Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The Lewis formula of
Concept Introduction:
Lewis Structure: A Lewis structure shows a covalent bond as pair of electrons shared between two atoms.
Procedure to write Lewis formulas:
- The symbols of the atoms that are bonded together in the molecule next to one another are arranged.
- The total number of valence electrons in the molecule is calculated by adding the number of valence electrons for all the atoms in the molecules. If the species is an ion, then the charge of ion into account by adding electrons, if it is a negative ion or subtracting electrons if it is a positive ion.
- A two-electron covalent bond is represented by placing a line between the atoms, which are assumed to be bonded to each other.
- The remaining valence electrons as lone pairs about each atom are arranged so that the octet rule is satisfied for each other.
Formal charge (F.C): The charges that assigned to each atom in a molecule or ion by a set of arbitrary rules and don not actually represent the actual charges on the atoms are called as formal charges.
The formal charge is calculated using the formula,
The Lewis structure with zero formal charge or least separated formal charges is the preferred structure of the molecule.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The total number of valence electrons in
Number of valence electrons in oxygen=
Number of valence electrons in chlorine=
Since there is a negative charge present in ion, one electron is added.
The total number of valence electrons is thirty-two.
One chlorine atom forms four bonds with oxygen that is eight electrons are used to form bonds and the remaining twenty-four atoms are used to satisfy the octet rule of oxygen atoms.
The Lewis formula is,
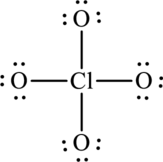
The formal charge for each atom is calculated as,
Formal charge on chlorine=
Formula charge on oxygen=
The Lewis formula is,
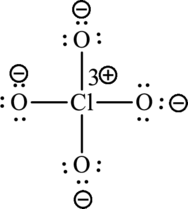
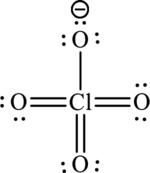
A large charge separation can be seen in the structure, this can be avoided by adding three pi bonds between oxygen and chlorine. The chlorine atom can expand the octet rule since it belongs to period three. The final Lewis structure is,
(b)
Interpretation:
The Lewis formula of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The total number of valence electrons in
Number of valence electrons in oxygen=
Number of valence electrons in chlorine=
The total number of valence electrons is thirteen.
One chlorine atom forms a bond with oxygen atom that is two electrons are used to form bonds and the remaining nine electrons are used to satisfy the octet rule of oxygen and chlorine atoms.
The Lewis formula is,
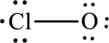
The formal charge for each atom is calculated as,
Formal charge on chlorine=
Formula charge on oxygen=
The Lewis formula is,
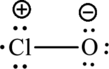
(c)
Interpretation:
The Lewis formula of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The total number of valence electrons in
Number of valence electrons in oxygen=
Number of valence electrons in chlorine=
Since there is a negative charge present in ion, one electron is added.
The total number of valence electrons is twenty-six.
One chlorine atom forms three bonds with oxygen that is six electrons are used to form bonds and the remaining twenty atoms are used to satisfy the octet rule of oxygen atoms.
The Lewis formula is,
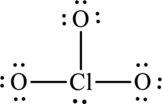
The formal charge for each atom is calculated as,
Formal charge on chlorine=
Formula charge on oxygen=
The Lewis formula is,
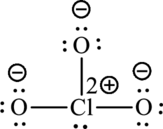
A large charge separation can be seen in the structure, this can be avoided by adding two pi bonds between oxygen and chlorine. The chlorine atom can expand the octet rule since it belongs to period three. The final Lewis structure is,
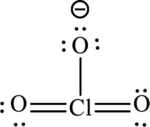
(d)
Interpretation:
The Lewis formula of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The total number of valence electrons in
Number of valence electrons in oxygen=
Number of valence electrons in chlorine=
The total number of valence electrons is nineteen.
One chlorine atom forms two bonds with oxygen atom that is four electrons are used to form bonds and the remaining fifteen atoms are used to satisfy the octet rule of oxygen atoms.
The Lewis formula is,
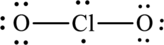
The formal charge for each atom is calculated as,
Formal charge on chlorine=
Formula charge on oxygen=
The Lewis formula becomes,
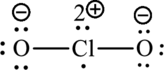
A large charge separation can be removed, by adding two pi bonds between chlorine and oxygen. Since chlorine belongs to third period, it can expand the octet rule. The final Lewis structure is,
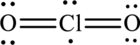
(e)
Interpretation:
The Lewis formula of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(e)
Explanation of Solution
The total number of valence electrons in
Number of valence electrons in oxygen=
Number of valence electrons in chlorine=
Since there is a negative charge present, one electron is added.
The total number of valence electrons is fourteen.
One chlorine atom forms a bond with oxygen atom that is two electrons are used to form bonds and the remaining twelve atoms are used to satisfy the octet rule of oxygen and chlorine atoms.
The Lewis formula is,
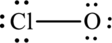
The formal charge for each atom is calculated as,
Formal charge on chlorine=
Formula charge on oxygen=
The Lewis formula is,
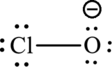
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Student Solutions Manual to Accompany General Chemistry
- What are the major products of the following organic reaction? Please include a detailed explanation as well as a drawing as to how the reaction proceeds.arrow_forwardWhat are the major products of the following reaction? Please provide a detailed explanation and a drawing to show how the reaction proceeds.arrow_forwardWhat are the major products of the following organic reaction? Please include a detailed explanation as well as a drawing as to how the reaction proceeds.arrow_forward
- Predict the organic product that forms in the reaction below: H + гон OH H+ H+ ☑ O Note: You may assume you have an excess of either reactant if the reaction requires more than one of those molecules to form the product. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the missing organic product X. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. S 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centearrow_forwardIn the analysis of Mg content in a 25 mL sample, a titration volume of 5 mL was obtained using 0.01 M EDTA. Calculate the Mg content in the sample if the Ca content is 20 ppmarrow_forwardPredict the organic products that form in the reaction below: H. H+ + OH H+ Y Note: You may assume you have an excess of either reactant if the reaction requires more than one of those molecules to form the products. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic products X and Y. You may draw the structures in any arrangement that you like, so long as they aren't touching. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. G X C © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Access +arrow_forward
- 111 Carbonyl Chem Choosing reagants for a Wittig reaction What would be the best choices for the missing reagents 1 and 3 in this synthesis? 1. PPh3 3 1 2 2. n-BuLi • Draw the missing reagents in the drawing area below. You can draw them in any arrangement you like. Do not draw the missing reagent 2. If you draw 1 correctly, we'll know what it is. • Note: if one of your reagents needs to contain a halogen, use bromine. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. × ©2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Usearrow_forwardA student proposes the transformation below in one step of an organic synthesis. There may be one or more reactants missing from the left-hand side, but there are no products missing from the right-hand side. There may also be catalysts, small inorganic reagents, and other important reaction conditions missing from the arrow. • Is the student's transformation possible? If not, check the box under the drawing area. . If the student's transformation is possible, then complete the reaction by adding any missing reactants to the left-hand side, and adding required catalysts, inorganic reagents, or other important reaction conditions above and below the arrow. • You do not need to balance the reaction, but be sure every important organic reactant or product is shown. + T X O O лет-ле HO OH HO OH This transformation can't be done in one step.arrow_forwardDetermine the structures of the missing organic molecules in the following reaction: X+H₂O H* H+ Y OH OH Note: Molecules that share the same letter have the exact same structure. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic molecules X and Y. You may draw the structures in any arrangement that you like, so long as they aren't touching. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X Sarrow_forward
- Predict the major products of this organic reaction. If there aren't any products, because nothing will happen, check the box under the drawing area instead. No reaction. HO. O :☐ + G Na O.H Click and drag to start drawing a structure. XS xs H₂Oarrow_forwardWhat are the angles a and b in the actual molecule of which this is a Lewis structure? H H C H- a -H b H Note for advanced students: give the ideal angles, and don't worry about small differences from the ideal groups may have slightly different sizes. a = b = 0 °arrow_forwardWhat are the angles a and b in the actual molecule of which this is a Lewis structure? :0: HCOH a Note for advanced students: give the ideal angles, and don't worry about small differences from the ideal that might be caused by the fact that different electron groups may have slightly different sizes. a = 0 b=0° Sarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





