
Concept explainers
Three boxes are connected by ropes and pulled across a smooth, horizontal surface with an acceleration a, as shown in Figure 6-21. The force applied to the first box on the right is F, the tension in the rope connecting the first
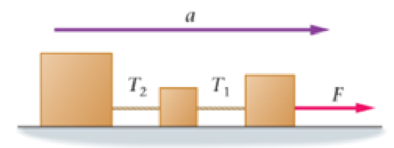
Figure 6-21 Enhance Your Understanding 4
and second boxes is T1, and the tension in the rope connecting the second and third boxes is T2.Rank the three forces (F, T1, T2) in order of increasing magnitude. Indicate ties where appropriate.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 6 Solutions
Physics (5th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry (7th Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
- Please see the attached image and answer the set of questions with proof.arrow_forwardHow, Please type the whole transcript correctly using comma and periods as needed. I have uploaded the picture of a video on YouTube. Thanks,arrow_forwardA spectra is a graph that has amplitude on the Y-axis and frequency on the X-axis. A harmonic spectra simply draws a vertical line at each frequency that a harmonic would be produced. The height of the line indicates the amplitude at which that harmonic would be produced. If the Fo of a sound is 125 Hz, please sketch a spectra (amplitude on the Y axis, frequency on the X axis) of the harmonic series up to the 4th harmonic. Include actual values on Y and X axis.arrow_forward
- Sketch a sign wave depicting 3 seconds of wave activity for a 5 Hz tone.arrow_forwardSketch a sine wave depicting 3 seconds of wave activity for a 5 Hz tone.arrow_forwardThe drawing shows two long, straight wires that are suspended from the ceiling. The mass per unit length of each wire is 0.050 kg/m. Each of the four strings suspending the wires has a length of 1.2 m. When the wires carry identical currents in opposite directions, the angle between the strings holding the two wires is 20°. (a) Draw the free-body diagram showing the forces that act on the right wire with respect to the x axis. Account for each of the strings separately. (b) What is the current in each wire? 1.2 m 20° I -20° 1.2 marrow_forward
- 2). How much energy is stored in the 50-μF capacitor when Va - V₁ = 22V? 25 µF b 25 µF 50 µFarrow_forward9). A series RC circuit has a time constant of 1.0 s. The battery has a voltage of 50 V and the maximum current just after closing the switch is 500 mA. The capacitor is initially uncharged. What is the charge on the capacitor 2.0 s after the switch is closed? R 50 V a. 0.43 C b. 0 66 C c. 0.86 C d. 0.99 C Carrow_forward1). Determine the equivalent capacitance of the combination shown when C = 12 pF. +11/20 2C C Carrow_forward
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





