
Hidden tasks performed by DBMS when users update and retrieve data.
Explanation of Solution
A DBMS is of no use to any user if it's not capable of providing some functions. Updation and retrieval are the fundamental job of a DBMS. Thus, a DBMS must provide to its users the ability to perform same. These tasks are solely the responsibility of a DBMS and a user needs not be aware of them.
The general steps followed in almost all operations are in diagram below:
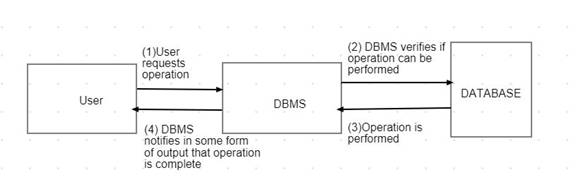
An operation contains instructions given by users and some tasks that are performed at the backend.
The difference usually occurs at step 2 and 3 where more than one sub operations might be needed to complete the task.
An updation operation can be performed by a user in the following way: by adding a new record, changing an existing records or it's deletion. All these consist of some instructions given by user and some task performed by DBMS.
Updation:
1. adding new records:
User enters an item and requests the DBMS to add a new item into database.
Following tasks are performed by DBMS following the request:
- It checks whether the records already exist in Database
- If not, it creates a new record and adds it to the database.
- Informs the user that the operation is complete, and the record is now a part of the database.
2. Changing a record:
User requests the DBMS to change an item from the database.
Following tasks are performed by DBMS following the request:
- It reads the data from database that needs to be changed.
- It displays the current data to user so that new value can be provided for changing.
- It changes the value as soon as new value is provided.
3. Deleting a record:
User requests the DBMS to delete an item from the database.
Following tasks are performed by DBMS following the request:
- It reads the data from database that needs to be deleted.
- It displays the current data to user so that user is able to see what will be deleted.
- It deletes the value as soon as user confirms the deletion action.
Retrieval:
A user is capable of reading a value from database. Following are the steps performed by DBMS to complete the operation:
- It finds and reads the record from database
- It displays the record to user
Thus, an operation consists of both the task done by a user and the tasks performed by a user. The DBMs is fully capable of performing these sub tasks at backend without the user being aware of it.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Concepts of Database Management, Loose-Leaf Version
- Given the following addresses, which two addresses conflict in the cache: The numb of locations in the cache is 2048, the cahche is indexed by address bits 15 to 5 and the tag bits are from 31 to 16. (a) 0x0000 0100 (b) 0x0000 1400 (c) 0x0010 0100 (d) 0x0100 0140arrow_forward5. RetailItem ClassWrite a class named RetailItem that holds data about an item in a retail store. The class should store the following data in attributes: item description, units in inventory, and price. Once you have written the class, write a program that creates three RetailItem objects and stores the following data in them: Description Units in Inventory PriceItem #1 Jacket 12 59.95Item #2 Designer Jeans 40 34.95Item #3 Shirt 20 24.95arrow_forwardWrite a class named Patient that has attributes for the following data: First name, middle name, and last name Address, city, state, and ZIP code Phone number Name and phone number of emergency contact The Patient class’s _ _init_ _ method should accept an argument for each attribute. The Patient class should also have accessor and mutator methods for each attribute. Next, write a class named Procedure that represents a medical procedure that has been performed on a patient. The Procedure class should have attributes for the following data: Name of the procedure Date of the procedure Name of the practitioner who performed the procedure Charges for the procedure The Procedure class’s _ _init_ _ method should accept an argument for each attribute. The Procedure class should also have accessor and mutator methods for each attribute. Next, write a program that creates an instance of the Patient class, initialized with sample data. Then, create three instances of the Procedure class,…arrow_forward
- 1 Vo V₁ V3 V₂ V₂ 2arrow_forwardI want a full report on Sperani security according to Project Mingment.arrow_forwardGiven a 8-bit addressable (256) locations in memory and 32 locations in cache, 3 bits are in the cache Tag. What is the cache location for memory address of 0x0100 0100? Provide the answer in decimal form.arrow_forward
- Q2: Solve the equation using the simplex method Max. Z 13x1 +11x2 Subject to constraints 4x1 +5x21500 5x1 +3x21575 x1 +2x2 <420 x1, x2≥0arrow_forwardBasically, you must build a desktop/android application that utilizes cryptographic techniques/protocols to secure communication (or data at rest). Try to achieve confidentiality, integrity, availability, authentication, non-repudiation (preferably all of them, otherwise few of them based on the requirement).You must demonstrate the use of these cryptographic techniques by showing some outputs/visualization results or captured traffic such as through Wireshark.1. Secure Chat ApplicationDescription: Build an encrypted chat application for desktop or Android that ensures confidentiality, integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation.Features:-- End-to-end encryption using AES-256 or Signal Protocol.--Digital signatures for non-repudiation.--Message integrity verification using HMAC.Secure login using two-factor authentication (2FA).--Server-side availability mechanisms (e.g., load balancing, backup storage). Technologies: Python (PyQt + PyCryptodome), Java (Android), Firebase for…arrow_forwardQ1: Draw the equation of z with constraints according to the graphic method Max Z-3 P1+5 P2 s.t. P1 4 P2 6 3 P1+2 P2 <18 P1, P2 20arrow_forward
- Many employees and suppliers are resistant to adopting the new e-procurement system. They are accustomed to traditional procurement methods and are hesitant to embrace the change. How would you effectively manage this resistance and ensure a smooth transition to the new system?arrow_forwardswitch status (learning, listening, for wording) Write a detailed explanation of the topic. networkarrow_forwardSolve thisarrow_forward
 Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780133594140Author:James Kurose, Keith RossPublisher:PEARSON
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780133594140Author:James Kurose, Keith RossPublisher:PEARSON Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780124077263Author:David A. Patterson, John L. HennessyPublisher:Elsevier Science
Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780124077263Author:David A. Patterson, John L. HennessyPublisher:Elsevier Science Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)Computer EngineeringISBN:9781337569330Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean AndrewsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)Computer EngineeringISBN:9781337569330Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean AndrewsPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of Database ManagementComputer EngineeringISBN:9781337093422Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. LastPublisher:Cengage Learning
Concepts of Database ManagementComputer EngineeringISBN:9781337093422Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. LastPublisher:Cengage Learning Prelude to ProgrammingComputer EngineeringISBN:9780133750423Author:VENIT, StewartPublisher:Pearson Education
Prelude to ProgrammingComputer EngineeringISBN:9780133750423Author:VENIT, StewartPublisher:Pearson Education Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...Computer EngineeringISBN:9781119368830Author:FITZGERALDPublisher:WILEY
Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...Computer EngineeringISBN:9781119368830Author:FITZGERALDPublisher:WILEY





