
a-1.
Journalize the receipt of note on August 1, Year 1.
a-1.
Explanation of Solution
Debit and credit rules:
- Debit an increase in asset account, increase in expense account, decrease in liability account, and decrease in
stockholders’ equity accounts. - Credit decrease in asset account, increase in revenue account, increase in liability account, and increase in stockholders’ equity accounts.
Journalize the receipt of note on August 1, Year 1.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| Year 1 | ||||||
| September | 1 | Notes Receivable | 43,200 | |||
| 43,200 | ||||||
| (Record note receivable received in settlement of account receivable) | ||||||
Table (1)
Description:
- Notes Receivable is an asset account. The amount to be received increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Accounts Receivable is an asset account. Since accounts receivable is settled by receipt of note, amount to be received decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
2.
Journalize the
2.
Explanation of Solution
Journalize the adjustment entry of accrued interest revenue on December 31, Year 1.
| Date | Accounts and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| Year 1 | ||||||
| December | 31 | Interest Receivable | 1,620 | |||
| Interest Revenue | 1,620 | |||||
| (Record accrued interest on note) | ||||||
Table (2)
Description:
- Interest Receivable is an asset account. Since interest to be received has increased, asset value increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Interest Revenue is a revenue account. Since revenues increase equity, equity value is increased, and an increase in equity is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of interest accrued on December 31, Year 1.
3.
Journalize the collection of principal and interest on the note on January 31, Year 2.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Journalize the collection of principal and interest on the note on January 31, Year 2.
| Date | Accounts and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| Year 2 | ||||||
| January | 31 | Cash | 45,144 | |||
| Notes Receivable | 43,200 | |||||
| Interest Receivable | 1,620 | |||||
| Interest Revenue | 324 | |||||
| (Record principal and interest collected on note) | ||||||
Table (3)
Description:
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Notes Receivable is an asset account. Since the note receivable is received, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
- Interest Receivable is an asset account. Since interest to be received is received, asset value decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
- Interest Revenue is a revenue account. Since revenues increase equity, equity value is increased, and an increase in equity is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of interest revenue on January 31, Year 2.
b.
Journalize the transaction of the note being defaulted on January 31, Year 2.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Journalize the transaction of the note being defaulted on January 31, Year 2.
| Date | Accounts and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| Year 2 | ||||||
| January | 31 | Accounts Receivable | 45,144 | |||
| Notes Receivable | 43,200 | |||||
| Interest Receivable | 1,620 | |||||
| Interest Revenue | 324 | |||||
| (Record the note being defaulted) | ||||||
Table (4)
Description:
- Accounts Receivable is an asset account. Since amount to be received has increased, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Notes Receivable is an asset account. Since the note receivable is received, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
- Interest Receivable is an asset account. Since interest to be received is received, asset value decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
- Interest Revenue is a revenue account. Since revenues increase equity, equity value is increased, and an increase in equity is credited.
b.
Indicate the effects of the transactions (1) to (4) in Part (a) on the given financial statement elements, as I (increase), or D (decrease), or NE (no effect).
b.
Explanation of Solution
Indicate the effects of the transactions (1) to (4) in Part (a) on the given financial statement elements, as I (increase), or D (decrease), or NE (no effect).
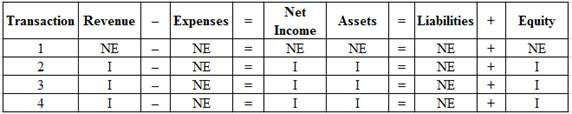
Table (5)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
GEN COMBO FINANCIAL & MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING; CONNECT ACCESS CARD
- Cash Accounts Receivable Supplies Prepaid Insurance Equipment Notes Payable Accounts Payable The Lexington Group Unadjusted Trial Balance May 31, 2016 Debit Balances Credit Balances 20,350 37,000 1,100 200 171,175 36,000 26,000 Common Stock 50,000 Retained Earnings 94,150 Dividends 15,000 Fees Earned 429,850 Wages Expense 270,000 Rent Expense 63,000 Advertising Expense 25,200 Miscellaneous Expense 5,100 608,125 636,000arrow_forwardTrial Balance Rocky Mountain Tours Co. is a travel agency. The nine transactions recorded by Rocky Mountain Tours during June 20Y2, its first month of operations, are indicated in the following T accounts: Cash (1) 40,000 (2) 4,000 (7) 13,100 (3) 5,000 (4) 6,175 (6) 6,000 (9) 1,500 Equipment (3) 15,000 Dividends (9) 1,500 Accounts Receivable Accounts Payable Service Revenue (5) 20,500 (7) 13,100 (6) 6,000 (3) 10,000 (5) 20,500 Supplies (2) 4,000 (8) 2,200 Common Stock Operating Expenses (1) 40,000 (4) 6,175 (8) 2,200arrow_forwardQ1: Wyatt Company had three intangible assets at the end of 2024 (end of the fiscal year): Computer software and Web development technology purchased on January 1, 2024, for $70,000. The technology is expected to have a useful life of four years. A patent purchased from R. Jay on January 1, 2024 for a cash cost of $6,000. Jay had registered the patent with the Canadian Intellectual Property Office seven years earlier on January 1, 2017. The cost of the patent is amortized over its legal life. A trademark that was internally developed and registered with the Canadian government for $13,000 on November 1, 2023. Management decided that the trademark has an indefinite life. Required: 1. What is the acquisition cost of each intangible asset? tech 70k patent 6k trademark 13k 2. Compute the amortization of each intangible asset at December 31, 2024. The company does not use contra accounts. (Round the final answers to the nearest whole dollar.) tech 17.5k patent: ???? 3-a.…arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





