
(a)
To show that the values of array and auxiliary values after each iterations of while loop using HOARE-PARTITION.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given Information: The array is
Explanation: According to the HOARE-PARTITION,
Consider that
Now the array and auxiliary after each pass through HOARE-PARTITION algorithm will show in below table-
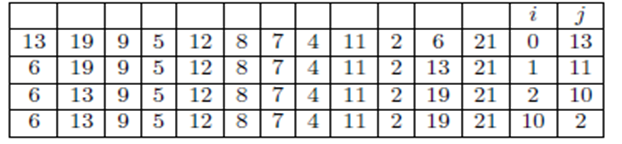
After the iteration

Hence, the HOARE-PARTITION algorithm exit the while loop with the auxiliary values of
(b)
To showthat the indices i and j are such that we never access an element of array A outside the sub-array.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
In the beginning of while loop when
Consider that it has an element k and
If it takes parameter
Hence, it is can be concluded that the indices i and j are such that one never access an element of array A outside the sub-array.
(c)
To explain that when HOARE-PARTITION terminates, it returns a value j such that
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The value of jis decreased after every iteration and at the final iteration of the loop i will equals to 1but greater than r .
Line 11 of HOARE-PARTITION illustrate that
Therefore, the HOARE-PARTITION algorithm terminates and returns
(d)
To explain that the every element of array is less than or equal to every element of
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Consider that it just finished the iteration of the loop in which j went to j1 and j2 and I went to i1 to i2 . The elements of the array
Similarly, the elements of the array
Now putting all the conditions of the array defined in the algorithm it has condition that is
Since at the termination of the algorithm
Therefore, the every element of array
(e)
To rewrite the QUICK-SORT procedure by using HOARE-PARTITION algorithm.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
QUICKSORT(A,p,r). If then q =HOARE-PARTITION(A,p,r). QUICKSORT(A,p,q-1). QUICKSORT(A,q+1,r). End if. HOARE-PARTITION(A,p,r) while TRUE repeat until . repeat . until . if then exchange with . else return j. end if. end while.
The quick sort algorithm is based on recursion. It first sets the parameters and then check the initial condition.
If the initial condition is true then it call the HOARE-PARTITION algorithm with recursion of calling itself again and again until the initial condition becomes false.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Introduction To Algorithms, Third Edition (international Edition)
- 123456 A ROP (Return-Oriented Programming) attack can be used to execute arbitrary instructions by chaining together small pieces of code called "gadgets." Your goal is to create a stack layout for a ROP attack that calls a function located at 'Ox4018bd3'. Below is the assembly code for the function 'getbuf, which allocates 8 bytes of stack space for a 'char' array. This array is then passed to the 'gets' function. Additionally, you are provided with five useful gadgets and their addresses. Use these gadgets to construct the stack layout. Assembly for getbuf 1 getbuf: sub mov $8, %rsp %rsp, %rdi call gets add $8, %rsp 6 ret #Allocate 8 bytes for buffer #Load buffer address into %rdi #Call gets with buffer #Restore the stack pointer #Return to caller Stack each Layout (fill in Gadgets 8-byte section) Address Gadget Address Value (8 bytes) 0x7fffffffdfc0 0x7fffffffdfb8 0x7fffffffdfb0 0x7fffffffdfa8 0x7fffffffdfa0 0x7fffffffdf98 0x7fffffffdf90 0x7fffffffdf88 Original 0x4006a7 pop %rdi;…arrow_forwardCharacter Hex value || Character Hex value | Character Hex value 'A' 0x41 יני Ox4a 'S' 0x53 0x42 'K' 0x4b 'T" 0x54 0x43 'L' Ox4c 0x55 0x44 'M' Ox4d 0x56 0x45 'N' Ox4e 'W' 0x57 0x46 Ox4f 'X' 0x58 0x47 'P' 0x50 'Y' 0x59 'H' 0x48 'Q' 0x51 'Z' Охба 'T' 0x49 'R' 0x52 '\0' 0x00 Now consider what happens on a Linux/x86 machine when callfoo calls foo with the input string "ZYXWVUTSRQPONMLKJIHGFEDCBA". A. On the left draw the state of the stack just before the execution of the instruction at address Ox40053a; make sure to show the frames for callfoo and foo and the exact return address, in Hex at the bottom of the callfoo frame. Then, on the right, draw the state of the stack just after the instruction got executed; make sure to show where the string "ZYXWVUTSRQPONMLKJIHGFEDCBA" is placed and what part, if any, of the above return address has been overwritten. B. Immediately after the ret instruction at address 0x400543 executes, what is the value of the program counter register %rip? (That is…arrow_forwardDraw out the way each of these structs looks in memory, including padding! Number the offsets in memory. 1 struct okay Name 2 { short a; 3 4 long number; 5 int also_a_number; 6 7 }; char* text; 1 struct badName 2 { 3 4 5 }; short s; struct okay Name n;arrow_forward
- You can create your own AutoCorrect entries. Question 19Select one: True Falsearrow_forwardBy default, all text is formatted using the Normal Style. Question 20Select one: True Falsearrow_forwardNode.js, Express.js, MongoDB, and Mongoose: Create, Read, Update, and Delete Operations There is a program similar to this assignment given as the last example, CRUD, in the lecture notes for the week that discusses the introduction to MongoDB. Basically, you need to adapt this example program to the data given in this assignment. This program will take more time that previous assignments. So, hopefully you'll start early and you've kept to the schedule in terms of reading the lecture notes. You can use compass if you want to create this database. Or, when your connection string in the model runs it will create the database for you if one does not yet exist. So, ⚫ create a Mongoose model based on the info given below. The index.html page is given in the same folder as these notes. • When you successfully run index.js and instantiate the model, your database is created. • Once the database is created, you need to perfect the addCar route so you can add data using the index.html page. •…arrow_forward
- 1. Enabled with SSL, HTTPS protocol is widely used to provide secure Web services to Web users using Web browsers on the Internet. How is a secure communication channel established at the start of communication between a Web server running HTTPS and a Web browser? Consider the following threats to Web security and how each of these threats is countered by a particular feature of SSL. Man-in-the-middle attack: An attacker interposes during key exchange, acting as the client to the server and as the server to the client. Password sniffing: Passwords in HTTP or other application traffic are “eavesdropped.” SYN flooding: An attacker sends TCP SYN messages to request a connection but does not respond to the final message to establish the connection fully. The attacked TCP module typically leaves the “half-open” connection around for a few minutes. Repeated SYN messages can clog the TCP module.arrow_forwardSQL Injection on UPDATE Statement for educational purpose only Based on the information below how do i update this code in order to update the emplyees field, eg admin nickname, email,address, phone number etc? ' ; UPDATE users SET NickName='Hacked' WHERE role='admin' -- If a SQL injection vulnerability happens to an UPDATE statement, the damage will be more severe, because attackers can use the vulnerability to modify databases. In our Employee Management application, there is an Edit Profile page (Figure 2) that allows employees to update their profile information, including nickname, email, address, phone number, and password. To go to this page, employees need to log in first. When employees update their information through the Edit Profile page, the following SQL UPDATE query will be executed. The PHP code implemented in unsafe edit backend.php file is used to update employee’s profile information. The PHP file is located in the /var/www/SQLInjection directory.arrow_forwardAnswer two JAVA OOP questions.arrow_forward
 C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage LearningProgramming Logic & Design ComprehensiveComputer ScienceISBN:9781337669405Author:FARRELLPublisher:Cengage
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage LearningProgramming Logic & Design ComprehensiveComputer ScienceISBN:9781337669405Author:FARRELLPublisher:Cengage Systems ArchitectureComputer ScienceISBN:9781305080195Author:Stephen D. BurdPublisher:Cengage Learning
Systems ArchitectureComputer ScienceISBN:9781305080195Author:Stephen D. BurdPublisher:Cengage Learning New Perspectives on HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScriptComputer ScienceISBN:9781305503922Author:Patrick M. CareyPublisher:Cengage Learning
New Perspectives on HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScriptComputer ScienceISBN:9781305503922Author:Patrick M. CareyPublisher:Cengage Learning C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology PtrCOMPREHENSIVE MICROSOFT OFFICE 365 EXCEComputer ScienceISBN:9780357392676Author:FREUND, StevenPublisher:CENGAGE L
C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology PtrCOMPREHENSIVE MICROSOFT OFFICE 365 EXCEComputer ScienceISBN:9780357392676Author:FREUND, StevenPublisher:CENGAGE L





