
Concept explainers
This problem concerns the m. o module from Figure 7.5 and the following version of the swap, c function that counts the number of times it has been called:

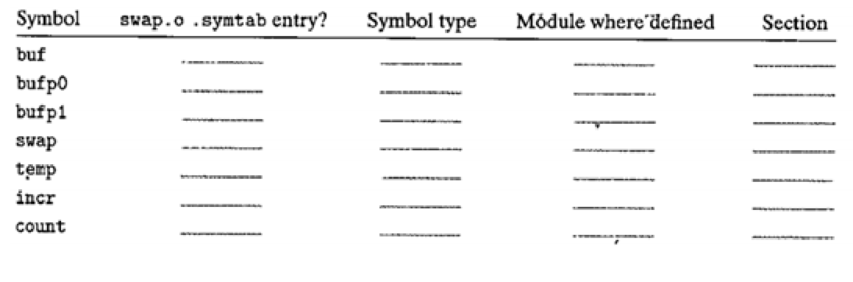
For each symbol that is defined and referenced in swap. o, indicate if it will have a symbol table entry in the symbol section in module swap. o. If so, indicate the module that defines the symbol (swap .o or m. o), the symbol type (local, global, or extern), and the section (.text, .data, or bss) it occupies in that module.
Sections in relocatable object files:
There are many sections in a relocatable object file. They are given below:
- “.text”:
- It is the machine code of the compiled program.
- “.rodata”:
- This section is used to read only the data in the format such as
- Strings in “printf” statements.
- Jump tables for switch statements.
- This section is used to read only the data in the format such as
- “.data”:
- This section is used in the initialized “C” variables of global variable and static “C” variables.
- Local “C” variables are initialized at execution time on the stack.
- It does not show in either the “.data” or “.bss” sections.
- “.bss”:
- It is used in the uninitialized global and static “C” variables, along with any global or static variables that are assigned to zero.
- “.symtab”:
- It is a symbol table.
- It contains the information about functions and global variables that are defined and referenced in the program.
- “.rel.text”:
- This section contains a list of locations in the “.text” section.
- It will require to be changed once the linker merges this object file with others.
- This section contains a list of locations in the “.text” section.
- “.rel.data”:
- This section contains relocation information for any global variables that are referenced or defined by the module.
- “.debug”:
- It is a symbol table for debugging
- It contains entries for following
- Definition of Local variables, global variables and typedefs variables and original “C” source file.
- “.line”:
- It is a mapping between line numbers in the given program
- That is in original “C” source program and machine code instructions in the “.text” section.
- It is a mapping between line numbers in the given program
- “.strtab”:
- It is a string table.
- It contains symbol tables in the “.symtab” and “.debug” sections.
- It is the table for section names in the section headers.
- It is a string table.
Explanation of Solution
For symbol “buf”:
- “.symtab” entry:
- It is occurs in the symbol table.
- Symbol type:
- It is an “extern” type. Because, the variable “buf” is declared in “extern” type which is present in “swap.c” file.
- Module defined position:
- The “buf” type is defined in “m.o” module.
- Because, the symbol “buf” are defined in “m.c” file”.
- When converting source file “m.c” to a relocatable object file, the given file becomes “m.o”.
- Section:
- The symbol “buf” is defined in “.data” section. It is the initialized global variable of “m.c” file.
For symbol “bufp0”:
- “.symtab” entry:
- It is occurs in the symbol table.
- Symbol type:
- It is a “global” symbol type. Because, the variable “bufp0” is declared outside the function in “swap.c” file.
- Module defined position:
- The “bufp0” type is defined in “swap.o” module.
- Because, the symbol “bufp0” are defined in “swap.c” file”.
- When converting source file “swap.c” to a relocatable object file, the given file becomes “swap.o”.
- Section:
- The symbol “bufp0” is defined in “.data” section. It is the initialized global variable of “swap.c” file
For symbol “bufp1”:
- “.symtab” entry:
- It is occurs in the symbol table.
- Symbol type:
- It is a “local” type. Because, the variable “bufp1” with “static” type in “swap.c” file.
- Module defined position:
- The “bufp1” type is defined in “swap.o” module.
- Because, the symbol “bufp1” are defined in “swap.c” file”.
- When converting source file “swap.c” to a relocatable object file, the given file becomes “swap.o”.
- Section:
- The symbol “bufp1” is defined in “.bss” section. It is the uninitialized static “C” variable of “swap.c” file
For symbol “swap”:
- “.symtab” entry:
- It is occurs in the symbol table.
- Symbol type:
- It is a “global” type. Because, the symbol “swap” is used in the entire program.
- Module defined position:
- The “swap” type is defined in “swap.o” module.
- Because, the symbol “swap” are defined in “swap.c” file”.
