
The effect of change in the
Explanation of Solution
The Elasticity of
Social surplus is the sum total of both
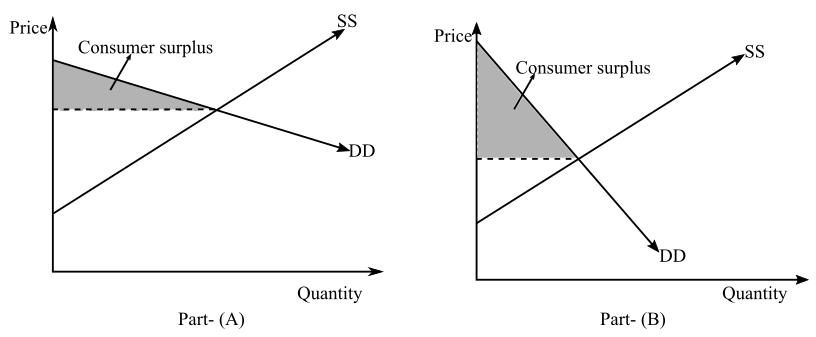
In part (a) of the above diagram, DD is the demand and elastic demand curve, SS is the supply curve, and the
So, if the elasticity of demand is higher, consumer surplus will be lower as what a consumer is willing to pay becomes equal to what they actually pay.
Thus, the social surplus will also be lower as it consists of consumer surplus.
Similarly,
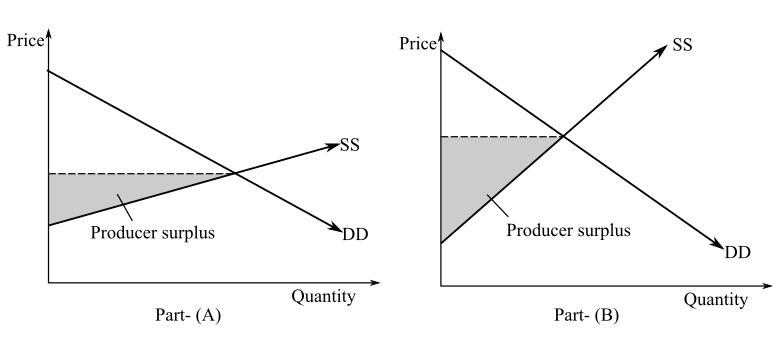
DD is the demand curve, SS is the elastic supply curve and the equilibrium price is where DD and SS intersect. Producer surplus is calculated between the price and above the supply curve, which means the higher the elasticity of supply, the lower is the producer surplus which will decrease social surplus. As the elasticity of supply increases, producer surplus also increases as shown in part ( b ) of the diagram, which will increase social surplus.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- Styrofoam is non-biodegradable and is not easily recyclable. Many cities and at least one state have enacted laws that ban the use of polystyrene containers. These locales understand that banning these containers will force many businesses to turn to other more expensive forms of packaging and cups, but argue the ban is environmentally important. Shane owns a firm with a conventional production function resulting in U-shaped ATC, AVC, and MC curves. Shane's business sells takeout food and drinks that are currently packaged in styrofoam containers and cups. Graph the short-run AFC0, AVC0, ATC0, and MC0 curves for Shane's firm before the ban on using styrofoam containers.arrow_forwardd-farrow_forwarda-c pleasearrow_forward
- d-farrow_forwardPART II: Multipart Problems wood or solem of triflussd aidi 1. Assume that a society has a polluting industry comprising two firms, where the industry-level marginal abatement cost curve is given by: MAC = 24 - ()E and the marginal damage function is given by: MDF = 2E. What is the efficient level of emissions? b. What constant per-unit emissions tax could achieve the efficient emissions level? points) c. What is the net benefit to society of moving from the unregulated emissions level to the efficient level? In response to industry complaints about the costs of the tax, a cap-and-trade program is proposed. The marginal abatement cost curves for the two firms are given by: MAC=24-E and MAC2 = 24-2E2. d. How could a cap-and-trade program that achieves the same level of emissions as the tax be designed to reduce the costs of regulation to the two firms?arrow_forwardOnly #4 please, Use a graph please if needed to help provearrow_forward
- a-carrow_forwardFor these questions, you must state "true," "false," or "uncertain" and argue your case (roughly 3 to 5 sentences). When appropriate, the use of graphs will make for stronger answers. Credit will depend entirely on the quality of your explanation. 1. If the industry facing regulation for its pollutant emissions has a lot of political capital, direct regulatory intervention will be more viable than an emissions tax to address this market failure. 2. A stated-preference method will provide a measure of the value of Komodo dragons that is more accurate than the value estimated through application of the travel cost model to visitation data for Komodo National Park in Indonesia. 3. A correlation between community demographics and the present location of polluting facilities is sufficient to claim a violation of distributive justice. olsvrc Q 4. When the damages from pollution are uncertain, a price-based mechanism is best equipped to manage the costs of the regulator's imperfect…arrow_forwardFor environmental economics, question number 2 only please-- thank you!arrow_forward
- For these questions, you must state "true," "false," or "uncertain" and argue your case (roughly 3 to 5 sentences). When appropriate, the use of graphs will make for stronger answers. Credit will depend entirely on the quality of your explanation. 1. If the industry facing regulation for its pollutant emissions has a lot of political capital, direct regulatory intervention will be more viable than an emissions tax to address this market failure. cullog iba linevoz ve bubivorearrow_forwardExercise 3 The production function of a firm is described by the following equation Q=10,000-3L2 where L stands for the units of labour. a) Draw a graph for this equation. Use the quantity produced in the y-axis, and the units of labour in the x-axis. b) What is the maximum production level? c) How many units of labour are needed at that point? d) Provide one reference with you answer.arrow_forwardExercise 1 Consider the market supply curve which passes through the intercept and from which the market equilibrium data is known, this is, the price and quantity of equilibrium PE=50 and QE=2000. Considering those two points, find the equation of the supply. Draw a graph of this line. Provide one reference with your answer. Exercise 2 Considering the previous supply line, determine if the following demand function corresponds to the market demand equilibrium stated above. QD=3000-2p.arrow_forward
 Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning









