
a-1.
Journalize the receipt of note on August 1, Year 1.
a-1.
Explanation of Solution
Debit and credit rules:
- Debit an increase in asset account, increase in expense account, decrease in liability account, and decrease in
stockholders’ equity accounts. - Credit decrease in asset account, increase in revenue account, increase in liability account, and increase in stockholders’ equity accounts.
Journalize the receipt of note on August 1, Year 1.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| Year 1 | ||||||
| September | 1 | Notes Receivable | 43,200 | |||
| 43,200 | ||||||
| (Record note receivable received in settlement of account receivable) | ||||||
Table (1)
Description:
- Notes Receivable is an asset account. The amount to be received increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Accounts Receivable is an asset account. Since accounts receivable is settled by receipt of note, amount to be received decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
2.
Journalize the
2.
Explanation of Solution
Journalize the adjustment entry of accrued interest revenue on December 31, Year 1.
| Date | Accounts and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| Year 1 | ||||||
| December | 31 | Interest Receivable | 1,620 | |||
| Interest Revenue | 1,620 | |||||
| (Record accrued interest on note) | ||||||
Table (2)
Description:
- Interest Receivable is an asset account. Since interest to be received has increased, asset value increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Interest Revenue is a revenue account. Since revenues increase equity, equity value is increased, and an increase in equity is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of interest accrued on December 31, Year 1.
3.
Journalize the collection of principal and interest on the note on January 31, Year 2.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Journalize the collection of principal and interest on the note on January 31, Year 2.
| Date | Accounts and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| Year 2 | ||||||
| January | 31 | Cash | 45,144 | |||
| Notes Receivable | 43,200 | |||||
| Interest Receivable | 1,620 | |||||
| Interest Revenue | 324 | |||||
| (Record principal and interest collected on note) | ||||||
Table (3)
Description:
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Notes Receivable is an asset account. Since the note receivable is received, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
- Interest Receivable is an asset account. Since interest to be received is received, asset value decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
- Interest Revenue is a revenue account. Since revenues increase equity, equity value is increased, and an increase in equity is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of interest revenue on January 31, Year 2.
b.
Journalize the transaction of the note being defaulted on January 31, Year 2.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Journalize the transaction of the note being defaulted on January 31, Year 2.
| Date | Accounts and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| Year 2 | ||||||
| January | 31 | Accounts Receivable | 45,144 | |||
| Notes Receivable | 43,200 | |||||
| Interest Receivable | 1,620 | |||||
| Interest Revenue | 324 | |||||
| (Record the note being defaulted) | ||||||
Table (4)
Description:
- Accounts Receivable is an asset account. Since amount to be received has increased, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Notes Receivable is an asset account. Since the note receivable is received, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
- Interest Receivable is an asset account. Since interest to be received is received, asset value decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
- Interest Revenue is a revenue account. Since revenues increase equity, equity value is increased, and an increase in equity is credited.
b.
Indicate the effects of the transactions (1) to (4) in Part (a) on the given financial statement elements, as I (increase), or D (decrease), or NE (no effect).
b.
Explanation of Solution
Indicate the effects of the transactions (1) to (4) in Part (a) on the given financial statement elements, as I (increase), or D (decrease), or NE (no effect).
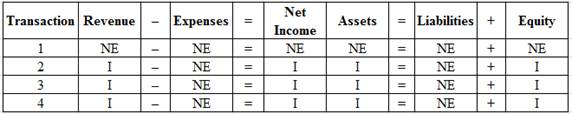
Table (5)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Financial Accounting
- Under which method of inventory accounting are the most recent inventory costs matched with current revenues?a) LIFO (Last-In, First-Out)b) FIFO (First-In, First-Out)c) Average Cost Methodd) Specific Identification Methodarrow_forwardWhat is the goal of cost accounting? Explain itarrow_forwardTwo parts of this probarrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





