
a.
To identify:
Discount:
Discount refers to a situation where price issued for the bond is below the par value of the bond.
Premium:
Premium refers to a situation where price issued for the bond is above the par value of the bond.
Par value of bonds:
Par value of bond also mentioned as the face value of the bond is the original price printed on the bond certificate. A bond is considered to be issued at par when yield to maturity of a bond is equal to coupon rate of the bond.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Yield to maturity is 9%.
Bond A has 7% annual coupon rate.
Bond B has 9% annual coupon rate.
Bond C has 11% annual coupon rate.
Bond A has an annual coupon rate of 7% which is less than the required return of 9%, it means that the bond is being traded at below the par value or at discount.
Bond B has an annual coupon rate of 9% which is equal to the required return of 9%, it means that the bond is being traded at par value.
Bond C has an annual coupon rate of 11% which is more than the required return of 9%, it means that the bond is being traded at above the par value or at a premium.
b.
To compute: Price of bonds.
Bonds:
Bonds are a financial instrument, generally issued to raise debt generally for activities which require a significant amount of funds, with an undertaking to repay the amount with appropriate interest.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Bond A
Given,
The coupon rate is 7% or 0.07.
Par value is $1,000
Yield to maturity is 9%
Number of periods is 12
PVIF is 0.35553
PVIFA is 7.1607
The formula to compute the price of bonds:
Where,
i is the interest rate
n is number of time period
PVIFA is
PVIF is Present Value Interest Factor
Substitute $1,000 for the par value of the bond, 0.35553 for PVIF (i,n), $70 for interest to be paid each year and 7.1607 for PVIFA (i,n)
Bond B
Given,
The coupon rate is 9% or 0.09.
Par value is $1,000
Yield to maturity is 9%
Number of periods is 12
PVIF is 0.35553
PVIFA is 7.1607
Since bond B is issued at par, the price of the bond will be its value $1,000.
Bond C
Given,
The coupon rate is 11% or 0.11.
Par value is $1,000
Yield to maturity is 9%
Number of periods is 12
PVIF is 0.35553
PVIFA is 7.1607
The formula to compute the price of bonds:
Where,
i is the interest rate
n is number of time period
PVIFA is Present Value Interest Factor of Annuity
PVIF is Present Value Interest Factor
Substitute $1,000 for the par value of the bond, 0.35553 for PVIF (i,n), $110 for interest to be paid each year and 7.1607 for PVIFA (i,n)
Working Note:
Bond A
Calculation of interest to be paid each year:
Bond B
Calculation of interest to be paid each year:
Bond C
Calculation of interest to be paid each year:
Hence, the price of the bond A, B and C are computed to be $856.78, $1,000 and $1,143.21.
c.
To compute: Current yield.
Current Yield:
Current yield is the anticipated
The formula for current yield:
c.
Explanation of Solution
Bond A
Given,
Annual coupon payment as computed is $70.
Current price as computed is $856.78.
The formula to calculate the current yield of Bond A:
Substitute $70 for annual coupon payment and $856.78 for the current price,
Bond B
Given,
Annual coupon payment as computed is $90.
Current price as computed is $1,000.
The formula to calculate the current yield of Bond B:
Substitute $90 for annual coupon payment and $1,000 for the current price,
Bond C
Given,
Annual coupon payment as computed is $110.
Current price as computed is $1,143.21.
The formula to calculate the current yield of Bond C:
Substitute $110 for annual coupon payment and $1,143.21 for the current price,
Hence, the current yield of Bond A, B and C are computed to be $8.17%, 9.00%, and 9.62%.
d.
To compute: Price of each bond 1 year from now. Expected
Bonds:
Bonds are a financial instrument, generally issued to raise debt generally for activities which require a significant amount of funds, with an undertaking to repay the amount with appropriate interest.
d.
Explanation of Solution
Price of each bond one year from now:
Bond A
Given,
The coupon rate is 7% or 0.07.
Par value is $1,000
Yield to maturity is 9%
Number of periods is 11
PVIF is 0.3875
PVIFA is 6.8052
The formula to compute the price of bonds:
Where,
i is the interest rate
n is number of time period
PVIFA is Present Value Interest Factor of
PVIF is Present Value Interest Factor
Substitute $1,000 for the par value of the bond, 0.3875 for PVIF (i,n), $70 for interest to be paid each year and 6.8052 for PVIFA (i,n)
Bond B
Given,
The coupon rate is 9% or 0.09.
Par value is $1,000
Yield to maturity is 9%
A number of periods is 11.
PVIF is 0.3875
PVIFA is 6.8052
Since bond B is issued at par, the price of the bond will be its value $1,000.
Bond C
Given,
The coupon rate is 11% or 0.11.
Par value is $1,000
Yield to maturity is 9%
Number of periods is 11.
PVIF is 0.3875
PVIFA is 6.8052
The formula to compute the price of bonds:
Where,
i is the interest rate
n is number of time period
PVIFA is Present Value Interest Factor of Annuity
PVIF is Present Value Interest Factor
Substitute $1,000 for the par value of the bond, 0.3875 for PVIF (i,n), $110 for interest to be paid each year and 6.8052 for PVIFA (i,n)
Expected total return for each bond:
Expected total return for each bond is equal to YTM which is 9%.
Expected capital gains yield for each bond:
Bond A
Given,
Expected total return for bond A, B and C is 9%.
The current yield of bond A as computed is 8.17%.
The formula to calculate capital gain yield for Bond A:
Substitute 9% for total return and 8.17% for current yield,
Bond B
Given,
Expected total return for bond A, B and C is 9%.
The current yield of bond A as computed is 9%.
The formula to calculate capital gain yield for Bond B:
Substitute 9% for total return and 9% for current yield,
Bond C
Given,
Expected total return for bond A, B and C is 9%.
The current yield of bond C as computed is 9.62%.
The formula to calculate capital gain yield for Bond A:
Substitute 9% for total return and 9.62% for current yield,
Working Note:
Bond A
Calculation of interest to be paid each year:
Bond B
Calculation of interest to be paid each year:
Bond C
Calculation of interest to be paid each year:
Hence, the price of the bond A, B and C are computed to be $863.86, $1,000 and $1,136.07 respectively. The capital gain yield of Bond A, B and C are computed to be 0.83%, 0% and -0.62% respectively. Expected total return for each bond is computed to be 9%.
e.1.
To compute: Bond’s normal yield to maturity.
e.1.
Explanation of Solution
Bond D
Given,
The semi-annual coupon rate is 8% or 0.08.
Par value is $1,000
Number of periods is 18
Bond price is $1,150.
The formula to compute bond’s nominal yield to maturity:
Where,
C is coupon value
FV is face value
P is the price of the bond
n is number of periods
Substituting $80 for C, $1,000 for FV, $1,150 for P and 18 months for n,
Working note:
Calculation of semiannual rate:
Interest is
Hence, yield to maturity is computed to be 5.88%
2.
To compute: Yield to call
2.
Explanation of Solution
Given,
Semi-annual coupon rate is 8% or 0.08.
Par value is $1,000
Number of periods is 10
The call price is $1,040
The formula to compute bond’s nominal yield to maturity:
Where,
C is coupon value
FV is face value
P is the price of the bond
n is number of periods
Substituting $80 for C, $1,150 for FV, $1,040 for P and 10 months for n,
Hence, yield to maturity is computed to be 5.29.
3.
To identify: Decision to choose between yield to maturity or yield to call.
3.
Answer to Problem 19SP
Mr. C will earn Yield to call in the given case.
Explanation of Solution
Since the bonds are trading at a premium, it indicates that interest rates have fallen.
In case interest rates remain to be constant at present level, Mr. C should anticipate the bond to be called.
As a result, he will earn Yield to call.
Hence, Mr. C will earn Yield to call in the given case.
f.
To identify: Difference between price risk and reinvestment risk. Bonds which have highest reinvestment risk.
f.
Explanation of Solution
Price risk
Price risk is the possibility of the fall in the price of bonds due to rising in the interest rates.
Price risk is higher on bonds having longer maturity period as it gives sufficient time to bondholder to replace the bond.
Reinvestment risk
Reinvestment risk is the possibility of fall in the interest rates which will subsequently result in fall in income from the bond portfolio.
Reinvestment risk is higher on short-term bonds as less high old coupon bonds will be replaced with a new low-coupon bond.
Bonds have been ranked in order from the most interest rate risk to the least interest rate risk:
18 year bond with a 9% annual coupon
A 10-year bond with a zero coupon
A 10-year bond with a 9% annual coupon
A 5-year bond with a zero coupon
A 5-year bond with a 9% annual coupon
Hence, bonds have been ranked above from the most interest rate risk to the least interest rate risk.
g.1.
To compute: Expected interest rate for each bond in each year.
g.1.
Explanation of Solution
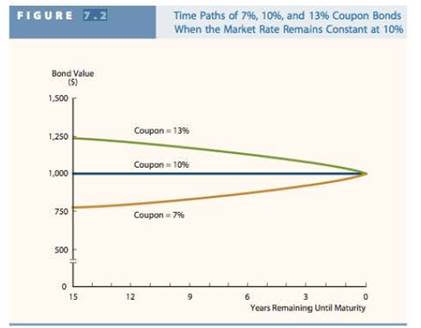
Expected interest yield or current yield for each bond in each year:
| N | Bond A | Bond B | Bond C |
| 12 | 8.17% | 9.00% | 9.62% |
| 11 | 8.10% | 9.00% | 9.68% |
| 10 | 8.03% | 9.00% | 9.75% |
| 9 | 7.95% | 9.00% | 9.82% |
| 8 | 7.87% | 9.00% | 9.90% |
| 7 | 7.78% | 9.00% | 9.99% |
| 6 | 7.69% | 9.00% | 10.09% |
| 5 | 7.59% | 9.00% | 10.21% |
| 4 | 7.48% | 9.00% | 10.33% |
| 3 | 7.37% | 9.00% | 10.47% |
| 2 | 7.26% | 9.00% | 10.63% |
| 1 | 7.13% | 9.00% | 10.80% |
Hence, above table shows the expected interest yield or current yield for each bond in each year.
