
1-4 Modeling Periodic Data A set of data is given.
(a) Make a
(b) Find a cosine function of the form
(c) Graph the function you found in part (b) together with the scatter plot. How well does the curve fit the data?
(d) Use a graphing calculator to find the sine function that best fits the data, as in Example 2.
(e) Compare the functions you found in parts (b) and (d). [Use the reduction formula
| t | y |
| 0 | 2.1 |
| 2 | 1.1 |
| 4 |
|
| 6 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 10 | 0.6 |
| 12 | 1.9 |
| 14 | 1.5 |
(a)
To find:
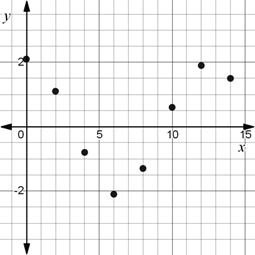
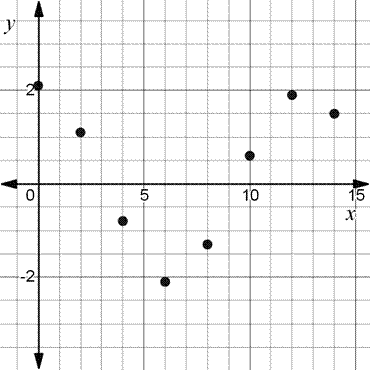
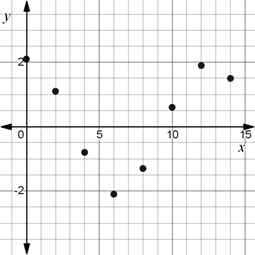
A scatter plot of the data.
Answer to Problem 1P
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The scatter plot for the given data is given by
Final statement:
(b)
To find:
A cosine function of the form
Answer to Problem 1P
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Here, the maximum value is 2.1 and the minimum value is -2.1.
The maximum value occurs at time 0 and the minimum value occurs at time 6.
The vertical shift
The amplitude
The time between consecutive maximum and minimum values is half of one period.
That is,
Since the maximum value of the data occurs at
There is no horizontal shift.
Apply the values in the function
Since cosine is an even function,
Final statement:
(c)
To find:
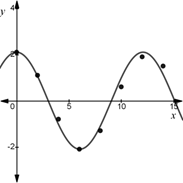
The graph of the function from part (b).
Answer to Problem 1P
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The graph of the function
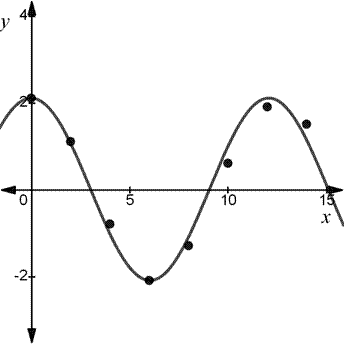
Final statement:
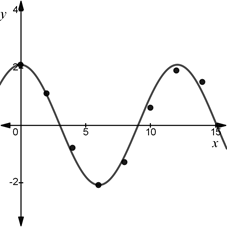
(d)
To find:
The sine function that fits the data.
Answer to Problem 1P
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Using the given data and the SinReg command on the T1-83 calculator, we get a function of the form
Here,
Apply the values in the function
Final statement:
(e)
To find:
The comparison between the functions from part (b) and (d).
Answer to Problem 1P
Solution:
It is same as (b), corrected to one decimal.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
From part (d),
Apply the reduction formula
So,
It is same as (b), corrected to one decimal.
Final statement:
It is same as (b), corrected to one decimal.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Elementary & Intermediate Algebra
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)
Elementary Statistics Using The Ti-83/84 Plus Calculator, Books A La Carte Edition (5th Edition)
University Calculus
Elementary Statistics ( 3rd International Edition ) Isbn:9781260092561
- Jamal wants to save $48,000 for a down payment on a home. How much will he need to invest in an account with 11.8% APR, compounding daily, in order to reach his goal in 10 years? Round to the nearest dollar.arrow_forwardr nt Use the compound interest formula, A (t) = P(1 + 1)". An account is opened with an intial deposit of $7,500 and earns 3.8% interest compounded semi- annually. Round all answers to the nearest dollar. a. What will the account be worth in 10 years? $ b. What if the interest were compounding monthly? $ c. What if the interest were compounded daily (assume 365 days in a year)? $arrow_forwardKyoko has $10,000 that she wants to invest. Her bank has several accounts to choose from. Her goal is to have $15,000 by the time she finishes graduate school in 7 years. To the nearest hundredth of a percent, what should her minimum annual interest rate be in order to reach her goal assuming they compound daily? (Hint: solve the compound interest formula for the intrerest rate. Also, assume there are 365 days in a year) %arrow_forward
- 3:56 wust.instructure.com Page 0 Chapter 5 Test Form A of 2 - ZOOM + | Find any real numbers for which each expression is undefined. 2x 4 1. x Name: Date: 1. 3.x-5 2. 2. x²+x-12 4x-24 3. Evaluate when x=-3. 3. x Simplify each rational expression. x²-3x 4. 2x-6 5. x²+3x-18 x²-9 6. Write an equivalent rational expression with the given denominator. 2x-3 x²+2x+1(x+1)(x+2) Perform the indicated operation and simplify if possible. x²-16 x-3 7. 3x-9 x²+2x-8 x²+9x+20 5x+25 8. 4.x 2x² 9. x-5 x-5 3 5 10. 4x-3 8x-6 2 3 11. x-4 x+4 x 12. x-2x-8 x²-4 ← -> Copyright ©2020 Pearson Education, Inc. + 5 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. T-97arrow_forwardProblem #5 Suppose you flip a two sided fair coin ("heads" or "tails") 8 total times. a). How many ways result in 6 tails and 2 heads? b). How many ways result in 2 tails and 6 heads? c). Compare your answers to part (a) and (b) and explain in a few sentences why the comparison makes sense.arrow_forwardA local company has a 6 person management team and 20 employees. The company needs to select 3 people from the management team and 7 employees to attend a regional meeting. How many different possibilities are there for the group that can be sent to the regional meeting?arrow_forward
- I have 15 outfits to select from to pack for my business trip. I would like to select three of them to pack in my suitcase. How many packing possibilities are there?arrow_forwardThere are 15 candidates running for any of 5 distinct positions on the local school board. In how many different ways could the 5 positions be filled?arrow_forwardCelina is picking a new frame for a custom piece of artwork. She has to select a frame size, material, and color. There are four different frame sizes, three different frame materials, and six different frame colors. She must chose one option only from each category. How many different possible frames could Celina pick from?arrow_forward
- A research study in the year 2009 found that there were 2760 coyotes in a given region. The coyote population declined at a rate of 5.8% each year. How many fewer coyotes were there in 2024 than in 2015? Explain in at least one sentence how you solved the problem. Show your work. Round your answer to the nearest whole number.arrow_forwardAnswer the following questions related to the following matrix A = 3 ³).arrow_forwardExplain the following termsarrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
