
a.
Interpretation: The geometry of
Concept Introduction:
Hybridization: It relates to the mixing of atomic orbitals into new hybrid orbitals that have varied energies and shapes. It is appropriate for the pairing of the electrons for forming
The main concept behind this theory is that the electron pairs are always present in the outermost shell i.e. valence shell of an atom of a molecule and they repel each other due to which they try to attain the best possible position so that the value of their repulsion is the least. Hence, the electrons occupy such positions around the atom that reduces their repulsion and provides a molecule to their shape.
Here the electrons that take part in the bonding of a molecule are known as the bonding pair and the electrons that do not take part in the bonding are known as the lone pairs. The bond pairs are in the influence of the two bonding atoms whereas the lone pairs are in the influence of only of the atom.
Due to the presence of lone pairs, there is more space occupied between the atoms of the molecules. Now they suffer the repulsion between the lone pair-lone pair and bond pair-lone pair. Their repulsion can be represented as:-
lp-lp>lp-bp>bp-bp
a.
Answer to Problem 7.73PAE
Solution: The geometry of
Explanation of Solution
The electronic configuration of I is
Structure of
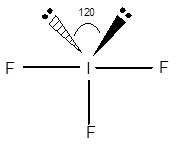
The geometry of
b.
Interpretation:
The geometry of
Concept Introduction
Hybridization: It relates to the mixing of atomic orbitals into new hybrid orbitals that have varied energies and shapes. It is appropriate for the pairing of the electrons for forming chemical bonds in the Valence Bond Theory. We can predict the shape of a particular molecule by the knowledge of their atomic numbers and VSEPR theory according to which the atoms take such a position that there is a minimum possible repulsion between the bonded atoms and the lone pair of electrons if any.
The main concept behind this theory is that the electron pairs are always present in the outermost shell i.e. valence shell of an atom of a molecule and they repel each other due to which they try to attain the best possible position so that the value of their repulsion is the least. Hence, the electrons occupy such positions around the atom that reduces their repulsion and provides a molecule to their shape.
Here the electrons that take part in the bonding of a molecule are known as the bonding pair and the electrons that do not take part in the bonding are known as the lone pairs. The bond pairs are in the influence of the two bonding atoms whereas the lone pairs are in the influence of only of the atom.
Due to the presence of lone pairs, there is more space occupied between the atoms of the molecules. Now they suffer the repulsion between the lone pair-lone pair and bond pair-lone pair. Their repulsion can be represented as:-
lp-lp>lp-bp>bp-bp.
b.
Answer to Problem 7.73PAE
Solution:
The geometry of
Explanation of Solution
The electronic configuration of Cl is
Structure of
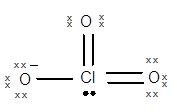
The geometry of
c.
Interpretation:
The geometry of
Concept Introduction
Hybridization: It relates to the mixing of atomic orbitals into new hybrid orbitals that have varied energies and shapes. It is appropriate for the pairing of the electrons for forming chemical bonds in the Valence Bond Theory. We can predict the shape of a particular molecule by the knowledge of their atomic numbers and VSEPR theory according to which the atoms take such a position that there is a minimum possible repulsion between the bonded atoms and the lone pair of electrons if any.
The main concept behind this theory is that the electron pairs are always present in the outermost shell i.e. valence shell of an atom of a molecule and they repel each other due to which they try to attain the best possible position so that the value of their repulsion is the least. Hence, the electrons occupy such positions around the atom that reduces their repulsion and provides a molecule to their shape.
Here the electrons that take part in the bonding of a molecule are known as the bonding pair and the electrons that do not take part in the bonding are known as the lone pairs. The bond pairs are in the influence of the two bonding atoms whereas the lone pairs are in the influence of only of the atom.
Due to the presence of lone pairs, there is more space occupied between the atoms of the molecules. Now they suffer the repulsion between the lone pair-lone pair and bond pair-lone pair. Their repulsion can be represented as:-
lp-lp>lp-bp>bp-bp
c.
Answer to Problem 7.73PAE
Solution:
The geometry of
is trigonal pyramidal as the hybridization of I is sp3d
Explanation of Solution
The electronic configuration of Tellurium is
Structure of
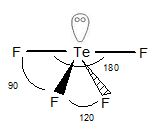
The geometry of
d.
Interpretation:
The geometry of
Concept Introduction:
Hybridization: It relates to the mixing of atomic orbitals into new hybrid orbitals that have varied energies and shapes. It is appropriate for the pairing of the electrons for forming chemical bonds in the Valence Bond Theory. We can predict the shape of a particular molecule by the knowledge of their atomic numbers and VSEPR theory according to which the atoms take such a position that there is a minimum possible repulsion between the bonded atoms and the lone pair of electrons if any.
The main concept behind this theory is that the electron pairs are always present in the outermost shell i.e. valence shell of an atom of a molecule and they repel each other due to which they try to attain the best possible position so that the value of their repulsion is the least. Hence, the electrons occupy such positions around the atom that reduces their repulsion and provides a molecule to their shape.
Here the electrons that take part in the bonding of a molecule are known as the bonding pair and the electrons that do not take part in the bonding are known as the lone pairs. The bond pairs are in the influence of the two bonding atoms whereas the lone pairs are in the influence of only of the atom.
Due to the presence of lone pairs, there is more space occupied between the atoms of the molecules. Now they suffer the repulsion between the lone pair-lone pair and bond pair-lone pair. Their repulsion can be represented as:-
lp-lp>lp-bp>bp-bp
d.
Answer to Problem 7.73PAE
Solution:
The geometry of
Explanation of Solution
The electronic configuration of Tellurium is
Structure of
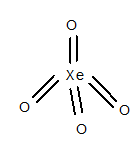
The geometry of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
CHEM FOR ENGNRNG SDNTS (EBOOK) W/ACCES
- 8:16 PM Sun Mar 30 K Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Proble 1. CH3MgBr 2. H3O+ F Drawingarrow_forwardо но оarrow_forwardName the major organic product of the following action of 4-chloro-4-methyl-1-pentanol in neutral pollution 10+ Now the product. The product has a molecular formula f b. In a singly hain, the starting, material again converts into a secule with the molecular kormula CIO. but with comply Draw the major organic structure inhalationarrow_forward
- Macmillan Learning Alcohols can be oxidized by chromic acid derivatives. One such reagent is pyridinium chlorochromate, (C,H,NH*)(CICTO3), commonly known as PCC. Draw the proposed (neutral) intermediate and the organic product in the oxidation of 1-butanol by PCC when carried out in an anhydrous solvent such as CH₂C₁₂. PCC Intermediate OH CH2Cl2 Draw the intermediate. Select Draw Templates More с H Cr о Product Draw the product. Erase Select Draw Templates More H о Erasearrow_forwardIf I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound A, I have to add NaOH and another compound. Indicate which compound that would be. A C6H5 CH3arrow_forwardProvide the reagents for the following reactions.arrow_forward
- If I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound Z, I have to add two compounds A1 and A2. Indicate which compounds are needed. P(C6H5)3arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Assume that the water side product is continuously removed to drive the reaction toward products. O CH3CH2NH2, TSOH Select to Draw >arrow_forwardPredict the major organic product(s) for the following reaction.arrow_forward
- Predict the major organic product(s) for the following reactions.arrow_forwardProvide the complete mechanism for the reactions below. You must include appropriate arrows,intermediates, and formal charges.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by reacting fluorobenzene with a sulfonitric mixture.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning

