
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether the given substrate undergoes E2 elimination step with base
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 7.29P
The given substrate cannot undergo E2 elimination step with base
Explanation of Solution
The given substrate is
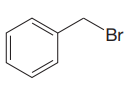
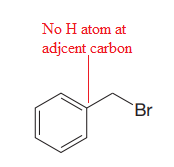
Thus, the given substrate cannot undergo
No H atom on adjacent carbon atom.
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether the given substrate undergoes E2 elimination step with base
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 7.29P
The given substrate undergoes E2 elimination step.
The E2 elimination step for the given substrate is drawn as:
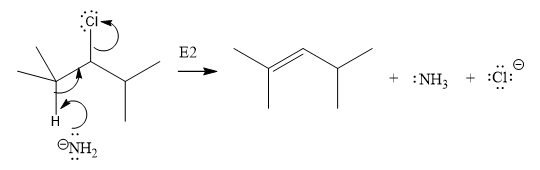
Explanation of Solution
The given substrate is:
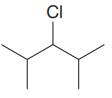
In the above given substrate, Cl acts as a leaving group with one H atom on each side. Any one of the hydrogen atom is taken away forming a C=C bond. The first curved arrow is drawn from the lone pair of nitrogen atom of a base

The product of
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether the given substrate undergo E2 elimination step with base
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 7.29P
The given substrate undergoes E2 elimination step.
The E2 elimination step for the given substrate is drawn as:
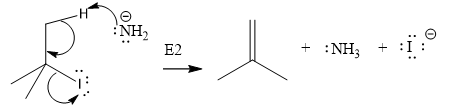
Explanation of Solution
The given substrate is:
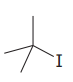
In the above given substrate,
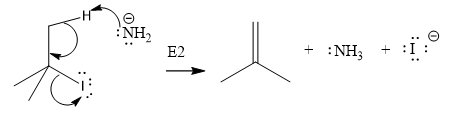
The product of
(d)
Interpretation:
Whether the given substrate undergoes E2 elimination step with base
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 7.29P
The given substrate cannot undergoes E2 elimination step with base
Explanation of Solution
The given substrate is
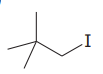
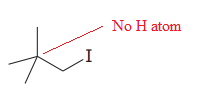
Thus, the given substrate cannot undergo
There is no H atom on the adjacent carbon atom.
(e)
Interpretation:
Whether the given substrate undergo E2 elimination step with base
Concept introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 7.29P
The given substrate undergoes E2 elimination step.
The E2 elimination step for the given substrate is drawn as:
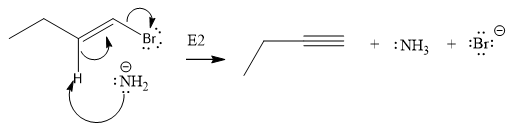
Explanation of Solution
The given substrate is
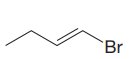
In the above given substrate,
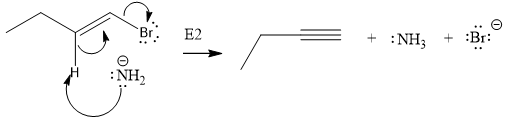
The product of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: PRINCIPLES AND M
- answer with mechanisms and steps. handwritten please!arrow_forwardHello I need some help with Smartwork. For drawing structure B, I know the correct answer is CH₃B₂, but when I try to type it in, it keeps giving me CH₄BH₃ instead. Do you know how I should write it properly? Should I use a bond or something else?arrow_forwardTrue or false, chemistryarrow_forward
- answer thse questions with mechanisms and steps. handwritten please!arrow_forwardC app.aktiv.com Draw the product of the following reaction sequence. Ignore any inorganic byproducts formed. H O 1. (CH3CH2)2CuLi, THF 2. CH3Br Drawingarrow_forwardDraw the product of the following reaction sequence. Ignore any inorganic byproducts formed. H O 1. (CH3CH2)2CuLi, THF 2. CHзBr Drawingarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
