
(1)
Note receivable:
Note receivable refers to a written promise for the amounts to be received within a stipulated period of time. This written promise is issued by a debtor or borrower to lender or creditor. Notes receivable is an asset of a business.
To prepare:
(1)
Explanation of Solution
Journal entries of FL bank are as follows:
FL bank agreed to settle the debt in exchange for land worth $16 million.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Land | 16,000,000 | |||
| Loss on debt restructuring | 6,000,000 | |||
| Note receivable | 20,000,000 | |||
| Accrued interest receivable (1) | 2,000,000 | |||
| (To record the settlement of land for the debt) |
Table (1)
Working note:
(2) (a)
To prepare: Journal entries to record the following transaction.
(2) (a)
Explanation of Solution
Interest accrued from last year.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| January 1, 2016 | Loss on troubled debt restructuring | 8,584,980 | ||
| Accrued interest receivable (1) | 2,000,000 | |||
| Note receivable
|
6,584,980 | |||
| (To record accrued interest) |
Table (2)
Working note:
|
|
$ | $ |
| Previous value: | ||
| Interest Accrued 2015 (1) | 2,000,000 | |
| Principal | 20,000,000 | |
| Carrying amount of the receivables | 22,000,000 | |
| New value: | ||
| Interest
|
3,169,870 | |
| Principal
|
10,245,150 | |
| Present value of the receivable | (13,415,02) | |
| Loss | 8,584,980 |
Table (3)
- PV factor of 3.16987 (Present value of an ordinary annuity of $1: n = 4, i = 10%) is taken from the table value (Refer Table 4 in Appendix from textbook).
- PV factor of 0.68301 (Present value of $1: n = 4, i = 10%) is taken from the table value (Refer Table 2 in Appendix from textbook).
(2) (b)
To prepare: Journal entries to record the following transaction.
(2) (b)
Explanation of Solution
Reduce the interest payment to $1 Million each:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| December 31, 2016 | Cash (required by new agreement) | 1,000,000 | ||
| Note receivable (Balance) | 341,502 | |||
| Interest revenue
|
1,341,502 | |||
| (To record the interest revenue ) |
Table (4)
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| December 31, 2017 | Cash (required by new agreement) | 1,000,000 | ||
| Note receivable (Balance) | 375,652 | |||
| Interest revenue
|
1,375,652 | |||
| (To record the interest revenue ) |
Table (5)
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| December 31, 2018 | Cash (required by new agreement) | 1,000,000 | ||
| Note receivable (Balance) | 413,217 | |||
| Interest revenue
|
1,413,217 | |||
| (To record the interest revenue ) |
Table (6)
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| December 31, 2019 | Cash (required by new agreement) | 1,000,000 | ||
| Note receivable (Balance) | 454,609 | |||
| Interest revenue
|
1,454,609 | |||
| (To record the interest revenue ) |
Table (7)
(2) (c)
To prepare: Journal entries to record the following transaction.
(2) (c)
Explanation of Solution
Reduce the principal to $15 Million:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| December 31, 2019 | Cash (required by new agreement) | 15,000,000 | ||
| Note receivable (Balance) | 15,000,000 | |||
| (To record the principal ) |
Table (8)
Note:
- $15,000,000 is rounded to amortize the note.
Working note:
Amortization schedule:
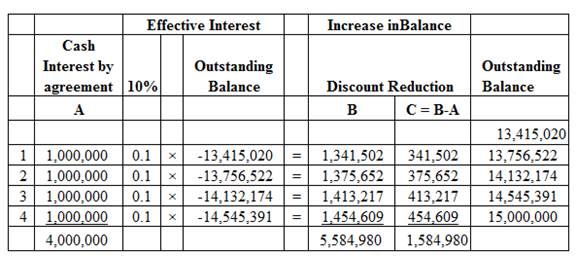
Image (1)
(3)
To prepare: Journal entries to record the following transaction.
(3)
Explanation of Solution
To defer all payments until the maturity date:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| January 1, 2016 | Loss on troubled debt restructuring | 3,029,397 | ||
| Accrued interest receivable (1) | 2,000,000 | |||
| Note receivable
|
1,029,397 | |||
| (To record the loss on debt ) | ||||
| December 31, 2016 | Note receivable (Balance) | 1,897,060 | ||
| Interest revenue
|
1,897,060 | |||
| (To record the interest revenue ) | ||||
| December 31, 2017 | Note receivable (Balance) | 2,086,766 | ||
| Interest revenue
|
2,086,766 | |||
| (To record the interest revenue ) | ||||
| December 31, 2018 | Note receivable (Balance) | 2,295,443 | ||
| Interest revenue (Refer schedule) | 2,295,443 | |||
| To record the interest revenue ) | ||||
| December 31, 2019 | Note receivable (Balance) | 2,295,443 | ||
| Interest revenue (Refer schedule) | 2,295,443 | |||
| To record the interest revenue ) | ||||
| December 31, 2019 | Cash (required by new agreement) | 27,775,000 | ||
| Note receivable (Balance) | 27,775,000 | |||
| (To record the principal ) | ||||
Table (8)
Working notes:
|
|
$ |
| Previous value: | |
| Interest Accrued 2015 (1) | 2,000,000 |
| Principal | 20,000,000 |
| Carrying amount of the receivables | |
| New value: | |
| Principal
|
18,970,603 |
| Loss | 3,029,397 |
Table (9)
- PV factor of 0.68301 (Present value of $1: n = 4, i = 10%) is taken from the table value (Refer Table 2 in Appendix from textbook).
Amortization schedule:
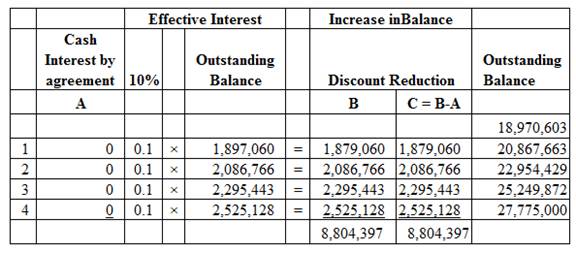
Image (2)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
INTERMEDIATE ACCT.-CONNECT PLUS ACCESS
- Given the solution and general accountingarrow_forwardThe city of Greenfield is considering building a community sports complex on vacant commercial land. The estimated benefit to the community is $2,400,000. Contractors have estimated the net cost to build the sports complex and rezone the property at $3,200,000. Should the city build the sports complex? A. 0.75 and Yes B. 0.75 and No C. 1.33 and Yes D. 1.33 and Noarrow_forwardMadison Industries uses the FIFO (first-in, first-out) method in its process costing system. The mixing department had $4,800 in material cost in its beginning work in process inventory, and $68,000 in material cost was added during the period. The equivalent units of production for materials during the period were 17,000 units. What is the cost per equivalent unit for materials? Helparrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





