
Concept explainers
A cylindrical cast-iron casting has an axial bole extending partway through the casting, as shown. Locate the center of gravity of the casting.

The location of the center of gravity of the casting.
Answer to Problem 7.1P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Given a cylindrical cast iron casting having an axial hole extending pathway through the casting.
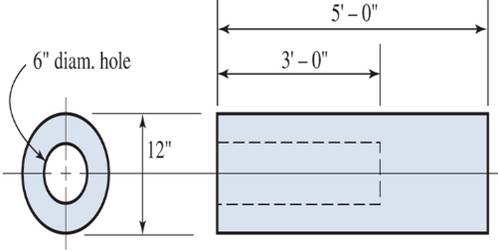
The centroid of a body can be found with two axes taken into consideration. As, the given figure is symmetrical about X-axis, so the centroid must lie on the X-axis. Now, by calculating the weight of the given member with reference to densities taken from U S Customary codes for typical average properties of some common materials. Thereby, in reference to the codes the weight of cast iron is taken as
Calculation:
Let W1the weight of the whole cylinder and W2 the weight of the empty space considering its density same as that of the cast iron.
Now we have,
Conclusion:
Therefore, the location of center of gravity of the casting is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
Modern Database Management
Introduction To Programming Using Visual Basic (11th Edition)
Starting Out With Visual Basic (8th Edition)
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
- A cantilevered rectangular prismatic beam has three loads applied. 10,000N in the positive x direction, 500N in the positive z direction and 750 in the negative y direction. You have been tasked with analysing the stresses at three points on the beam, a, b and c. 32mm 60mm 24mm 180mm 15mm 15mm 40mm 750N 16mm 500N x 10,000N Figure 2: Idealisation of the structure and the applied loading (right). Photograph of the new product (left). Picture sourced from amazon.com.au. To assess the design, you will: a) Determine state of stress at all points (a, b and c). These points are located on the exterior surface of the beam. Point a is located along the centreline of the beam, point b is 15mm from the centreline and point c is located on the edge of the beam. When calculating the stresses you must consider the stresses due to bending and transverse shear. Present your results in a table and ensure that your sign convention is clearly shown (and applied consistently!) (3%) b) You have identified…arrow_forward7.82 Water flows from the reservoir on the left to the reservoir on the right at a rate of 16 cfs. The formula for the head losses in the pipes is h₁ = 0.02(L/D)(V²/2g). What elevation in the left reservoir is required to produce this flow? Also carefully sketch the HGL and the EGL for the system. Note: Assume the head-loss formula can be used for the smaller pipe as well as for the larger pipe. Assume α = 1.0 at all locations. Elevation = ? 200 ft 300 ft D₁ = 1.128 ft D2=1.596 ft 12 2012 Problem 7.82 Elevation = 110 ftarrow_forwardHomework#5arrow_forwardA closed-cycle gas turbine unit operating with maximum and minimum temperature of 760oC and 20oC has a pressure ratio of 7/1. Calculate the ideal cycle efficiency and the work ratioarrow_forwardConsider a steam power plant that operates on a simple, ideal Rankine cycle and has a net power output of 45 MW. Steam enters the turbine at 7 MPa and 500°C and is cooled in the condenser at a pressure of 10 kPa by running cooling water from a lake through the tubes of the condenser at a rate of 2000 kg/s. Show the cycle on a T-s diagram with respect to saturation lines, and determine The thermal efficiency of the cycle,The mass flow rate of the steam and the temperature rise of the cooling waterarrow_forwardTwo reversible heat engines operate in series between a source at 600°C, and a sink at 30°C. If the engines have equal efficiencies and the first rejects 400 kJ to the second, calculate: the temperature at which heat is supplied to the second engine, The heat taken from the source; and The work done by each engine. Assume each engine operates on the Carnot cyclearrow_forwardA steam turbine operates at steady state with inlet conditions of P1 = 5 bar, T1 = 320°C. Steam leaves the turbine at a pressure of 1 bar. There is no significant heat transfer between the turbine and its surroundings, and kinetic and potential energy changes between inlet and exit are negligible. If the isentropic turbine efficiency is 75%, determine the work developed per unit mass of steam flowing through the turbine, in kJ/kgarrow_forwardYou are asked to design a unit to condense ammonia. The required condensation rate is 0.09kg/s. Saturated ammonia at 30 o C is passed over a vertical plate (10 cm high and 25 cm wide).The properties of ammonia at the saturation temperature of 30°C are hfg = 1144 ́10^3 J/kg andrv = 9.055 kg/m 3 . Use the properties of liquid ammonia at the film temperature of 20°C (Ts =10 o C):Pr = 1.463 rho_l= 610.2 kf/m^3 liquid viscosity= 1.519*10^-4 kg/ ms kinematic viscosity= 2.489*10^-7 m^2/s Cpl= 4745 J/kg C kl=0.4927 W/m Ca)Calculate the surface temperature required to achieve the desired condensation rate of 0.09 kg/s( should be 688 degrees C) b) Show that if you use a bigger vertical plate (2.5 m-wide and 0.8 m-height), the requiredsurface temperature would be now 20 o C. You may use all the properties given as an initialguess. No need to iterate to correct for Tf. c) What if you still want to use small plates because of the space constrains? One way to getaround this problem is to use small…arrow_forwardUsing the three moment theorem, how was A2 determined?arrow_forwardDraw the kinematic diagram of the following mechanismarrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_iosRecommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L