
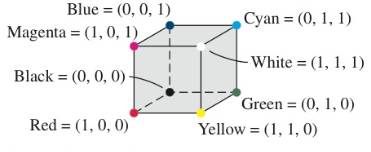
Representing Colors Colors for computer monitors are often described using ordered triples. One model, called the RGB system, uses red, green, and blue to generate all colors. The figure describes the relationships of these colors in this system. Red is (1, 0, 0), green is (0, 1, 0), and blue is (0, 0, 1). Since equal amounts of red and green combine to form yellow, yellow is represented by (1, 1, 0). Similarly, magenta (a deep reddish purple) is a mixture of blue and red and is represented by (1, 0, 1).
Cyan is (0, 1, 1), since it is a mixture of blue and green.
Another color model uses cyan, magenta, and yellow. Referred to as the CMY model, it is used in the four-color printing process for textbooks like this one. In this system, cyan is (1, 0, 0), magenta is (0, 1, 0), and yellow is (0, 0, 1).
In the CMY model, red is created by mixing magenta and yellow. Thus, red is (0, 1, 1) in this system. To convert ordered triples in the RGB model to ordered triples in the CMY model, we can use the following matrix equation. In both of these systems, color intensities vary between 0 and I. (Sources: I. Kerlow, The Art of 3-D Computer Animation and Imaging; R. Wolff.)
2. In the RGB model, rust is (0.552, 0.168, 0.066). Use the matrix equation to determine the mixture of cyan, magenta, and yellow that makes rust in the CMY model.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
College Algebra With Modeling And Visualization
- Solve questions by Course Name (Ordinary Differential Equations II 2)arrow_forwardplease Solve questions by Course Name( Ordinary Differential Equations II 2)arrow_forwardInThe Northern Lights are bright flashes of colored light between 50 and 200 miles above Earth. Suppose a flash occurs 150 miles above Earth. What is the measure of arc BD, the portion of Earth from which the flash is visible? (Earth’s radius is approximately 4000 miles.)arrow_forward
- e). n! (n - 1)!arrow_forwardSuppose you flip a fair two-sided coin four times and record the result. a). List the sample space of this experiment. That is, list all possible outcomes that could occur when flipping a fair two-sided coin four total times. Assume the two sides of the coin are Heads (H) and Tails (T).arrow_forwarde). n! (n - 1)!arrow_forward
- Evaluate the following expression and show your work to support your calculations. a). 6! b). 4! 3!0! 7! c). 5!2! d). 5!2! e). n! (n - 1)!arrow_forwardAmy and Samiha have a hat that contains two playing cards, one ace and one king. They are playing a game where they randomly pick a card out of the hat four times, with replacement. Amy thinks that the probability of getting exactly two aces in four picks is equal to the probability of not getting exactly two aces in four picks. Samiha disagrees. She thinks that the probability of not getting exactly two aces is greater. The sample space of possible outcomes is listed below. A represents an ace, and K represents a king. Who is correct?arrow_forwardConsider the exponential function f(x) = 12x. Complete the sentences about the key features of the graph. The domain is all real numbers. The range is y> 0. The equation of the asymptote is y = 0 The y-intercept is 1arrow_forward
 Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage

