
Concept explainers
(a)
Calculate
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Straight-line method: Under the straight-line method of depreciation, the same amount of depreciation is allocated every year over the estimated useful life of an asset. The following is the formula to calculate the depreciation.
Determine depreciation expense, accumulated depreciation, and book value at the end of sixth year under straight line depreciation method.
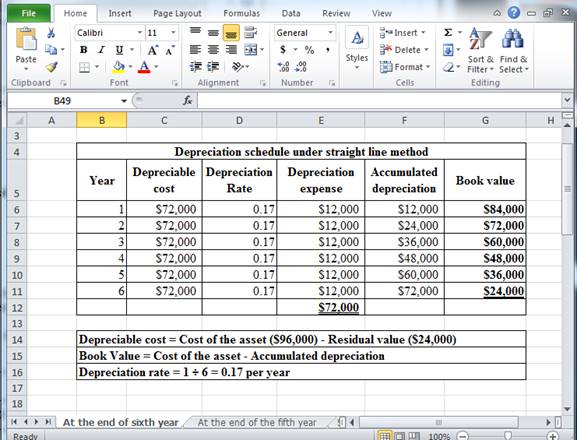
Table (1)
Hence, the depreciation expense, accumulated depreciation, and book value at the end of the sixth year, under straight line method are $12,000, $72,000 and $24,000 respectively.
Record the adjusting entry for depreciation expense at the end of the third year under straight line depreciation method.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Depreciation expense – Equipment (Refer table (1)) | 12,000 | |||
| Accumulated depreciation -Equipment | 12,000 | |||
| (To record the depreciation expense) |
Table (2)
To record the adjusting entry for depreciation expense at the end of the third year:
- Depreciation expense is an expense (decreases the
stockholders’ equity ) and it is increased by $12,000. Therefore, debit depreciation account with $12,000. - Accumulated depreciation is a contra-asset. Increase in the accumulated depreciation account decreases the related asset account. Therefore, credit accumulated depreciation account with $12,000.
Working Note:
The above calculation is computed using spreadsheet as follows:
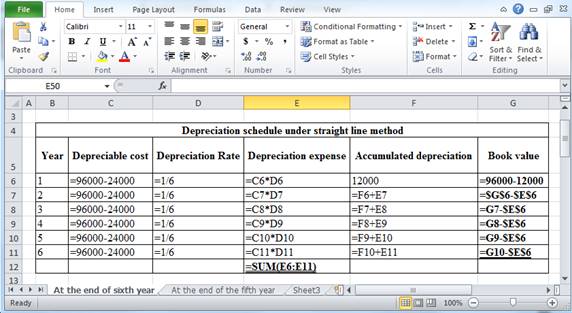
Table (3)
(b)
Calculate depreciation expense, accumulated depreciation, and book value for each of the six years using double-declining-balance method and record the adjusting entry for depreciation expense at the end of the third year under each method.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Double-declining-balance method: The depreciation method which assumes that the consumption of economic benefits of long-term asset is high in the early years but gradually declines towards the end of its useful life is referred to as double-declining-balance method.
Determine depreciation expense, accumulated depreciation, and book value at the end of sixth year under double declining balance method.
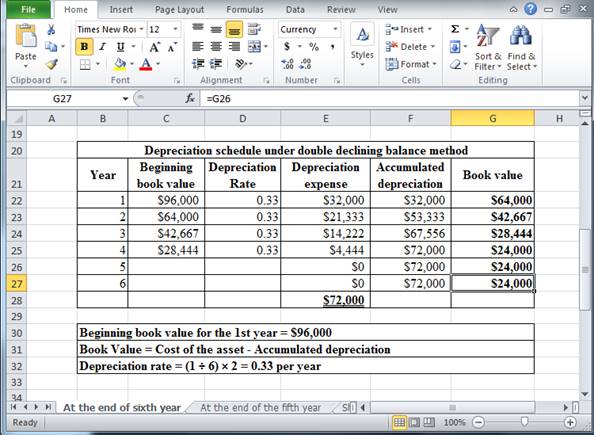
Table (4)
Hence, the depreciation expense, accumulated depreciation, and book value at the end of the sixth year, under double declining balance method are $0, $72,000 and $24,000 respectively.
Record the adjusting entry for depreciation expense at the end of the third year under double declining balance method.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Depreciation expense – Equipment (Refer table (4)) | 14,222 | |||
| Accumulated depreciation -Equipment | 14,222 | |||
| (To record the depreciation expense) |
Table (5)
To record the adjusting entry for depreciation expense at the end of the third year:
- Depreciation expense is an expense (decreases the stockholders’ equity) and it is increased by $14,222. Therefore, debit depreciation account with $14,222.