2.
To compute: Expected capital gains yield for each bond in each year.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Expected capital gains yield for each bond in each year:
| N | Bond A | Bond B | Bond C |
| 12 | 0.83% | 0.00% | -0.62% |
| 11 | 0.90% | 0.00% | -0.68% |
| 10 | 0.97% | 0.00% | -0.75% |
| 9 | 1.05% | 0.00% | -0.82% |
| 8 | 1.13% | 0.00% | -0.90% |
| 7 | 1.22% | 0.00% | -0.99% |
| 6 | 1.31% | 0.00% | -1.09% |
| 5 | 1.41% | 0.00% | -1.21% |
| 4 | 1.52% | 0.00% | -1.33% |
| 3 | 1.63% | 0.00% | -1.47% |
| 2 | 1.74% | 0.00% | -1.63% |
| 1 | 1.87% | 0.00% | -1.80% |
Hence, above table shows the expected capital gains yield for each bond in each year.
3.
To compute: Total return for each bond in each year.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Given,
Expected total return for bond A, B and C is 9%.
Total return for each bond in each year:
| N | Bond A | Bond B | Bond C |
| 12 | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% |
| 11 | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% |
| 10 | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% |
| 9 | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% |
| 8 | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% |
| 7 | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% |
| 6 | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% |
| 5 | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% |
| 4 | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% |
| 3 | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% |
| 2 | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% |
| 1 | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% |
Hence, above table shows the total return for each bond in each year.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Fundamentals Of Financial Management, Concise Edition (mindtap Course List)
- King’s Park, Trinidad is owned and operated by a private company, Windy Sports Ltd. You work as the Facilities Manager of the Park and the CEO of the company has asked you to evaluate whether Windy should embark on the expansion of the facility given there are plans by the Government to host next cricket championship. The project seeks to increase the number of seats by building four new box seating areas for VIPs and an additional 5,000 seats for the general public. Each box seating area is expected to generate $400,000 in incremental annual revenue, while each of the new seats for the general public will generate $2,500 in incremental annual revenue. The incremental expenses associated with the new boxes and seating will amount to 60 percent of the revenues. These expenses include hiring additional personnel to handle concessions, ushering, and security. The new construction will cost $15 million and will be fully depreciated (to a value of zero dollars) on a straight-line basis over…arrow_forwardA brief introduction and overview of the company"s (a) uk vodaphone -300word history and current position in respective marketplace.A graphical illustration, together with a short written summary, of the five year trends in sales, profits,costs and dividends paid-100wordarrow_forwardA brief introduction and overview of the company"s (a) uk vodaphone (b) uk Hsbc bank, (c)uk coca-cola history and current position in respective marketplace.arrow_forward
- King’s Park, Trinidad is owned and operated by a private company,Windy Sports Ltd. You work as the Facilities Manager of the Park andthe CEO of the company has asked you to evaluate whether Windy shouldembark on the expansion of the facility given there are plans by theGovernment to host next cricket championship.The project seeks to increase the number of seats by building fournew box seating areas for VIPs and an additional 5,000 seats for thegeneral public. Each box seating area is expected to generate $400,000in incremental annual revenue, while each of the new seats for thegeneral public will generate $2,500 in incremental annual revenue.The incremental expenses associated with the new boxes and seatingwill amount to 60 percent of the revenues. These expenses includehiring additional personnel to handle concessions, ushering, andsecurity. The new construction will cost $15 million and will be fullydepreciated (to a value of zero dollars) on a straight-line basis overthe 5-year…arrow_forwardYou are called in as a financial analyst to appraise the bonds of Ollie’s Walking Stick Stores. The $5,000 par value bonds have a quoted annual interest rate of 8 percent, which is paid semiannually. The yield to maturity on the bonds is 12 percent annual interest. There are 12 years to maturity. a. Compute the price of the bonds based on semiannual analysis. b. With 8 years to maturity, if yield to maturity goes down substantially to 6 percent, what will be the new price of the bonds?arrow_forwardLonnie is considering an investment in the Cat Food Industries. The $10,000 par value bonds have a quoted annual interest rate of 12 percent and the interest is paid semiannually. The yield to maturity on the bonds is 14 percent annual interest. There are seven years to maturity. Compute the price of the bonds based on semiannual analysis.arrow_forward
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