- When converting source file “swap.c” to a relocatable file, the given file becomes “swap.o”.
- Section:
- The symbol “swap” is present in “.text” section. It is the machine code of the compiled program.
For symbol “temp”:
- “.symtab” entry:
- The local variable “temp” does not a have a symbol table entry.
- So, it does not have a symbol type, module defined position and section.
- The local variable “temp” does not a have a symbol table entry.
For symbol “incr”:
- “.symtab” entry:
- It is occurs in the symbol table.
- Symbol type:
- It is a “local” type. Because, the function “incr” uses return type of “static” in “swap.c” file.
- Module defined position:
- The “swap” type is defined in “swap.o” module.
- Because, the symbol “swap” are defined in “swap.c” file”.
- When converting source file “swap.c” to a relocatable file, the given file becomes “swap.o”.
- Section:
- The symbol “swap” is present in “.text” section. It is the machine code of the compiled program.
For symbol “count”:
- “.symtab” entry:
- It is occurs in the symbol table.
- Symbol type:
- It is a “local” type. Because, the variable “count” declared in “static” type in the “swap.c” file.
- Module defined position:
- The “swap” type is defined in “swap.o” module.
- Because, the symbol “swap” are defined in “swap.c” file”.
- When converting source file “swap.c” to a relocatable file, the given file becomes “swap.o”.
- Section:
- The symbol “swap” is present in “.bss” section. Here, the static variables “count” are initialized to “0” in “swap.c” file.
The final table is
| Symbol | .symtab entry? | Symbol type | Module where defined | Section |
| buf | Yes | extern | m.o | .data |
| bufp0 | Yes | global | swap.o | .data |
| bufp1 | Yes | local | swap.o | .bss |
| swap | Yes | global | swap.o | .text |
| temp | No | - | - | - |
| incr | Yes | local | swap.o | .text |
| count | Yes | local | swap.o | .bss |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Computer Systems: A Programmer's Perspective Plus Mastering Engineering With Pearson Etext -- Access Card Package (3rd Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Web Development and Design Foundations with HTML5 (8th Edition)
- Describe three (3) Multiplexing techniques common for fiber optic linksarrow_forwardCould you help me to know features of the following concepts: - commercial CA - memory integrity - WMI filterarrow_forwardBriefly describe the issues involved in using ATM technology in Local Area Networksarrow_forward
- For this question you will perform two levels of quicksort on an array containing these numbers: 59 41 61 73 43 57 50 13 96 88 42 77 27 95 32 89 In the first blank, enter the array contents after the top level partition. In the second blank, enter the array contents after one more partition of the left-hand subarray resulting from the first partition. In the third blank, enter the array contents after one more partition of the right-hand subarray resulting from the first partition. Print the numbers with a single space between them. Use the algorithm we covered in class, in which the first element of the subarray is the partition value. Question 1 options: Blank # 1 Blank # 2 Blank # 3arrow_forward1. Transform the E-R diagram into a set of relations. Country_of Agent ID Agent H Holds Is_Reponsible_for Consignment Number $ Value May Contain Consignment Transports Container Destination Ф R Goes Off Container Number Size Vessel Voyage Registry Vessel ID Voyage_ID Tonnagearrow_forwardI want to solve 13.2 using matlab please helparrow_forward
- a) Show a possible trace of the OSPF algorithm for computing the routing table in Router 2 forthis network.b) Show the messages used by RIP to compute routing tables.arrow_forwardusing r language to answer question 4 Question 4: Obtain a 95% standard normal bootstrap confidence interval, a 95% basic bootstrap confidence interval, and a percentile confidence interval for the ρb12 in Question 3.arrow_forwardusing r language to answer question 4. Question 4: Obtain a 95% standard normal bootstrap confidence interval, a 95% basic bootstrap confidence interval, and a percentile confidence interval for the ρb12 in Question 3.arrow_forward
 C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr
C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr New Perspectives on HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScriptComputer ScienceISBN:9781305503922Author:Patrick M. CareyPublisher:Cengage Learning
New Perspectives on HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScriptComputer ScienceISBN:9781305503922Author:Patrick M. CareyPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK JAVA PROGRAMMINGComputer ScienceISBN:9781337671385Author:FARRELLPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK JAVA PROGRAMMINGComputer ScienceISBN:9781337671385Author:FARRELLPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Microsoft Visual C#Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102100Author:Joyce, Farrell.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Microsoft Visual C#Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102100Author:Joyce, Farrell.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Systems ArchitectureComputer ScienceISBN:9781305080195Author:Stephen D. BurdPublisher:Cengage Learning
Systems ArchitectureComputer ScienceISBN:9781305080195Author:Stephen D. BurdPublisher:Cengage Learning C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning





