
Concept explainers
To determine: The bond’s price at different periods.
Introduction:
A bond refers to the debt securities issued by the governments or corporations for raising capital. The borrower does not return the face value until maturity. However, until the date of maturity, the investors will get the coupons, every year.
Answer to Problem 15QP
The price of the bond at different periods is as follows:
| Time to maturity (Years) | Bond X | Bond Y |
| 13 | $1,168.95 | $848.54 |
| 12 | $1,160.66 | $855.04 |
| 10 | $1,142.22 | $869.95 |
| 5 | $1,083.23 | $920.91 |
| 1 | $1,019.01 | $981.31 |
| 0 | $1,000.00 | $1,000.00 |
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Bond X is selling at a premium. The coupon rate of Bond X is 9 percent and its yield to maturity is 7 percent. The bond will mature in 13 years. Bond Y is selling at a discount. The coupon rate of Bond Y is 7 percent and its yield to maturity is 9 percent. The bond will mature in 13 years. Both the bonds make semiannual coupon payments. Assume that the face value of bonds is $1,000.
The formula to calculate the annual coupon payment:
The formula to calculate the current price of the bond:
Where,
“C” refers to the coupon paid per period,
“F” refers to the face value paid at maturity,
“r” refers to the yield to maturity,
“t” refers to the periods to maturity.
Compute the annual coupon payment of Bond X:
Hence, the annual coupon payment of Bond X is $90.
The bond value or the price of Bond X at present:
The bond pays the coupons semiannually. The annual coupon payment is $90. However, the bondholder will receive the same is two equal installments. Hence, semiannual coupon payment or the 6-month coupon payment is $45
Secondly, 13 years will be the maturity time. As the coupon payment is semiannual, the semiannual periods to maturity are 26 years
Thirdly, the yield to maturity is 7 percent per year. As the calculations are semiannual, the yield to maturity must also be semiannual. Hence, the semiannual or 6-month yield to maturity is 3.5 percent
Hence, the current price of the bond is $1,168.95.
The bond value or the price of Bond X after one year:
The bond pays the coupons semiannually. The annual coupon payment is $90. However, the bondholder will receive the same is two equal installments. Hence, semiannual coupon payment or the 6-month coupon payment is $45
Secondly, 12 years will be the maturity time after one year from now. As the coupon payment is semiannual, the semiannual periods to maturity are 24 years
Thirdly, the yield to maturity is 7 percent per year. As the calculations are semiannual, the yield to maturity must also be semiannual. Hence, the semiannual or 6-month yield to maturity is 3.5percent
Hence, the price of the bond will be $1,160.66 after one year.
The bond value or the price of Bond X after 3 years:
The bond pays the coupons semiannually. The annual coupon payment is $90. However, the bondholder will receive the same is two equal installments. Hence, semiannual coupon payment or the 6-month coupon payment is $45
Secondly, the remaining time to maturity is 10 years after three years from now. As the coupon payment is semiannual, the semiannual periods to maturity are 20 years
Thirdly, the yield to maturity is 7 percent per year. As the calculations are semiannual, the yield to maturity must also be semiannual. Hence, the semiannual or 6-month yield to maturity is 3.5percent
Hence, the price of the bond will be $1,142.22 after three years.
The bond value or the price of Bond X after eight years:
The bond pays the coupons semiannually. The annual coupon payment is $90. However, the bondholder will receive the same is two equal installments. Hence, semiannual coupon payment or the 6-month coupon payment is $45
Secondly, the remaining time to maturity is 5 years after eight years from now. As the coupon payment is semiannual, the semiannual periods to maturity are 10 years
Thirdly, the yield to maturity is 7 percent per year. As the calculations are semiannual, the yield to maturity must also be semiannual. Hence, the semiannual or 6-month yield to maturity is 3.5 percent
Hence, the price of the bond will be $1,083.23 after eight years.
The bond value or the price of Bond X after twelve years:
The bond pays the coupons semiannually. The annual coupon payment is $90. However, the bondholder will receive the same is two equal installments. Hence, semiannual coupon payment or the 6-month coupon payment is $45
Secondly, the remaining time to maturity is one year after twelve years from now. As the coupon payment is semiannual, the semiannual periods to maturity are two
Thirdly, the yield to maturity is 7 percent per year. As the calculations are semiannual, the yield to maturity must also be semiannual. Hence, the semiannual or 6-month yield to maturity is 3.5 percent
Hence, the price of the bond will be $1,019.01 after twelve years.
The bond value or the price of Bond X after thirteen years:
The thirteenth year is the year of maturity for Bond X. In this year, the bondholder will receive the bond’s face value. Hence, the price of the bond will be $1,000 after thirteen years.
Compute the annual coupon payment of Bond Y:
Hence, the annual coupon payment of Bond Y is $70.
The bond value or the price of Bond Y at present:
The bond pays the coupons semiannually. The annual coupon payment is $70. However, the bondholder will receive the same is two equal installments. Hence, semiannual coupon payment or the 6-month coupon payment is $35
Secondly, 13 years will be the maturity time. As the coupon payment is semiannual, the semiannual periods to maturity are 26 years
Thirdly, the yield to maturity is 9 percent per year. As the calculations are semiannual, the yield to maturity must also be semiannual. Hence, the semiannual or 6-month yield to maturity is4.5% that is
Hence, the current price of the bond is $848.54.
The bond value or the price of Bond Y after one year:
The bond pays the coupons semiannually. The annual coupon payment is $70. However, the bondholder will receive the same is two equal installments. Hence, semiannual coupon payment or the 6-month coupon payment is $35
Secondly, the remaining time to maturity is 12 years after one year from now. As the coupon payment is semiannual, the semiannual periods to maturity are 24
Thirdly, the yield to maturity is 8.5 percent per year. As the calculations are semiannual, the yield to maturity must also be semiannual. Hence, the semiannual or 6-month yield to maturity is 4.5 percent
Hence, the price of the bond is $855.04 after one year.
The bond value or the price of Bond Y after three years:
The bond pays the coupons semiannually. The annual coupon payment is $70. However, the bondholder will receive the same is two equal installments. Hence, semiannual coupon payment or the 6-month coupon payment is $35
Secondly, the remaining time to maturity is 10 years after three years from now. As the coupon payment is semiannual, the semiannual periods to maturity are 20 years
Thirdly, the yield to maturity is 9 percent per year. As the calculations are semiannual, the yield to maturity must also be semiannual. Hence, the semiannual or 6-month yield to maturity is 4.5 percent
Hence, the price of the bond is $869.95 after three years.
The bond value or the price of Bond Y after eight years:
The bond pays the coupons semiannually. The annual coupon payment is $70. However, the bondholder will receive the same is two equal installments. Hence, semiannual coupon payment or the 6-month coupon payment is $35
Secondly, the remaining time to maturity is 5 years after three years from now. As the coupon payment is semiannual, the semiannual periods to maturity are 10
Thirdly, the yield to maturity is 9 percent per year. As the calculations are semiannual, the yield to maturity must also be semiannual. Hence, the semiannual or 6-month yield to maturity is 4.5 percent
Hence, the price of the bond is $920.91 after eight years.
The bond value or the price of Bond Y after twelve years:
The bond pays the coupons semiannually. The annual coupon payment is $70. However, the bondholder will receive the same is two equal installments. Hence, semiannual coupon payment or the 6-month coupon payment is $35
Secondly, the remaining time to maturity is one year after twelve years from now. As the coupon payment is semiannual, the semiannual periods to maturity are two
Thirdly, the yield to maturity is 9 percent per year. As the calculations are semiannual, the yield to maturity must also be semiannual. Hence, the semiannual or 6-month yield to maturity is 4.5 percent
Hence, the price of the bond is $981.31 after twelve years.
