
Concept explainers
Complete this summary map of photosynthesis.
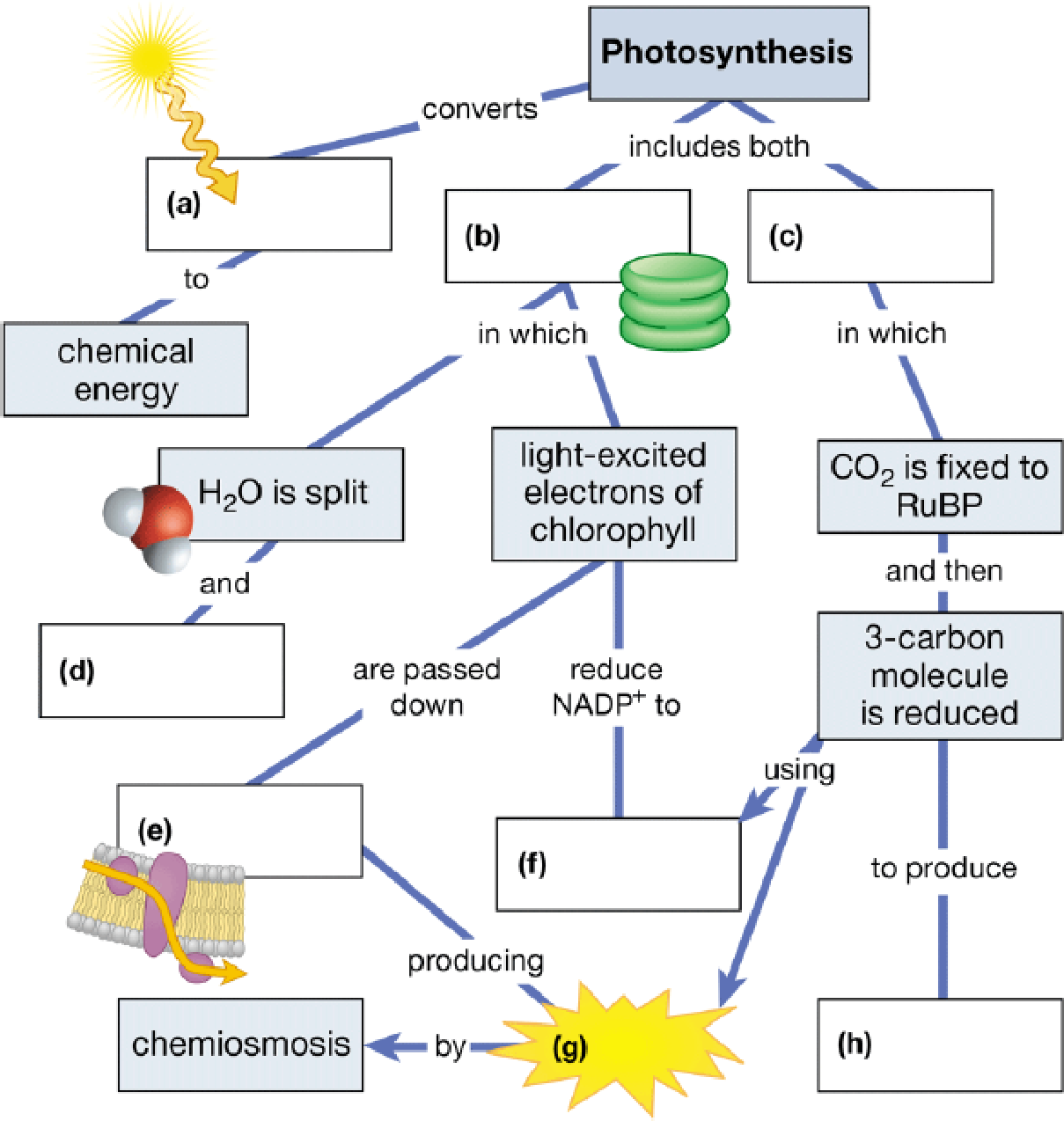
To complete: The connect map to summarize the major steps in photosynthesis.
Concept introduction: Photosynthesis is a vital process in primary producers, plants. Plants use light energy and carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere and produce sugars that are stored in various parts of the plants. The most edible ones are consumed by the primary consumers. Several compounds are converted and recycled in the process of photosynthesis. Several reactions of photosynthesis take place in the chloroplast of the plant cell, which contains the green pigment chlorophyll.
Answer to Problem 1CC
The Fig.1 shows all the key processes in photosynthesis.
Pictorial representation:
The Fig. 1shows the summary of all the processes involved in photosynthesis.
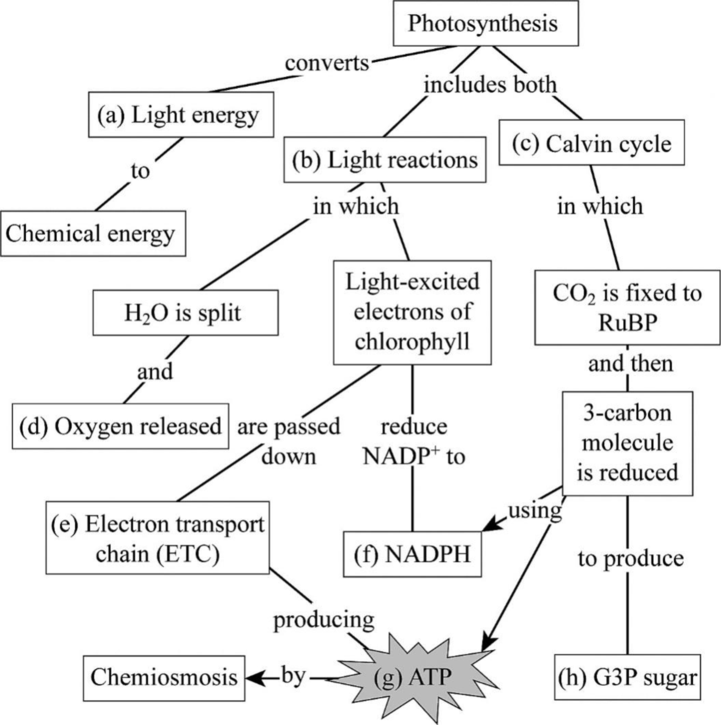
Fig 1: Summary of various steps in photosynthesis.
Explanation of Solution
(a)
Correct answer: Light energy
In the process of photosynthesis, photons from light energy are converted into chemical energy. In the visible spectrum of light, the red and blue wavelengths are used to initiate the reactions of photosynthesis. The light energy is used up to break the water molecule by the process called photolysis of water, which is the first step in photosynthesis.
Hence, the correct answer is light energy.
(b)
Correct answer: Light reactions
Photosynthesis includes two reactions, namely, light-dependent and light-independent reactions. Light reactions are those that are dependent on the incident light energy on the chloroplast. Light reactions include two sub steps. One reaction is the photolysis of water where light energy is used up to break the water molecules to produce an oxygen molecule and protons. The second reaction is where these protons and the energy released during photolysis of water are used up to excite the electrons in the chlorophyll.
Hence, the correct answer is light reactions.
(c)
Correct answer: Calvin cycle
The CBB (Calvin–Benson–Bassham) cycle or Calvin’s cycle is a series of reactions that take place in the stroma of the chloroplast. The Calvin’s cycle is a light-independent reaction, which is also known as the dark reaction. In the Calvin’s cycle, the atmospheric carbondioxide is fixed with ribulose1, 5-bisphosphate to produce two 3-carbon compounds. One of the two 3-carbon compounds is reduced to form another sugar.
Hence, the correct answer is the Calvin cycle
(d)
Correct answer: Oxygen released
During one of the light reactions, that is, photolysis of water, the light energy is used up to break two molecules of water to produce one molecule of oxygen, 4 electrons, and 4 protons (H+). The oxygen molecule then escapes the chloroplast and is released into the atmosphere.
Hence, the correct answer is oxygen released
(e)
Correct answer: Electrontransportchain(ETC)
During the second light reaction of photosynthesis, the electrons released from photolysis of water are passed on through the photosystem II and photosystem I and are then sent to the electron transport chain. In the electron transport chain, the protons released during photolysis of water are used by F0-F1 ATP synthase to produce ATP.
Hence, the correct answer is the electron transport chain (ETC)
(f)
Correct answer: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH)
During the second light reaction of photosynthesis, the electrons released from photolysis of water are passed on through the photosystem II and photosystem I, which at the end of photosystem II reduce NAD+ to NADPH. This NADPH is then used up during the hexose monophosphate pathway to produce several sugars, and it is also used during the Calvin’s cycle to produce sugars.
Hence, the correct answer is NADPH
(g)
Correct answer: ATP
The electrons released from photolysis of water are passed on through the photosystem II and then from the photosystem to the electron transport chain. In the electron transport chain, the protons released during photolysis of water are used by F0-F1 ATP synthase present on the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast to produce ATP. This ATP is used up along with NADPH to produce several sugars in the Calvin’s cycle.
Hence, the correct answer is ATP
(h)
Correct answer: Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P)(sugar)
During the Calvin’s cycle, the NADPH and ATP produced during the light reactions and F0-F1 ATP synthase, respectively, are used up to reduce ribulose 1.5-bisphosphate to produce two molecules of G3P. For every 3 molecules of carbondioxide entering the Calvin’s cycle, one G3P is produced. Few G3Ps are sent for the production of 6-carbon sugars and others are recycled back to produce ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate.
Hence, the correct answer is G3P (sugar)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
CAMP.BIO:CONC...MOD.MAST+PRINT>I<
- Normal dive (for diving humans) normal breathing dive normal breathing Oz level CO₂ level urgent need to breathe Oz blackout zone high CO₂ triggers breathing 6. This diagram shows rates of oxygen depletion and carbon dioxide accumulation in the blood in relation to the levels needed to maintain consciousness and trigger the urgent need to breathe in diving humans. • How might the location and slope of the O2 line differ for diving marine mammals such as whales and dolphins? • How might the location and slope of the CO2 line differ for diving marine mammals such as whales and dolphins? • • Draw in predicted lines for O2 and CO2, based on your reasoning above. How might the location of the Urgent Need to Breathe line and the O2 Blackout Zone line differ for diving marine mammals? What physiological mechanisms account for each of these differences, resulting in the ability of marine mammals to stay submerged for long periods of time?arrow_forwardHow much ATP will be produced during the following metabolic scenario: Aerobic respiration of a 5mM lipid solution that is made up of one glycerol and an 8-carbon fatty acid and 12-carbon fatty acid. Recall that when glycerol breaks down to Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate it costs one ATP but your get an extra FADH2. Every two carbons of a fatty acid break down to one acetyl-CoA. Units cannot be entered in this style of question but the units of your answer should be in mM of ATP.arrow_forwardIf a bacterium using aerobic respiration was to degrade one small protein molecule into 8 molecules of pyruvic acid, how many ATP would that cell make? Assume there is no other carbon source. Units cannot be entered in this style of question but the units of your answer should be in molecules of ATP.arrow_forward
- If a bacterium using aerobic respiration was to degrade a 30 mM solution of citric acid, how many ATP would that cell make? Assume no other carbon source is available. Units cannot be entered in this style of question but the units of your answer should be in mM of ATP.arrow_forwardHow much ATP will be produced during the following metabolic scenario: Aerobic respiration of a 5mM lipid solution that is made up of one glycerol and an 8-carbon fatty acid and 12-carbon fatty acid. Recall that when glycerol breaks down to Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate it costs one ATP but your get an extra FADH2. Every two carbons of a fatty acid break down to one acetyl-CoA. (pathways will be provided on the exam) Units cannot be entered in this style of question but the units of your answer should be in mM of ATP.arrow_forwardWhen beta-lactamase was isolated from Staphylcoccus aureus and treated with a phosphorylating agent, only the active site, serine was phosphorylated. Additionally, the serine was found to constitute 0.35% (by weight) of this beta-lactamase enzyme. Using this, calculate the molecular weight of this enzyme and estimate the number of amino acids present in the polypeptide.arrow_forward
- Based on your results from the Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) media, which of your bacteria were mannitol fermenters and which were not mannitol fermenters?arrow_forwardhelp tutor pleasearrow_forwardQ8. A researcher wants to study the effectiveness of a pill intended to reduce stomach heartburn in pregnant women. The researcher chooses randomly 400 women to participate in this experiment for 9 months of their pregnancy period. They all need to have the same diet. The researcher designs two groups of 200 participants: One group take the real medication intended to reduce heartburn, while the other group take placebo medication. In this study what are: Independent variable: Dependent variable: Control variable: Experimental group: " Control group: If the participants do not know who is consuming the real pills and who is consuming the sugar pills. This study is It happens that 40% of the participants do not find the treatment helpful and drop out after 6 months. The researcher throws out the data from subjects that drop out. What type of bias is there in this study? If the company who makes the medication funds this research, what type of bias might exist in this research work?arrow_forward
 Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning





