
Concept explainers
Using FIFO for Multiproduct Inventory Transactions (Chapters 6 and 7)
TrackR, Inc., (TI) has developed a coin-sized tracking tag that attaches to key rings, wallets, and other items and can be prompted to emit a signal using a smartphone app. TI sells these tags, as well as water-resistant cases for the tags, with terms FOB shipping point. Assume TI has no inventory at the beginning of the month, and it has outsourced the production of its tags and cases. TI uses FIFO and has entered into the following transactions:
| Jan. 2: | TI purchased and received 300 tags from Xioasi Manufacturing (XM) at a cost of $9 per tag, n/15. |
| Jan. 4: | TI purchased and received 100 cases from Bachittar Products (BP) at a cost of $2 per case, n/20. |
| Jan. 6: | TI paid cash for the tags purchased from XM on Jan. 2. |
| Jan. 8: | TI mailed 200 tags via the U.S. Postal Service (USPS) to customers at a price of $30 per tag, on account. |
| Jan. 11: | TI purchased and received 400 tags from XM at a cost of $12 per tag, n/15. |
| Jan. 14: | TI purchased and received 200 cases from BP at a cost of $3 per case, n/20. |
| Jan. 16: | TI paid cash for the cases purchased from BP on Jan. 4. |
| Jan. 9: | TI mailed 160 cases via the USPS to customers at a price of $10 per case, on account. |
| Jan. 21: | TI mailed 300 tags to customers at a price of $30 per tag. |
Required:
- 1. Prepare
journal entries for each of the above dates, assuming TI uses a perpetual inventory system. - 2. Calculate the dollars of gross profit and the gross profit percentage from selling (a) tags and (b) cases.
- 3. Which product line yields more dollars of profit?
- 4. Which product line yields more profit per dollar of sales?
1.
Prepare journal entries for the given transactions of Company TI; assume that the company uses perpetual inventory system.
Explanation of Solution
Journal entry: Journal entry is a set of economic events which can be measured in monetary terms. These are recorded chronologically and systematically.
Debit and credit rules:
- Debit an increase in asset account, increase in expense account, decrease in liability account, and decrease in stockholders’ equity accounts.
- Credit decrease in asset account, increase in revenue account, increase in liability account, and increase in stockholders’ equity accounts.
Perpetual inventory system: The method or system of maintaining, recording, and adjusting the inventory perpetually throughout the year, is referred to as perpetual inventory system.
Prepare journal entry for the given transaction of Company TAC; assume that the company uses weighted average in its perpetual inventory system as follows:
- Prepare journal entry for the transaction occurred on January 2.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| January | 2 | Inventories (Refer working note 1) | 2,700 | ||
| Accounts Payable | 2,700 | ||||
| (To record the purchase of 300 tags at a cost of $9 on account) | |||||
Table (1)
- Inventory is an asset and increased by $2,700. Therefore, debit the inventory account with $2,700.
- Accounts Payable is a liability and decreased by $2,700. Therefore, credit the accounts payable account with $2,700.
- Prepare journal entry for the transaction occurred on January 4.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| January | 4 | Inventories (Refer working note 1) | 200 | ||
| Accounts Payable | 200 | ||||
| (To record the purchase of 100 tags at a cost of $2 on account) | |||||
Table (2)
- Inventory is an asset and increased by $200. Therefore, debit the inventory account with $200.
- Accounts Payable is a liability and decreased by $200. Therefore, credit the accounts payable account with $200.
- Prepare journal entry for the transaction occurred on January 6.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| January | 6 | Accounts Payable | 2,700 | ||
| Cash | 2,700 | ||||
| (To record the payment of cash for the goods purchased on January 2) | |||||
Table (3)
- Accounts Payable is a liability and increased by $2,700. Therefore, debit the accounts payable account with $2,700.
- Cash is an asset and there is a decrease in the value of asset. So credit the cash account with $2,700
- Prepare journal entry for the transaction occurred on January 8.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| January | 8 | Accounts Receivable (Refer working note 1) | 6,000 | ||
| Sales Revenue | 6,000 | ||||
| (To record sale of inventories on account) | |||||
| Cost of Goods Sold (Refer working note 1) | 1,800 | ||||
| Inventories | 1,800 | ||||
| (To record the cost of goods sold ) | |||||
Table (4)
Description:
- Accounts Receivable is an asset and there is an increase in the value of asset. So debit the accounts receivable account with $6,000.
- Sales Revenue is a component of stockholder’s equity and there is an increase in the value of stockholder’s equity. So credit the sales revenue account for $6,000.
- Cost of goods sold is an expense and increased; hence it has decreased the equity by $1,800. Therefore, debit cost of goods sold account with $1,800.
- Inventory is an asset and decreased by $1,800. Therefore, credit the inventory account with $1,800.
- Prepare journal entry for the transaction occurred on January 11.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| January | 11 | Inventories (Refer working note 1) | 4,800 | ||
| Accounts Payable | 4,800 | ||||
| (To record the purchase of 300 tags at a cost of $9 on account) | |||||
Table (5)
- Inventory is an asset and increased by $4,800. Therefore, debit the inventory account with $4,800.
- Accounts Payable is a liability and decreased by $4,800. Therefore, credit the accounts payable account with $4,800.
- Prepare journal entry for the transaction occurred on January 14.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| January | 14 | Inventories (Refer working note 1) | 600 | ||
| Accounts Payable | 600 | ||||
| (To record the purchase of 300 tags at a cost of $9 on account) | |||||
Table (6)
- Inventory is an asset and increased by $600. Therefore, debit the inventory account with $600.
- Accounts Payable is a liability and decreased by $600. Therefore, credit the accounts payable account with $600.
- Prepare journal entry for the transaction occurred on January 16.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| January | 16 | Accounts Payable | 200 | ||
| Cash | 200 | ||||
| (To record the payment of cash for the goods purchased on January 4) | |||||
Table (7)
- Accounts Payable is a liability and increased by $200. Therefore, debit the accounts payable account with $200.
- Cash is an asset and there is a decrease in the value of asset. So credit the cash account with $200.
- Prepare journal entry for the transaction occurred on January 19.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| January | 19 | Accounts Receivable (Refer working note 1) | 1,600 | ||
| Sales Revenue | 1,600 | ||||
| (To record sale of inventories on account) | |||||
| Cost of Goods Sold (Refer working note 1) | 380 | ||||
| Inventories | 380 | ||||
| (To record the cost of goods sold ) | |||||
Table (8)
Description:
- Accounts Receivable is an asset and there is an increase in the value of asset. So debit the accounts receivable account with $6,000.
- Sales Revenue is a component of stockholder’s equity and there is an increase in the value of stockholder’s equity. So credit the sales revenue account for $6,000.
- Cost of goods sold is an expense and increased; hence it has decreased the equity by $380. Therefore, debit cost of goods sold account with $380.
- Inventory is an asset and decreased by $380. Therefore, credit the inventory account with $380.
- Prepare journal entry for the transaction occurred on January 21.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| January | 19 | Accounts Receivable (Refer working note 1) | 9,000 | ||
| Sales Revenue | 9,000 | ||||
| (To record sale of inventories on account) | |||||
| Cost of Goods Sold (Refer working note 1) | 3,300 | ||||
| Inventories | 3,300 | ||||
| (To record the cost of goods sold ) | |||||
Table (9)
Description:
- Accounts Receivable is an asset and there is an increase in the value of asset. So debit the accounts receivable account with $9,000.
- Sales Revenue is a component of stockholder’s equity and there is an increase in the value of stockholder’s equity. So credit the sales revenue account for $9,000.
- Cost of goods sold is an expense and increased; hence it has decreased the equity by $3,300. Therefore, debit cost of goods sold account with $3,300.
- Inventory is an asset and decreased by $3,300. Therefore, credit the inventory account with $3,300.
Working note 1:
Calculate the amount of sales, cost of goods sold, purchases and inventory on hand (Ending inventory) under FIFO method as follows:
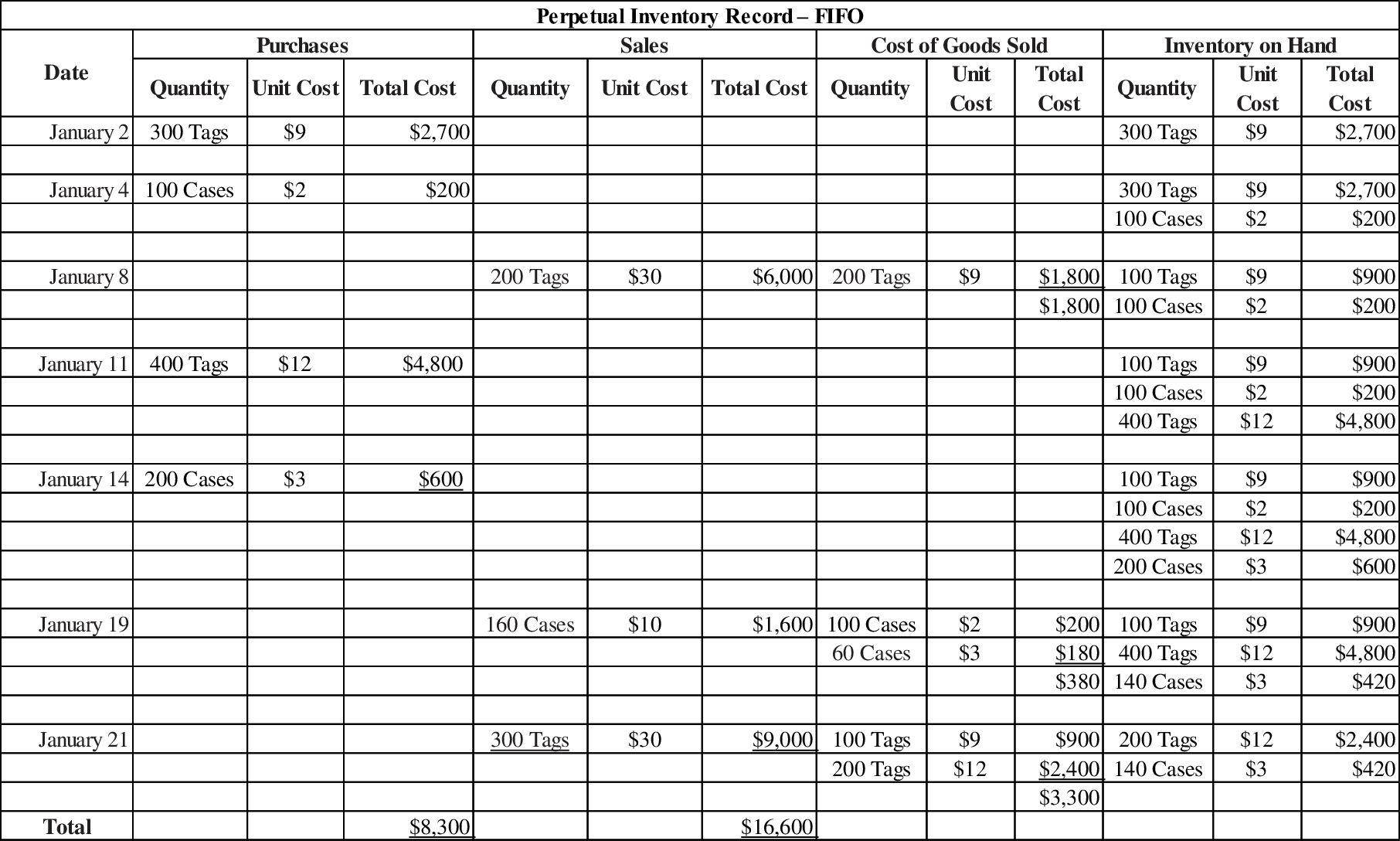
Figure (1)
2.
Calculate the dollars of gross profit and the gross profit percentage from selling the following items:
- a) Tags and
- b) Cases.
Explanation of Solution
Gross margin (gross profit): Gross margin is the amount of revenue earned from goods sold over the costs incurred for the goods sold.
Gross margin percentage: The percentage of gross profit generated by every dollar of net sales is referred to as gross profit percentage. This ratio measures the profitability of a company by quantifying the amount of income earned from sales revenue generated after cost of goods sold are paid. The higher the ratio, the more ability to cover operating expenses.
a. Calculate the dollars of gross profit and the gross profit percentage from the sale of Tags as follows:
Calculate the dollars of gross profit as follows:
| Particulars | $ |
| Sales Revenue (Refer working note 1) | $6,000 |
| Sales Revenue (Refer working note 1) | 9,000 |
| Total Sales | 15,000 |
| Less: Cost of Goods Sold | |
| On January 8 (Refer working note 1) | 1,800 |
| On January 21 (Refer working note 1) | 3,300 |
| Gross Profit | $9,900 |
Table (10)
Calculate the dollars of gross profit percentage as follows:
b. Calculate the dollars of gross profit and the gross profit percentage from the sale of Cases as follows:
Calculate the dollars of gross profit as follows:
| Particulars | $ |
| Sales Revenue (Refer working note 1) | $1,600 |
| Less: Cost of Goods Sold | |
| On January 19 (Refer working note 1) | 380 |
| Gross Profit | $1,220 |
Table (11)
Calculate the dollars of gross profit percentage as follows:
3.
State the product line that yields more dollars of profit.
Explanation of Solution
State the product line that yields more dollars of profit as follows:
In this case, the Tags product line yields more dollars of profit than Cases product line. From the above calculation it is clear that the gross profit of Tags product line ($9,900) is more than the gross profit of Cases product line ($1,220).
4.
State the product line that yields more profit per dollar of sales.
Explanation of Solution
State the product line that yields more profit per dollar of sales as follows:
The cases product line yields more profit per dollar of sales than the Tags product line. Since the cases product line has a higher gross profit percentage of 76.25%, while the tags product line has a gross profit percentage of only 66%.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
FUND. OF FINANCIAL ACCT. (LL) W/CONNECT
- The ending inventory isarrow_forwardhelparrow_forwardBansai, age 66, retires and receives a $1,450 per month annuity from his employer's qualified pension plan. Bansai made $87,600 of after-tax contributions to the plan before retirement. Under the simplified method, Bansai's number of anticipated payments is 240. What is the amount includible in income in the first year of withdrawals assuming 12 monthly payments? A. $10,560 B. $12,540 C. $17,400 D. $8,220arrow_forward
 Individual Income TaxesAccountingISBN:9780357109731Author:HoffmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
Individual Income TaxesAccountingISBN:9780357109731Author:HoffmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub

