
Hidden tasks performed by DBMS when users update and retrieve data.
Explanation of Solution
A DBMS is of no use to any user if it's not capable of providing some functions. Updation and retrieval are the fundamental job of a DBMS. Thus, a DBMS must provide to its users the ability to perform same. These tasks are solely the responsibility of a DBMS and a user needs not be aware of them.
The general steps followed in almost all operations are in diagram below:
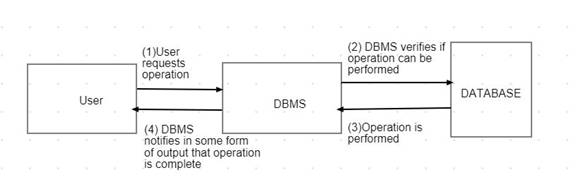
An operation contains instructions given by users and some tasks that are performed at the backend.
The difference usually occurs at step 2 and 3 where more than one sub operations might be needed to complete the task.
An updation operation can be performed by a user in the following way: by adding a new record, changing an existing records or it's deletion. All these consist of some instructions given by user and some task performed by DBMS.
Updation:
1. adding new records:
User enters an item and requests the DBMS to add a new item into database.
Following tasks are performed by DBMS following the request:
- It checks whether the records already exist in Database
- If not, it creates a new record and adds it to the database.
- Informs the user that the operation is complete, and the record is now a part of the database.
2. Changing a record:
User requests the DBMS to change an item from the database.
Following tasks are performed by DBMS following the request:
- It reads the data from database that needs to be changed.
- It displays the current data to user so that new value can be provided for changing.
- It changes the value as soon as new value is provided.
3. Deleting a record:
User requests the DBMS to delete an item from the database.
Following tasks are performed by DBMS following the request:
- It reads the data from database that needs to be deleted.
- It displays the current data to user so that user is able to see what will be deleted.
- It deletes the value as soon as user confirms the deletion action.
Retrieval:
A user is capable of reading a value from database. Following are the steps performed by DBMS to complete the operation:
- It finds and reads the record from database
- It displays the record to user
Thus, an operation consists of both the task done by a user and the tasks performed by a user. The DBMs is fully capable of performing these sub tasks at backend without the user being aware of it.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
CONCEPTS OF DATABASE MANAGEMENT
- I need help with this problem and an step by step explanation of the solution from the image described below. (Introduction to Signals and Systems)arrow_forwardI need help with this problem and an step by step explanation of the solution from the image described below. (Introduction to Signals and Systems)arrow_forwardI need help with this problem and an step by step explanation of the solution from the image described below. (Introduction to Signals and Systems)arrow_forward
- Q1.A. Sketch a graph of f(x), then find the Fourier series of f(x) for three values and has a period of 2π. (8 marks) f(x) = { x² x²sin 3x -π≤ x ≤ 0) 0 ≤ x ≤ narrow_forwardQ3.A. Given the flow graph below, Find the H(z)? x(z) y(z) (7 marks) z-1 ↓arrow_forwardQ2.A. Find the inverse Z-Transforms using partial fraction method of the following function: (8 marks) Z-1 F(z) = 2+3Z-1 + (1-2-1) (1-12-12arrow_forward
- this module is java 731 , follow all instructions and make sure the outputs are like what they expect and make sure the code is 100% correct . include all comments , layout and structure to be perfect too, thanks. Question 1: (40 MARKS) E-Hailing Bicycle Management System Case Study:An e-hailing company that rents out bicycles needs a system to manage its bicycles, users, and borrowing process. Each user can borrow up to 2 bicycles at a time, specifically for families with children 18 years or below. The system must track the bicycles (name, make, type, and availability) and users (name, ID, and borrowed bicycles). The company also wants to ensure that the system uses a multidimensional array to store information about the bicycles. Requirements: Add and View Bicycles: Borrow Bicycles: Return Bicycles Display Borrowed Bicycles and Search for a bicycle Create a menu-driven program to implement the above. Sample Output: Add Bicycle View All Bicycles Borrow Bicycle…arrow_forwardthis module is java 371. please answer all questions correctly , include all comments etc and follow all requirements. Question 1: (40 MARKS) E-Hailing Bicycle Management System Case Study:An e-hailing company that rents out bicycles needs a system to manage its bicycles, users, and borrowing process. Each user can borrow up to 2 bicycles at a time, specifically for families with children 18 years or below. The system must track the bicycles (name, make, type, and availability) and users (name, ID, and borrowed bicycles). The company also wants to ensure that the system uses a multidimensional array to store information about the bicycles. Requirements: Add and View Bicycles: Borrow Bicycles: Return Bicycles Display Borrowed Bicycles and Search for a bicycle Create a menu-driven program to implement the above. Sample Output: Add Bicycle View All Bicycles Borrow Bicycle Return Bicycle View Borrowed Bicycles Search Bicycle ExitEnter your choice: Question 2…arrow_forwardNode.js, Express, Nunjucks, MongoDB, and Mongoose There are a couple of programs similar to this assignment given in the lecture notes for the week that discusses CRUD operations. Specifically, the Admin example and the CIT300 example both have index.js code and nunjucks code similar to this assignment. You may find some of the other example programs useful as well. It would ultimately save you time if you have already studied these programs before giving this assignment a shot. Either way, hopefully you'll start early and you've kept to the schedule in terms of reading the lecture notes. You will need to create a database named travel using compass, then create a collection named trips. Use these names; your code must work with my database. The trips documents should then be imported unto the trips collection by importing the JSON file containing all the data as linked below. The file itself is named trips.json, and is available on the course website in the same folder as this…arrow_forward
 Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780133594140Author:James Kurose, Keith RossPublisher:PEARSON
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780133594140Author:James Kurose, Keith RossPublisher:PEARSON Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780124077263Author:David A. Patterson, John L. HennessyPublisher:Elsevier Science
Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780124077263Author:David A. Patterson, John L. HennessyPublisher:Elsevier Science Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)Computer EngineeringISBN:9781337569330Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean AndrewsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)Computer EngineeringISBN:9781337569330Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean AndrewsPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of Database ManagementComputer EngineeringISBN:9781337093422Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. LastPublisher:Cengage Learning
Concepts of Database ManagementComputer EngineeringISBN:9781337093422Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. LastPublisher:Cengage Learning Prelude to ProgrammingComputer EngineeringISBN:9780133750423Author:VENIT, StewartPublisher:Pearson Education
Prelude to ProgrammingComputer EngineeringISBN:9780133750423Author:VENIT, StewartPublisher:Pearson Education Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...Computer EngineeringISBN:9781119368830Author:FITZGERALDPublisher:WILEY
Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...Computer EngineeringISBN:9781119368830Author:FITZGERALDPublisher:WILEY





