
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
Based on the structure given, the different types of stereoisomers for each of the conditions given are to be identified.
Concept introduction:
A chiral carbon atom is attached to four different atoms or groups of atoms. The number of stereoisomers is determined by using the formula
Stereoisomers arise from chiral centers as well as the arrangement of atoms or groups attached to the double bonded carbon atoms.
The pair of isomers designated
Enantiomers are non-superimposable mirror images of each other.
Stereoisomers that are not mirror images are diastereomers.
Answer to Problem 35P
Solution:
a) The number of stereoisomers represented by the given constitution is
b) If the substituents on the five-membered ring are cis to each other, then there are four stereoisomers represented by the given constitution.
c) If the butenyl side chain has the Z configuration of its double bond, the given constitutional isomer has four possible stereoisomers.
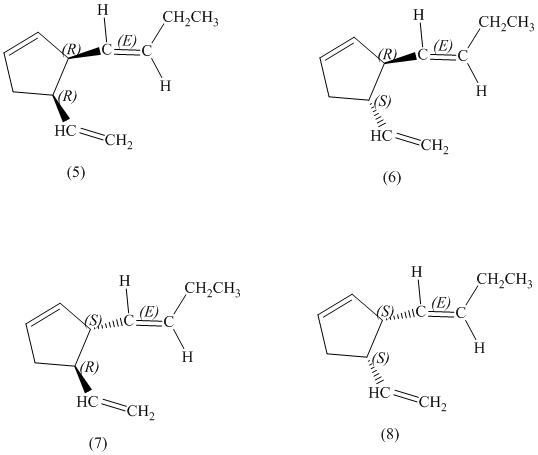
d) Stereochemically accurate representations of all the stereoisomers are as follows:
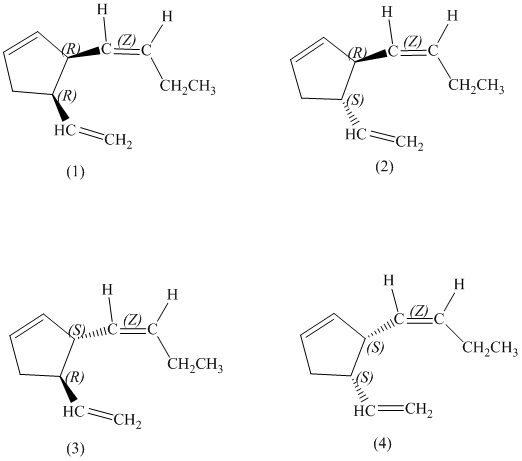
e) The pairs of enantiomers are as follows:
The pairs of diastereomers are as follows:
Explanation of Solution
a)
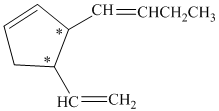
In the given structure, there are two chiral carbon atoms indicated by
Also, the double bond of butenyl side chain can form E and Z isomers, so the total number of possible stereoisomers will be:
Therefore, the number of stereoisomers represented by the given constitution is
b)
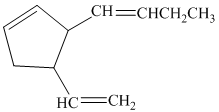