- Accumulated depreciation is a contra-asset. Increase in the accumulated depreciation account decreases the related asset account. Therefore, credit accumulated depreciation account with $14,222.
Working Note:
The above calculation is computed using spreadsheet as follows:
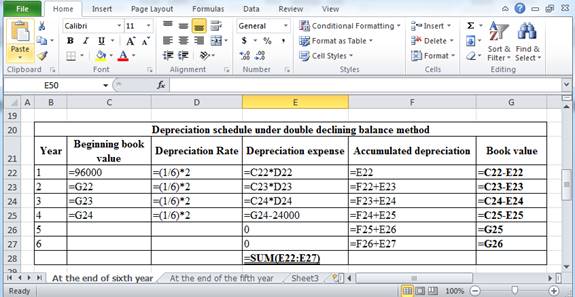
Table (6)
(c)
Calculate depreciation expense, accumulated depreciation, and book value for each of the six years using activity-based method and record the adjusting entry for depreciation expense at the end of the third year under each method.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Activity based method: In this method of depreciation, the amount of depreciation is charged based on the units of production each year.
Determine depreciation expense, accumulated depreciation, and book value at the end of sixth year under activity based method.
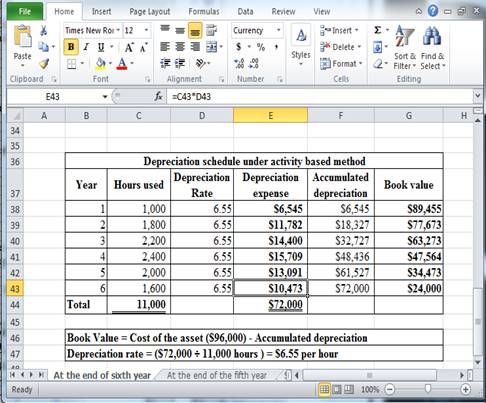
Table (7)
Hence, the depreciation expense, accumulated depreciation, and book value at the end of the sixth year, under activity based method are $10,473, $72,000 and $24,000 respectively.
Record the adjusting entry for depreciation expense at the end of the third year under activity based method.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Depreciation expense – Equipment (Refer table (7)) | 14,400 | |||
| Accumulated depreciation -Equipment | 14,400 | |||
| (To record the depreciation expense) |
Table (8)
To record the adjusting entry for depreciation expense at the end of the third year:
- Depreciation expense is an expense (decreases the stockholders’ equity) and it is increased by $14,400. Therefore, debit depreciation account with $14,400.
- Accumulated depreciation is a contra-asset. Increase in the accumulated depreciation account decreases the related asset account. Therefore, credit accumulated depreciation account with $14,400.
Working Note:
The above calculation is computed using spreadsheet as follows:
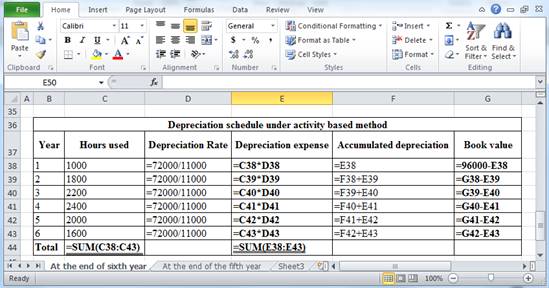
Table (9)
Calculate depreciation expense, accumulated depreciation, and book value for each of the fifth years using (a) straight-Line, (b) double-declining-balance, and (c) activity-based if the company had initially estimated the residual value to be $16,000 and the useful life to be five years.
Explanation of Solution
(a)
Straight-line method: Under the straight-line method of depreciation, the same amount of depreciation is allocated every year over the estimated useful life of an asset. The following is the formula to calculate the depreciation.
Determine depreciation expense, accumulated depreciation, and book value at the end of sixth year under straight line depreciation method.
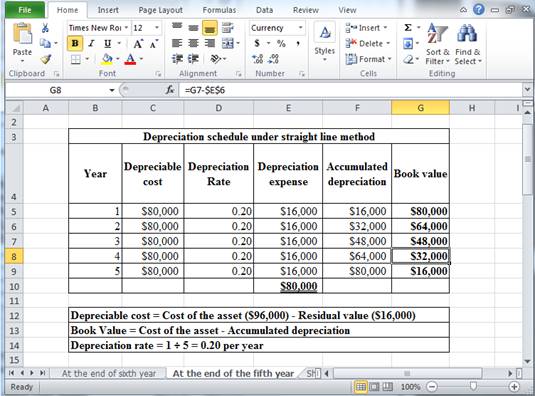
Table (10)
Hence, the depreciation expense, accumulated depreciation, and book value at the end of the sixth year, under straight line method are $16,000, $80,000 and $16,000 respectively.
