
Concept explainers
(1)
Note receivable:
Note receivable refers to a written promise for the amounts to be received within a stipulated period of time. This written promise is issued by a debtor or borrower to lender or creditor. Notes receivable is an asset of a business.
To prepare:
(1)
Explanation of Solution
Journal entries of FL bank are as follows:
FL bank agreed to settle the debt in exchange for land worth $16 million.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Land | 16,000,000 | |||
| Loss on debt restructuring | 6,000,000 | |||
| Note receivable | 20,000,000 | |||
| Accrued interest receivable (1) | 2,000,000 | |||
| (To record the settlement of land for the debt) |
Table (1)
Working note:
(2)(a)
Interest accrued from last year.
(2)(a)
Explanation of Solution
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| January 1, 2018 | Loss on troubled debt restructuring | 8,584,980 | ||
| Accrued interest receivable (1) | 2,000,000 | |||
| Note receivable
|
6,584,980 | |||
| (To record accrued interest) |
Table (2)
Working note:
| $ | $ | |
| Previous value: | ||
| Interest Accrued 2017 (1) | 2,000,000 | |
| Principal | 20,000,000 | |
| Carrying amount of the receivables | 22,000,000 | |
| New value: | ||
| Interest
|
3,169,870 | |
| Principal
|
10,245,150 | |
| Present value of the receivable | (13,415,02) | |
| Loss | 8,584,980 |
Table (3)
- PV factor of 3.16987 (Present value of an ordinary annuity of $1: n = 4, i = 10%) is taken from the table value (Refer Table 4 in Appendix from textbook).
- PV factor of 0.68301 (Present value of $1: n = 4, i = 10%) is taken from the table value (Refer Table 2 in Appendix from textbook).
(b)
Reduce the interest payment to $1 Million each:
(b)
Explanation of Solution
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| December 31, 2018 | Cash (required by new agreement) | 1,000,000 | ||
| Note receivable (Balance) | 341,502 | |||
| Interest revenue
|
1,341,502 | |||
| (To record the interest revenue ) |
Table (4)
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| December 31, 2019 | Cash (required by new agreement) | 1,000,000 | ||
| Note receivable (Balance) | 375,652 | |||
| Interest revenue
|
1,375,652 | |||
| (To record the interest revenue ) |
Table (5)
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| December 31, 2020 | Cash (required by new agreement) | 1,000,000 | ||
| Note receivable (Balance) | 413,217 | |||
| Interest revenue
|
1,413,217 | |||
| (To record the interest revenue ) |
Table (6)
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| December 31, 2021 | Cash (required by new agreement) | 1,000,000 | ||
| Note receivable (Balance) | 454,609 | |||
| Interest revenue
|
1,454,609 | |||
| (To record the interest revenue ) |
Table (7)
(c)
Reduce the principal to $15 Million:
(c)
Explanation of Solution
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| December 31, 2021 | Cash (required by new agreement) | 15,000,000 | ||
| Note receivable (Balance) | 15,000,000 | |||
| (To record the principal ) |
Table (8)
Note:
- $15,000,000 is rounded to amortize the note.
Working note:
Amortization schedule:
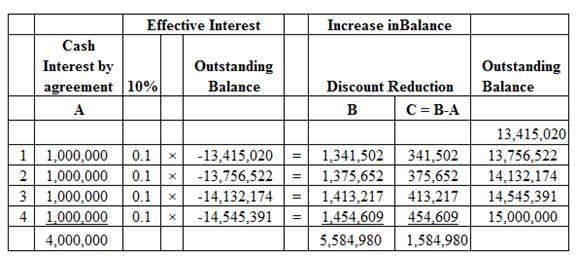
Image (1)
(3)
To defer all payments until the maturity date:
(3)
Explanation of Solution
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| January 1, 2018 | Loss on troubled debt restructuring | 3,029,397 | ||
| Accrued interest receivable (1) | 2,000,000 | |||
| Note receivable
|
1,029,397 | |||
| (To record the loss on debt ) | ||||
| December 31, 2018 | Note receivable (Balance) | 1,897,060 | ||
| Interest revenue
|
1,897,060 | |||
| (To record the interest revenue ) | ||||
| December 31, 2019 | Note receivable (Balance) | 2,086,766 | ||
| Interest revenue
|
2,086,766 | |||
| (To record the interest revenue ) | ||||
| December 31, 2020 | Note receivable (Balance) | 2,295,443 | ||
| Interest revenue (Refer schedule) | 2,295,443 | |||
| To record the interest revenue ) | ||||
| December 31, 2021 | Note receivable (Balance) | 2,295,443 | ||
| Interest revenue (Refer schedule) | 2,295,443 | |||
| To record the interest revenue ) | ||||
| December 31, 2021 | Cash (required by new agreement) | 27,775,000 | ||
| Note receivable (Balance) | 27,775,000 | |||
| (To record the principal ) | ||||
Table (8)
Working notes:
| $ | |
| Previous value: | |
| Interest Accrued 2017 (1) | 2,000,000 |
| Principal | 20,000,000 |
| Carrying amount of the receivables | |
| New value: | |
| Principal
|
18,970,603 |
| Loss | 3,029,397 |
Table (9)
- PV factor of 0.68301 (Present value of $1: n = 4, i = 10%) is taken from the table value (Refer Table 2 in Appendix from textbook).
Amortization schedule:
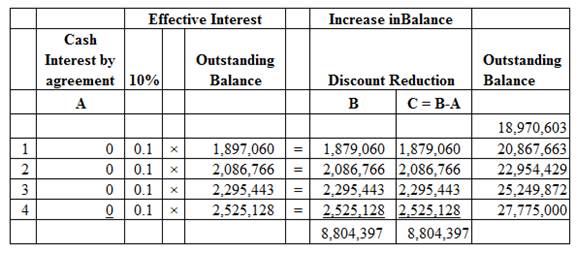
Image (2)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
INTERMEDIATE ACCOUNTING(LL)-W/CONNECT
- Hi expert please given correct answer with accounting questionarrow_forwardAccountingarrow_forwardmighty Manny, Incorporated manufactures ice scrapers and distributes them across the midwestern United States. Mighty Manny is incorporated and headquartered in Michigan. It has product sales to customers in Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Minnesota, and Wisconsin. It has sales personnel only in the states discussed and all these states have adopted Wayfair legislation. Determine the state in which Mighty Manny does not have sales and nexus given the following scenarios:arrow_forward
- Please provide the answer to this general accounting question with proper steps.arrow_forwardNullarrow_forwardThirst Quencher produced 20,000 cases of powdered drink mix and sold 17,000 cases in April. The sales price was $22 per case, variable costs were $14 per case ($10 manufacturing and $4 selling and administrative), and total fixed costs were $55,000 ($40,000 manufacturing overhead and $15,000 selling and administrative). The company had no beginning Finished Goods Inventory. Requirements1. Prepare the April income statement using absorption costing.Known - OI $87,000 2. Determine the product cost per unit and the total cost of the 3,000 cases in Finished Goods Inventory as of April 30. 3. Is the April 30 balance in Finished Goods Inventory higher or lower than variable costing? Explain why.arrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning



