
Concept explainers
(a)
Find the quantity of water flowing through the sample per hour.
(a)
Answer to Problem 7.1CTP
The quantity of water flowing through the sample per hour is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The length of each soil layer
The total length of the soil layer H is 600 mm.
The diameter of the cylindrical tube d is 150 mm.
The constant head difference
The porosity of the soil layer I
The porosity of the soil layer II
The porosity of the soil layer III
The hydraulic conductivity of soil layer I
The hydraulic conductivity of soil layer II
The hydraulic conductivity of soil layer III
Calculation:
Determine the hydraulic conductivity in the vertical direction using the relation.
Substitute 600 mm for H, 200 mm for
Determine the hydraulic gradient using the relation.
Here, L is the total length of the soil layer.
Substitute 470 mm for
Determine the area of the cylindrical tube using the relation.
Substitute 150 mm for d.
Determine the rate of seepage per unit length of the dam using the relation.
Substitute
Therefore, the quantity of water flowing through the sample per hour is
(b)
Find the elevation head (Z), pressure head
(b)
Answer to Problem 7.1CTP
The elevation head (
The pressure head
The total head
The elevation head (
The pressure head
The total head
The elevation head (
The pressure head
The total head
The elevation head (
The pressure head
The total head
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The length of each soil layer
The total length of the soil layer H is 600 mm.
The diameter of the cylindrical tube d is 150 mm.
The constant head difference
The porosity of the soil layer I
The porosity of the soil layer II
The porosity of the soil layer III
The hydraulic conductivity of soil layer I
The hydraulic conductivity of soil layer II
The hydraulic conductivity of soil layer III
Calculation:
Determine the elevation head (
Here,
Substitute 220 mm for
Therefore, the elevation head (
Determine the pressure head
Substitute 470 mm for
Therefore, the pressure head
Determine the total head
Substitute 690 mm for
Therefore, the total head
Determine the elevation head (
Substitute 220 mm for
Therefore, the elevation head (
Determine the value of
Substitute
Determine the total head
Substitute 470 mm for
Therefore, the total head
Determine the pressure head
Substitute 436.3 mm for
Therefore, the pressure head
Determine the elevation head
Substitute 220 mm for
Therefore, the elevation head (
Determine the value of
Substitute
Determine the total head
Substitute 436.3 mm for
The total head
Determine the pressure head
Substitute 432.3 mm for
Therefore, The pressure head
Determine the elevation head
Substitute 220 mm for
Therefore, the elevation head (
Determine the value of
Substitute
Determine the total head
Substitute 432.3 mm for
Therefore, the total head
Determine the pressure head
Substitute 432.3 mm for
Therefore, the pressure head
(c)
Plot the variation of the elevation head, pressure head, and the total head with the horizontal distance along the sample axis (X–X).
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The length of each soil layer
The total length of the soil layer H is 600 mm.
The diameter of the cylindrical tube d is 150 mm.
The constant head difference
The porosity of the soil layer I
The porosity of the soil layer II
The porosity of the soil layer III
The hydraulic conductivity of soil layer I
The hydraulic conductivity of soil layer II
The hydraulic conductivity of soil layer III
Calculation:
Refer Part b)
Draw the graph between the elevation head pressure head, and the total head with the horizontal distance along the sample axis (X–X) as in Figure (1).
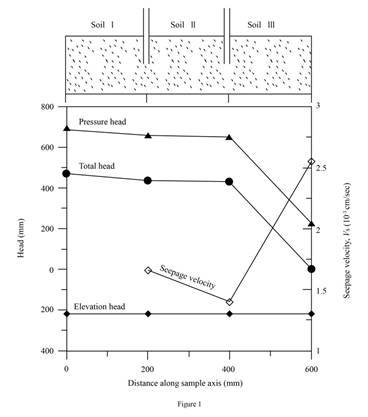
(d)
Plot the variation of the discharge velocity and the seepage velocity along the sample axis (X–X).
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The length of each soil layer
The total length of the soil layer H is 600 mm.
The diameter of the cylindrical tube d is 150 mm.
The constant head difference
The porosity of the soil layer I
The porosity of the soil layer II
The porosity of the soil layer III
The hydraulic conductivity of soil layer I
The hydraulic conductivity of soil layer II
The hydraulic conductivity of soil layer III
Calculation:
Determine the discharge velocity v using the relation.
Substitute
Determine the seepage velocity of soil I using the relation.
Here,
Substitute 0.000843 cm/sec for v and 0.5 for
Determine the seepage velocity of soil II using the relation.