Record the adjusting entry for depreciation expense at the end of the third year under straight line depreciation method.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Depreciation expense – Equipment (Refer table (10)) | 16,000 | |||
| Accumulated depreciation -Equipment | 16,000 | |||
| (To record the depreciation expense) |
Table (11)
To record the adjusting entry for depreciation expense at the end of the third year:
- Depreciation expense is an expense (decreases the stockholders’ equity) and it is increased by $16,000. Therefore, debit depreciation account with $16,000.
- Accumulated depreciation is a contra-asset. Increase in the accumulated depreciation account decreases the related asset account. Therefore, credit accumulated depreciation account with $16,000.
Working Note:
The above calculation is computed using spreadsheet as follows:
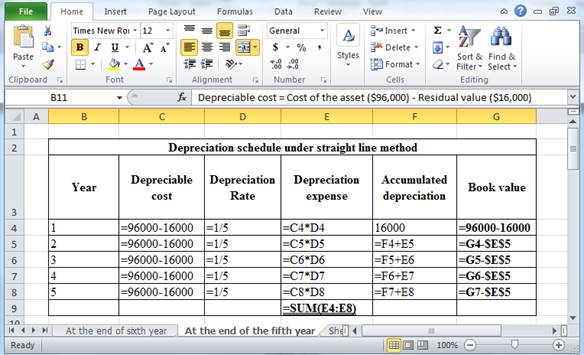
Table (12)
(b)
Double-declining-balance method: The depreciation method which assumes that the consumption of economic benefits of long-term asset is high in the early years but gradually declines towards the end of its useful life is referred to as double-declining-balance method.
Determine depreciation expense, accumulated depreciation, and book value at the end of sixth year under double declining balance method.
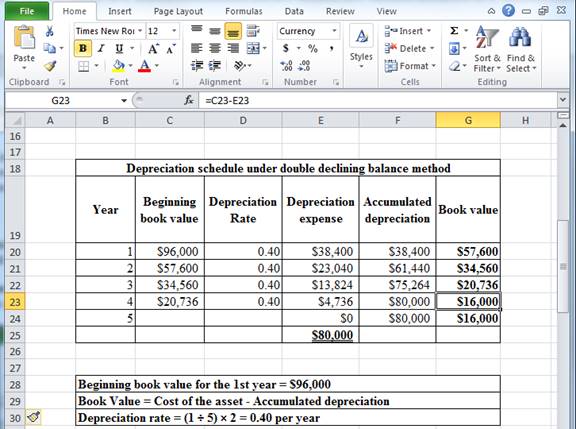
Table (13)
Hence, the depreciation expense, accumulated depreciation, and book value at the end of the fifth year, under s double declining balance method are $0, $80,000 and $16,000 respectively.
Record the adjusting entry for depreciation expense at the end of the third year under double declining balance method.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Depreciation expense – Equipment (Refer table (13)) | 13,824 | |||
| Accumulated depreciation -Equipment | 13,824 | |||
| (To record the depreciation expense) |
Table (14)
To record the adjusting entry for depreciation expense at the end of the third year:
- Depreciation expense is an expense (decreases the stockholders’ equity) and it is increased by $13,824. Therefore, debit depreciation account with $13,824.
- Accumulated depreciation is a contra-asset. Increase in the accumulated depreciation account decreases the related asset account. Therefore, credit accumulated depreciation account with $13,824.
Working Note:
The above calculation is computed using spreadsheet as follows:
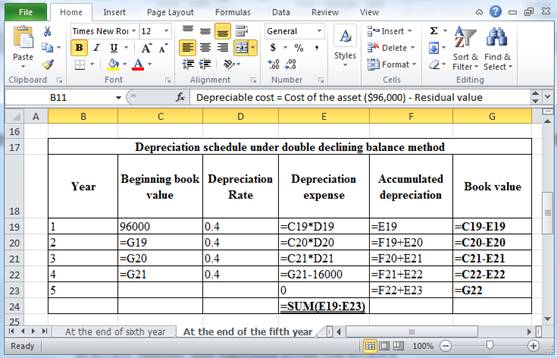
Table (15)
(c)
Activity based method: In this method of depreciation, the amount of depreciation is charged based on the units of production each year.
Determine depreciation expense, accumulated depreciation, and book value at the end of sixth year under activity based method.
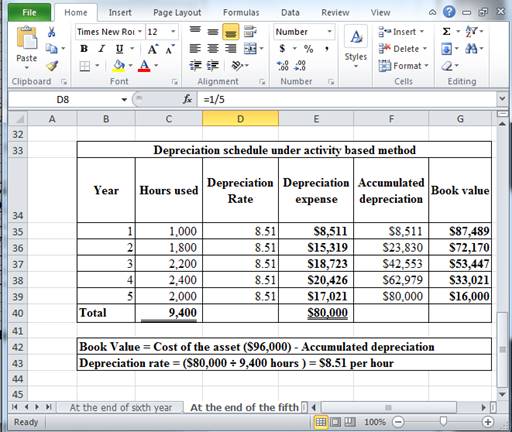
Table (16)
Hence, the depreciation expense, accumulated depreciation, and book value at the end of the fifth year, under activity based method are $17,021, $80,000 and $16,000 respectively.
Record the adjusting entry for depreciation expense at the end of the third year under activity based method.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Depreciation expense – Equipment (Refer table (16)) | 18,723 | |||
| Accumulated depreciation -Equipment | 18,723 | |||
| (To record the depreciation expense) |
Table (17)
To record the adjusting entry for depreciation expense at the end of the third year:
- Depreciation expense is an expense (decreases the stockholders’ equity) and it is increased by $18,723. Therefore, debit depreciation account with $18,723.
- Accumulated depreciation is a contra-asset. Increase in the accumulated depreciation account decreases the related asset account. Therefore, credit accumulated depreciation account with $18,723.
Working Note:
The above calculation is computed using spreadsheet as follows:
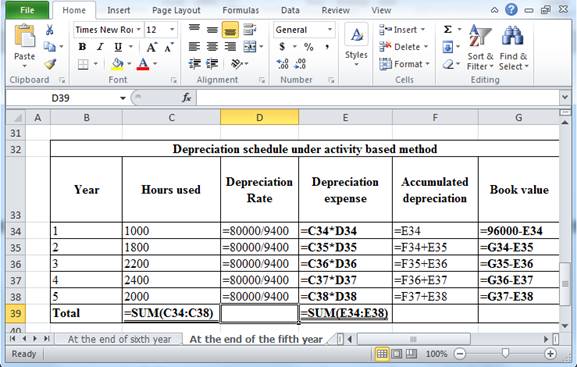
Table (18)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
FINANCIAL ACCT(LOOSELEAF)>CUSTOM<-W/COD
- incoporate the accounting conceptual frameworksarrow_forwarda) Define research methodology in the context of accounting theory and discuss the importance of selecting appropriate research methodology. Evaluate the strengths and limitations of quantitative and qualitative approaches in accounting research. b) Assess the role of modern accounting theories in guiding research in accounting. Discuss how contemporary theories, such as stakeholder theory, legitimacy theory, and behavioral accounting theory, shape research questions, hypotheses formulation, and empirical analysis. Question 4 Critically analyse the role of financial reporting in investment decision-making, emphasizing the qualitative characteristics that enhance the usefulness of financial statements. Discuss how financial reporting influences both investor confidence and regulatory decisions, using relevant examples.arrow_forwardFastarrow_forward
- CODE 14 On August 1, 2010, Cheryl Newsome established Titus Realty, which completed the following transactions during the month: a. Cheryl Newsome transferred cash from a personal bank account to an account to be used for the business in exchange for capital stock, $25,000. b. Paid rent on office and equipment for the month, $2,750. c. Purchased supplies on account, $950. d. Paid creditor on account, $400. c. Earned sales commissions, receiving cash, $18,100. f. Paid automobile expenses (including rental charge) for month, $1,000, and miscel- laneous expenses, $600. g. Paid office salaries, $2,150. h. Determined that the cost of supplies used was $575. i. Paid dividends, $2,000. REQUIREMENTS: 1. Determine increase - decrease of each account and new balance 2. Prepare 3 F.S: Income statement; Retained Earnings Statement; Balance Sheet Scanned with CamScannerarrow_forwardAssume that TDW Corporation (calendar-year-end) has 2024 taxable income of $952,000 for purposes of computing the §179 expense. The company acquired the following assets during 2024: (Use MACRS Table 1, Table 2, Table 3, Table 4, and Table 5.) Asset Machinery Computer equipment Furniture Total Placed in Service September 12 February 10 April 2 Basis $ 2,270,250 263,325 880,425 $ 3,414,000 b. What is the maximum total depreciation, including §179 expense, that TDW may deduct in 2024 on the assets it placed in service in 2024, assuming no bonus depreciation? Note: Round your intermediate calculations and final answer to the nearest whole dollar amount. Maximum total depreciation deduction (including §179 expense)arrow_forwardEvergreen Corporation (calendar-year-end) acquired the following assets during the current year: (Use MACRS Table 1 and Table 2.) Date Placed in Asset Machinery Service October 25 Original Basis $ 120,000 Computer equipment February 3 47,500 Used delivery truck* August 17 Furniture April 22 60,500 212,500 The delivery truck is not a luxury automobile. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to the nearest whole dollar amount. b. What is the allowable depreciation on Evergreen's property in the current year if Evergreen does not elect out of bonus depreciation and elects out of §179 expense?arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