The bond value or the price of Bond Y after thirteen years:
The thirteenth year is the year of maturity for Bond Y. In this year, the bondholder will receive the bond’s face value. Hence, the price of the bond will be $1,000 after thirteen years.
Table indicating the bond prices of Bond X and Bond Y at different maturities:
Table 1
| Time to maturity (Years) | Bond X | Bond Y |
| 13 | $1,168.95 | $848.54 |
| 12 | $1,160.66 | $855.04 |
| 10 | $1,142.22 | $869.95 |
| 5 | $1,083.23 | $920.91 |
| 1 | $1,019.01 | $981.31 |
| 0 | $1,000.00 | $1,000.00 |
Graphical representation of the bond prices of Bond X and Bond Y from Table 1:
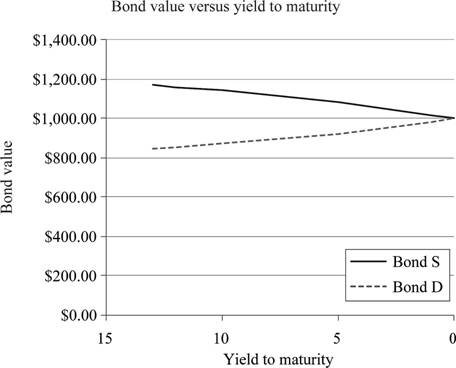
Explanation of the graph:
The graph indicates a “pull to par” effect on the prices of the bonds. The face value of both the bonds is $1,000. Although Bond X is at a premium and Bond Y is at a discount, both the bonds will reach their par values at the time of maturity. The effect of reaching the face value or par value from a discount or premium is known as “pull to par”.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Fundamentals of Corporate Finance Alternate Edition
- Dr Z. Mthembu is the owner of Mr Granite, a business in the Western Cape. After more than 28 years of operation, the business is thinking about taking on a new project that would provide a profitable new clientele. With only R1.5 million in resources, the company is now working on two competing projects. The starting costs for Project X and Project Y are R625,000 and R600000, respectively. These projected are estimated for the next 7 years timeframe. According to SARS, the tax rate is 28%, and a discount rate of 11.25% is applied.Projects X Project YProject X Project Y129000 145000154000 145000312000 145000168000 14500098250 14500088750 14500016050 145000arrow_forwardDr Z. Mthembu is the owner of Mr Granite, a business in the Western Cape. After more than 28 years of operation, the business is thinking about taking on a new project that would provide a profitable new clientele. With only R1.5 million in resources, the company is now working on two competing projects. The starting costs for Project X and Project Y are R625,000 and R600000, respectively. These projected are estimated for the next 7 years timeframe. According to SARS, the tax rate is 28%, and a discount rate of 11.25% is applied.Projects X Project YProject X Project Y129000 145000154000 145000312000 145000168000 14500098250 14500088750 14500016050 145000arrow_forwardDr Z. Mthembu is the owner of Mr Granite, a business in the Western Cape. After more than 28 years of operation, the business is thinking about taking on a new project that would provide a profitable new clientele. With only R1.5 million in resources, the company is now working on two competing projects. The starting costs for Project X and Project Y are R625,000 and R600000, respectively. These projected are estimated for the next 7 years timeframe. According to SARS, the tax rate is 28%, and a discount rate of 11.25% is applied.Projects X Project YProject X Project Y129000 145000154000 145000312000 145000168000 14500098250 14500088750 14500016050 145000arrow_forward
- Dr Z. Mthembu is the owner of Mr Granite, a business in the Western Cape. After more than 28 years of operation, the business is thinking about taking on a new project that would provide a profitable new clientele. With only R1.5 million in resources, the company is now working on two competing projects. The starting costs for Project X and Project Y are R625,000 and R600000, respectively. These projected are estimated for the next 7 years timeframe. According to SARS, the tax rate is 28%, and a discount rate of 11.25% is applied.Projects X Project YProject X Project Y129000 145000154000 145000312000 145000168000 14500098250 14500088750 14500016050 145000arrow_forwardAn investor buys 100 shares of a $40 stock that pays an annual cash dividend of $2 a share (a 5 percent dividend yield) and signs up for the DRIP. a. If neither the dividend nor the price changes, how many shares will the investor have at the end of 10 years? How much will the position in the stock be worth? Answer: 5.000 shares purchased in year 1 5.250 shares purchased in year 2 6.078 shares purchased in year 5 62.889 total shares purchased b. If the price of the stock rises by 6 percent annually but the dividend remains at $2 a share, how many shares are purchased each year for the next 10 years? How much is the total position worth at the end of 10 years? Answer: 4.717 shares purchased in year 1 4.592 shares in year 3 3.898 shares in year 10 Value of position: $10,280 c. If the price of the stock rises by 6 percent annually but the dividend rises by only 3 percent annually, how many shares are purchased each year for the next 10 years? How much is the total position worth at the…arrow_forwardDr Z. Mthembu is the owner of Mr Granite, a business in the Western Cape. After more than 28 years of operation, the business is thinking about taking on a new project that would provide a profitable new clientele. With only R1.5 million in resources, the company is now working on two competing projects. The starting costs for Project X and Project Y are R625,000 and R600000, respectively. These projected are estimated for the next 7 years timeframe. According to SARS, the tax rate is 28%, and a discount rate of 11.25% is applied.Projects X Project YProject X Project Y129000 145000154000 145000312000 145000168000 14500098250 14500088750 14500016050 145000 Calculate the IRR for the two proposed Projectsarrow_forward
- Your sibling want to go on a holiday in 7 years. The cost of a similar holiday today is R70,000 and the cost of the holiday increases by 5% per annum.If he/she can earn 11% per annum on a savings account, how much must he/she save per month as from today to have the money ready in 7 years time? Note: savings will be at the beginning of each month.arrow_forwardHow does corporate governance of a not-for-profit business vary from corporate governance of a traditional for profit business?Include references.arrow_forwardGiven the information below for HooYah! Corporation, compute the expected share price at the end of 2026 using price ratio analysis. Assume that the histor (arithmetic) average growth rates will remain the same for 2026. end of Year 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 Price $ 27.00 $ 63.50 $ 135.00 $ 212.00 $ 102.00 $ 32.50 EPS -7.00 -6.29 -2.30 -0.57 0.05 0.06 CFPS -18.00 -15.50 -3.30 -0.05 0.63 0.08 SPS 24.00 32.50 27.60 31.10 34.60 40.95 What is the expected share price at the end of 2026, using PE ratio? $110.45 $100.45 $120.45 $90.45 22 Multiple Choice Given the information below for HooYah! Corporation, compute the expected share price at the end of 2026 using price ratio analysis. Assume that the histor (arithmetic) average growth rates will remain the same for 2026. end of Year 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 Price $ 27.00 $ 63.50 $ 135.00 $ 212.00 $ 102.00 $ 32.50 EPS -7.00 -6.29 -2.30 -0.57 0.05 0.06 CFPS -18.00 -15.50 -3.30 -0.05 0.63 0.08 SPS 24.00 32.50 27.60 31.10 34.60 40.95…arrow_forward
- What is finance subject? how can this usefull with corporate finance?arrow_forwardwhat is corporate finance ? how this is added with finance. no aiarrow_forward(Annual percentage yield) Compute the cost of the following trade credit terms using the compounding formula, or effective annual rate. Note: Assume a 30-day month and 360-day year. a. 3/5, net 30 b. 3/15, net 45 c. 4/10, net 75 d. 3/15, net 45 ... a. When payment is made on the net due date, the APR of the credit terms of 3/5, net 30 is decimal places.) %. (Round to twoarrow_forward
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