Here,
Substitute 0.000843 cm/sec for v and 0.6 for
Determine the seepage velocity of soil III using the relation.
Here,
Substitute 0.000843 cm/sec for v and 0.33 for
Draw graph of variation of the discharge velocity and the seepage velocity along the sample axis (X–X).
Refer Figure (1) in Part (c).
(e)
Find the height of the vertical columns of water inside piezometers A and B installed on the sample axis.
(e)
Answer to Problem 7.1CTP
The height of the vertical columns of water at point A is
The height of the vertical columns of water at point B is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The length of each soil layer
The total length of the soil layer H is 600 mm.
The diameter of the cylindrical tube d is 150 mm.
The constant head difference
The porosity of the soil layer I
The porosity of the soil layer II
The porosity of the soil layer III
The hydraulic conductivity of soil layer I
The hydraulic conductivity of soil layer II
The hydraulic conductivity of soil layer III
Calculation:
The height of water column is equal to the Piezometric or pressure head at a point.
Determine the height of water in point A.
Substitute 656.3 mm for
Therefore, the height of the vertical columns of water at point A is
Determine the height of water in point B.
Substitute 652.3 mm for
Therefore, the height of the vertical columns of water at point B is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
PRIN.OF GEOTECHNICAL...-MINDTAP(2 SEM)
- Text Book Problem 7.82 (page 261) Consider the total head-loss in the system forthis flow is 18.56 ft (head-losses in first and second pipe are 13.83 ft and 4.73 ftrespectively). Please show numerical values for EGL/HGL at the beginning/end/intermediatechange point. (Point distribution: elevation determination 5 points, EGL, HGL lines 4points).(I think we are just using the values provided for head losses to solve this problem)arrow_forwardCalculate the BMs (bending moments) at all the joints of the beam shown in Fig.1 using the moment distribution method, and draw the Shear force diagram and Bending moment diagram for the beam shown. The beam is subjected to an UDL of w=65m. L=4.5m L1= 1.8m. Assume the support at C is pinned, and A and B are roller supports. E = 200GPa, I = 250x106 mm4.arrow_forwardCalculate the BMs (bending moments) at all the joints of the beam shown in Fig.1 using the Slope deflection method. The beam is subjected to an UDL of w=65m. L=4.5m L1= 1.8m. Assume the support at C is pinned, and A and B are roller supports. E = 200GPa, I = 250x106 mm4.arrow_forward
- Thank you for your help if you would also provide the equations used .arrow_forwardThe sectors are divided as follows:top right = 1, top left = 2, middle = 3, bottom = 4.(a) Determine the distance yˉ to the centroid of the beam’s cross-sectional area.Solve the next questions by building a table. (Table format Answers) (b) Determine the second moment of area (moment of inertia) about the x′ axis. (c) Determine the second moment of area (moment of inertia) about the y-axis.arrow_forwardinstructions: make sure to follow the instructions and provide complete and detailed solution create/draw a beam with uniformly distributed load and concentrated load after, find the shear and moment equation and ensure to draw it's shear and moment diagram once done, write it's conclusion or observation 4:57 PMarrow_forward
- Solve for forces on pin C and Darrow_forwardBorrow pit soil is being used to fill an 900,00 yd3 of depression. The properties of borrowpit and in-place fill soils obtained from laboratory test results are as follows:• Borrow pit soil: bulk density 105 pcf, moisture content = 8%, and specific gravity = 2.65• In-place fill soil: dry unit weight =120 pcf, and moisture content = 16%(a) How many yd3 of borrow soil is required?(b) What water mass is needed to achieve 16% moisture in the fill soil?(c) What is the in-place density after a long rain?arrow_forwardsolve for dt/dx=f(t,x)=x+t^2arrow_forward
- Calculate the BMs (bending moments) at all the joints of the beam shown in Fig.1 using the slope deflection method, draw the resulting shear force diagran and bending moment diagram. The beam is subjected to an UDL of w=65m. L=4.5m, L1= 1.8m. Assume the support at C is pinned, and A and B are roller supports. E = 200 GPa, I = 250x106 mm4.arrow_forwardProblem 2 (A is fixed and C is a pin) Find the reactions and A and C. 10 k- 6 ft 6 ft B A 2 k/ft 15 ftarrow_forward6. A lake with no outlet is fed by a river with a constant flow of 1200 ft3/s. Water evaporates from the surface at a constant rate of 13 ft3/s per square mile of surface area. The surface area varies with the depth h (in feet) as A (square miles) = 4.5 + 5.5h. What is the equilibrium depth of the lake? Below what river discharge (volume flow rate) will the lake dry up?arrow_forward
 Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning


