
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The name of the following molecule should be determined.
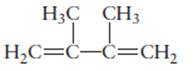
Concept Introduction:
Compounds consist of carbon and hydrogen is known as hydrocarbons.
Rules of naming
- First choose the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms having double bond known as parent chain.
- The numbering of parent chain should be done in a way that the double bond and substituents get the lowest number.
- The root name of the carbon chain is same as in case of
alkanes , but “−ane” ending is replaced by “−ene” - The appropriate name should be given to every alkyl group and denote its position on the parent chain with the number.
- The alkyl groups are written in alphabetical order.
(b)
Interpretation:
The name of the following molecule should be determined.
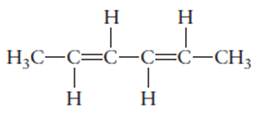
Concept Introduction:
Compounds consist of carbon and hydrogen is known as hydrocarbons. Unsaturated hydrocarbon having double bond is known as alkene having general molecular formula
Rules of naming alkenes are:
- First choose the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms having double bond known as parent chain.
- The numbering of parent chain should be done in a way that the double bond and substituents get the lowest number.
- The root name of the carbon chain is same as in case of alkanes, but “−ane” ending is replaced by “−ene”
- The appropriate name should be given to every alkyl group and denote its position on the parent chain with the number.
- The alkyl groups are written in alphabetical order.
(c)
Interpretation:
The name of the following molecule should be determined.
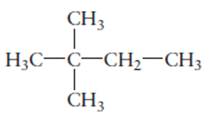
Concept Introduction:
Compounds consist of carbon and hydrogen is known as hydrocarbons. Saturated hydrocarbon is known as alkane having general molecular formula
Rules of naming alkanes are:
- First choose the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms known as parent chain and determines the base name of alkane.
- The numbering of parent chain should be done in a way that the substituents get the lowest number.
- The appropriate name should be given to every alkyl group and denote its position on the parent chain with the number.
- The alkyl groups are written in alphabetical order.
(d)
Interpretation:
The name of the following molecule should be determined.
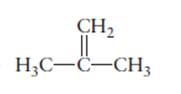
Concept Introduction:
Compounds consist of carbon and hydrogen is known as hydrocarbons. Unsaturated hydrocarbon having double bond is known as alkene having general molecular formula
Rules of naming alkenes are:
- First choose the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms having double bond known as parent chain.
- The numbering of parent chain should be done in a way that the double bond and substituents get the lowest number.
- The root name of the carbon chain is same as in case of alkanes, but “−ane” ending is replaced by “−ene”
- The appropriate name should be given to every alkyl group and denote its position on the parent chain with the number.
- The alkyl groups are written in alphabetical order.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
Bundle: Principles of Modern Chemistry, 8th + OWLv2, 1 term (6 months) Printed Access Card
- Arrange the following compounds / ions in increasing nucleophilicity (least to most nucleophilic) CH3NH2 CH3C=C: CH3COO 1 2 3 5 Multiple Choice 1 point 1, 2, 3 2, 1, 3 3, 1, 2 2, 3, 1 The other answers are not correct 0000arrow_forwardcurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. using the provided starting and product structures, draw the cured electron-pushing arrows for thw following reaction or mechanistic steps. be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond making stepsarrow_forwardUsing the graphs could you help me explain the answers. I assumed that both graphs are proportional to the inverse of time, I think. Could you please help me.arrow_forward
- Synthesis of Dibenzalacetone [References] Draw structures for the carbonyl electrophile and enolate nucleophile that react to give the enone below. Question 1 1 pt Question 2 1 pt Question 3 1 pt H Question 4 1 pt Question 5 1 pt Question 6 1 pt Question 7 1pt Question 8 1 pt Progress: 7/8 items Que Feb 24 at You do not have to consider stereochemistry. . Draw the enolate ion in its carbanion form. • Draw one structure per sketcher. Add additional sketchers using the drop-down menu in the bottom right corner. ⚫ Separate multiple reactants using the + sign from the drop-down menu. ? 4arrow_forwardShown below is the mechanism presented for the formation of biasplatin in reference 1 from the Background and Experiment document. The amounts used of each reactant are shown. Either draw or describe a better alternative to this mechanism. (Note that the first step represents two steps combined and the proton loss is not even shown; fixing these is not the desired improvement.) (Hints: The first step is correct, the second step is not; and the amount of the anhydride is in large excess to serve a purpose.)arrow_forwardHi I need help on the question provided in the image.arrow_forward
- Draw a reasonable mechanism for the following reaction:arrow_forwardDraw the mechanism for the following reaction: CH3 CH3 Et-OH Et Edit the reaction by drawing all steps in the appropriate boxes and connecting them with reaction arrows. Add charges where needed. Electron-flow arrows should start on the electron(s) of an atom or a bond and should end on an atom, bond, or location where a new bond should be created. H± EXP. L CONT. י Α [1] осн CH3 а CH3 :Ö Et H 0 N о S 0 Br Et-ÖH | P LL Farrow_forward20.00 mL of 0.150 M NaOH is titrated with 37.75 mL of HCl. What is the molarity of the HCl?arrow_forward
 World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax





