI tools. Solve the problem by hand on paper only and upload a photo of your handwritten solution."arrow_forwardSolve this "Do not use AI tools. Solve the problem by hand on paper only and upload a photo of your handwritten solution."arrow_forward"Do not use AI tools. Solve the problem by hand on paper only and upload a photo of your handwritten solution."arrow_forward
- "Do not use AI tools. Solve the problem by hand on paper only and upload a photo of your handwritten solution."arrow_forwardSpecifications: Part-1Part-1: DescriptionIn this part of the lab you will build a single operation ALU. This ALU will implement a bitwise left rotation. Forthis lab assignment you are not allowed to use Digital's Arithmetic components.IF YOU ARE FOUND USING THEM, YOU WILL RECEIVE A ZERO FOR LAB2!The ALU you will be implementing consists of two 4-bit inputs (named inA and inB) and one 4-bit output (named out). Your ALU must rotate the bits in inA by the amount given by inB (i.e. 0-15).Part-1: User InterfaceYou are provided an interface file lab2_part1.dig; start Part-1 from this file.NOTE: You are not permitted to edit the content inside the dotted lines rectangle. Part-1: ExampleIn the figure above, the input values that we have selected to test are inA = {inA_3, inA_2, inA_1, inA_0} = {0, 1, 0,0} and inB = {inB_3, inB_2, inB_1, inB_0} = {0, 0, 1, 0}. Therefore, we must rotate the bus 0100 bitwise left by00102, or 2 in base 10, to get {0, 0, 0, 1}. Please note that a rotation left is…arrow_forwardSolve this "Do not use AI tools. Solve the problem by hand on paper only and upload a photo of your handwritten solution."arrow_forward
 C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr
C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning Microsoft Visual C#Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102100Author:Joyce, Farrell.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Microsoft Visual C#Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102100Author:Joyce, Farrell.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Systems ArchitectureComputer ScienceISBN:9781305080195Author:Stephen D. BurdPublisher:Cengage Learning
Systems ArchitectureComputer ScienceISBN:9781305080195Author:Stephen D. BurdPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK JAVA PROGRAMMINGComputer ScienceISBN:9781337671385Author:FARRELLPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENTProgramming Logic & Design ComprehensiveComputer ScienceISBN:9781337669405Author:FARRELLPublisher:Cengage
EBK JAVA PROGRAMMINGComputer ScienceISBN:9781337671385Author:FARRELLPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENTProgramming Logic & Design ComprehensiveComputer ScienceISBN:9781337669405Author:FARRELLPublisher:Cengage