So, if the substituents on the five-membered ring are cis to each other, then the double bond in the butenyl side chain can be in the E or Z form. Thus, there are
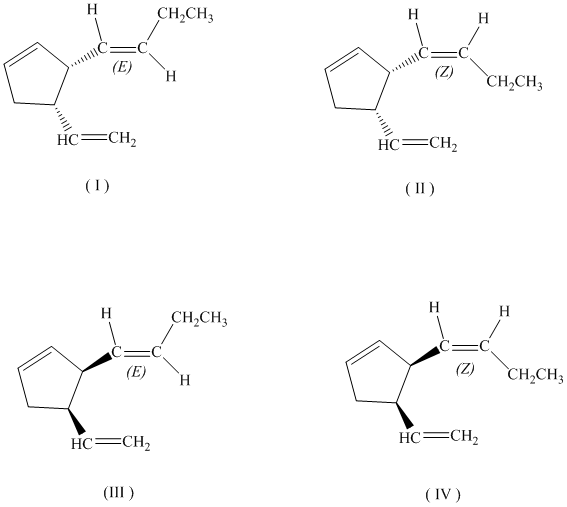
c)

If the butenyl side chain has the Z configuration of its double bond, the two substituents on the ring can be oriented in four different ways. The number of possible stereoisomers is
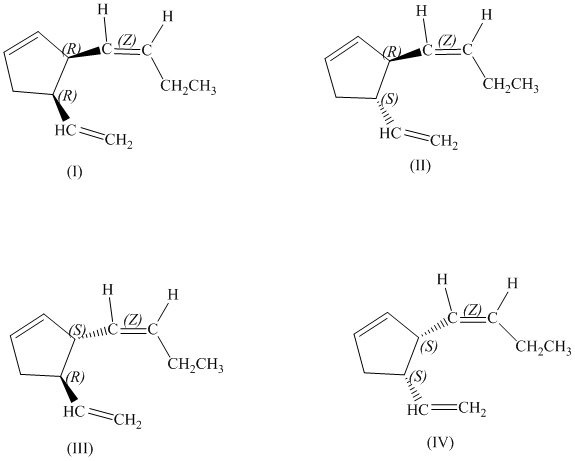
d)

There are total
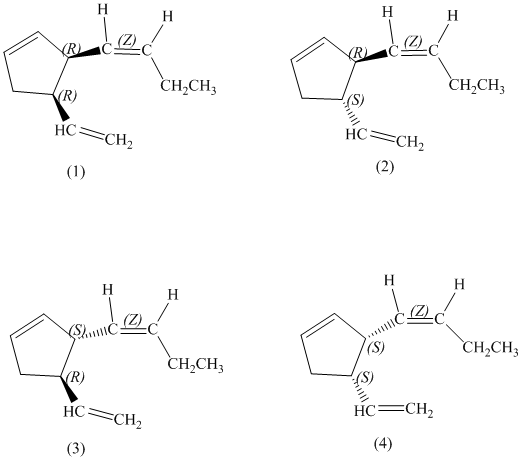
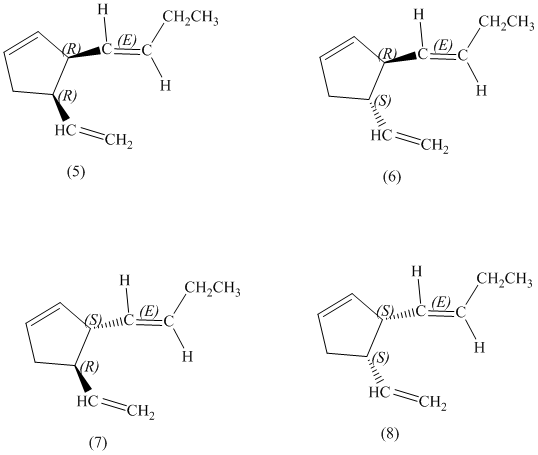
e)
Enantiomers are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. Diastereomers are the stereoisomers which are not mirror images.
The pairs of enantiomers are as follows:
The pairs of diastereomers are as follows:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL)-W/SOLN.>CUSTOM<
- drawing, no aiarrow_forwarddrawing, no aiarrow_forwardDraw the major organic product when each of the bellow reagents is added to 3,3-dimethylbutere. ✓ 3rd attempt Part 1 (0.3 point) H.C CH CH + 1. BHG THF 210 NaOH NJ 10000 Part 2 (0.3 point) HC- CH HC 2741 OH a Search 1. He|DA HO 2. NIBH さ 士 Ju See Periodic Table See Hint j = uz C H F F boxarrow_forward
- Indicate the product formed in each reaction. If the product exhibits tautomerism, draw the tautomeric structure. a) о + CH3-NH-NH2 CO2C2H5 b) + CoH5-NH-NH2 OC2H5arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the compound, that is the result of the N- alquilación (nucleofílic substitution), in which an additional lateral chain was formed (NH-CH2-COOMe). F3C. CF3 NH NH2 Br о OMe K2CO3, DABCO, DMFarrow_forwardSynthesis of 1-metilbenzotriazole from 1,2-diaminobenceno.arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

