Engineering Mechanics: Statics & Dynamics (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133915426
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 6.3, Problem 2PP
Identify the zero-force members in each truss.
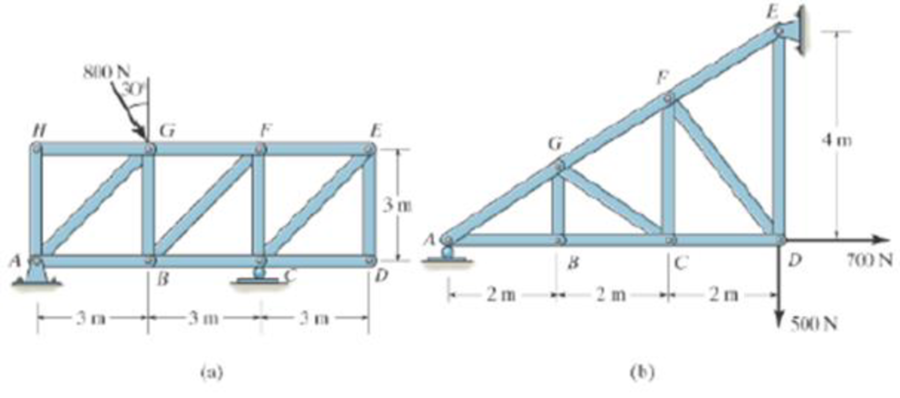
Prob. P6-2
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
!
Required information
A one-shell-pass and eight-tube-passes heat exchanger is used to heat glycerin (cp=0.60 Btu/lbm.°F) from 80°F to 140°F
by hot water (Cp = 1.0 Btu/lbm-°F) that enters the thin-walled 0.5-in-diameter tubes at 175°F and leaves at 120°F. The total
length of the tubes in the heat exchanger is 400 ft. The convection heat transfer coefficient is 4 Btu/h-ft²°F on the glycerin
(shell) side and 70 Btu/h-ft²°F on the water (tube) side.
NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part.
Determine the rate of heat transfer in the heat exchanger before any fouling occurs.
Correction factor F
1.0
10
0.9
0.8
R=4.0 3.0 2.0.15 1.0 0.8.0.6 0.4 0.2
0.7
0.6
R=
T1-T2
12-11
0.5
12-11
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0
(a) One-shell pass and 2, 4, 6, etc. (any multiple of 2), tube passes
P=
T₁-11
The rate of heat transfer in the heat exchanger is
Btu/h.
!
Required information
Air at 25°C (cp=1006 J/kg.K) is to be heated to 58°C by hot oil at 80°C (cp = 2150 J/kg.K) in a cross-flow heat exchanger
with air mixed and oil unmixed. The product of heat transfer surface area and the overall heat transfer coefficient is 750
W/K and the mass flow rate of air is twice that of oil.
NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part.
Air
Oil
80°C
Determine the effectiveness of the heat exchanger.
In an industrial facility, a counter-flow double-pipe heat exchanger uses superheated steam at a temperature of 155°C to
heat feed water at 30°C. The superheated steam experiences a temperature drop of 70°C as it exits the heat exchanger.
The water to be heated flows through the heat exchanger tube of negligible thickness at a constant rate of 3.47 kg/s. The
convective heat transfer coefficient on the superheated steam and water side is 850 W/m²K and 1250 W/m²K,
respectively. To account for the fouling due to chemical impurities that might be present in the feed water, assume
a fouling factor of 0.00015 m²-K/W for the water side.
The specific heat of water is determined at an average temperature of (30 +70)°C/2 = 50°C and is taken to be
J/kg.K.
Cp=
4181
Water
Steam
What would be the required heat exchanger area in case of parallel-flow arrangement?
The required heat exchanger area in case of parallel-flow arrangement is
1m².
Chapter 6 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Statics & Dynamics (14th Edition)
Ch. 6.3 - In each case, calculate the support reactions and...Ch. 6.3 - Identify the zero-force members in each truss....Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss....Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss....Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss....Ch. 6.3 - Determine the greatest load P that can be applied...Ch. 6.3 - Identify the zero-force members in the truss....Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss....Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...
Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss....Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Prob. 5PCh. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss,...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Prob. 9PCh. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the Pratt...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss in...Ch. 6.3 - Members AB and BC can each support a maximum...Ch. 6.3 - Members AB and BC can each support a maximum...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss....Ch. 6.3 - If the maximum force that any member can support...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Prob. 20PCh. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the double...Ch. 6.3 - Prob. 23PCh. 6.3 - The maximum allowable tensile force in the members...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss in...Ch. 6.3 - The maximum allowable tensile force in the members...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members BC, CF, and FE....Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members LK, KC, and CD of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members KJ, KD, and CD of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members EF, CF, and BC of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members GF, GD, and CD of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members DC, HI, and JI of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members DC, HC, and HI of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members ED, EH, and GH of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members HG, HE and DE of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members CD, HI, and CH of...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 31PCh. 6.4 - Prob. 32PCh. 6.4 - Prob. 33PCh. 6.4 - Prob. 34PCh. 6.4 - Determine the force in members EF, CF, and BC, and...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members AF, BF, and BC, and...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 39PCh. 6.4 - Determine the force in members CD, CF, and CG and...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force developed in members FE, EB,...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members BC, HC, and HG....Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members CD, CJ, GJ, and CG...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members BE, EF, and CB, and...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 45PCh. 6.4 - Determine the force in members BC, CH, GH, and CG...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members CD, CJ, and KJ and...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 48PCh. 6.4 - Determine the force in members HI, FI, and EF of...Ch. 6.6 - In each case, identify any two-force members, and...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force P needed to hold the 60-lb...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - If a 100-N force is applied to the handles of the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the normal force that the 100-lb plate A...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force P needed to lift the load....Ch. 6.6 - Prob. 19FPCh. 6.6 - Prob. 20FPCh. 6.6 - Determine the components of reaction at A and C....Ch. 6.6 - Determine the components of reaction at C. Prob....Ch. 6.6 - Determine the components of reaction at E. Prob....Ch. 6.6 - Determine the components of reaction at D and the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force P required to hold the 100-lb...Ch. 6.6 - In each case, determine the force P required to...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force P required to hold the 50-kg...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force P required to hold the 150-kg...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force that the smooth rotor C exerts...Ch. 6.6 - The bridge frame consists of three segments which...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the reactions at supports A and B. Prob....Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the reactions at the supports A, C, and...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the resultant force at pins A, B, and C...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the reactions at the supports at A, E,...Ch. 6.6 - The wall crane supports a load of 700 lb....Ch. 6.6 - The wall crane supports a load of 700 lb....Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - The two-member structure is connected at C by a...Ch. 6.6 - The compound beam is pin supported at B and...Ch. 6.6 - When a force of 2 lb is applied to the handles of...Ch. 6.6 - The toggle clamp is subjected to a force F at the...Ch. 6.6 - The hoist supports the 125-kg engine. Determine...Ch. 6.6 - A 5-lb force is applied to the handles of the vise...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force in members FD and DB of the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force that the smooth 20-kg cylinder...Ch. 6.6 - Prob. 85PCh. 6.6 - The pumping unit is used to recover oil. When the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force that the jaws J of the metal...Ch. 6.6 - Prob. 88PCh. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - The pipe cutter is clamped around the pipe P. If...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force created in tire hydraulic...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - The constant moment of 50 N m is applied to the...Ch. 6.6 - Five coins are stacked in the smooth plastic...Ch. 6.6 - The nail cutter consists of the handle and the two...Ch. 6.6 - A man having a weight of 175 lb attempts to hold...Ch. 6.6 - Prob. 97PCh. 6.6 - The two member frame is pin connected at E. The...Ch. 6.6 - If the 300 kg drum has a center of mass at point...Ch. 6.6 - Operation of exhaust and intake valves in an...Ch. 6.6 - If a clamping force of 300 N is required at A,...Ch. 6.6 - If a force of F = 350 N is applied to the handle...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - The hydraulic crane is used to lift the 1400-lb...Ch. 6.6 - Determine force P on the cable if the spring is...Ch. 6.6 - Prob. 106PCh. 6.6 - If a force of F = 50 lb is applied to the pads at...Ch. 6.6 - The skid-steer loader has a mass of 1.18 Mg, and...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force P on the cable if the spring...Ch. 6.6 - The spring has an unstretched length of 0.3 m....Ch. 6.6 - The spring has an unstretched length of 0.3 m....Ch. 6.6 - The piston C moves vertically between the two...Ch. 6.6 - Prob. 113PCh. 6.6 - The platform scale consists of a combination of...Ch. 6.6 - The three pin-connected members shown in the top...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force in member GJ and GC of the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force in members GF, FB, and BC of...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the resultant forces at pins B and C on...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Consider the following skeletal C program: void fun1(void); / prototype / void fun2(void); / prototype / void f...
Concepts Of Programming Languages
Porter’s competitive forces model: The model is used to provide a general view about the firms, the competitors...
Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm (16th Edition)
Heads or TaiLs Game This game is meant for two or more players. In this game, the players take turns flipping a...
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Describe a method that can be used to gather a piece of data such as the users age.
Web Development and Design Foundations with HTML5 (8th Edition)
Find the no-load value of υo in the circuit shown.
Find υo when RL is 150 Ω.
How much power is dissipated in th...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Give a Java statement that will display a dialog window on the screen with the message I Love You.
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A single-pass crossflow heat exchanger is used to cool jacket water (cp = 1.0 Btu/lbm.°F) of a diesel engine from 190°F to 140°F, using air (Cp = 0.245 Btu/lbm.°F) at inlet temperature of 90°F. Both air flow and water flow are unmixed. If the water and air mass flow rates are 85500 lbm/h and 400,000 lbm/h, respectively, determine the log mean temperature difference for this heat exchanger. Assume the correction factor F to be 0.92. Air flow (unmixed) Water flow (unmixed) The log mean temperature difference of the heat exchanger is °F.arrow_forwardusing the theorem of three moments, find all the reactions and supports, I need concise calculations only. the answers are at the bottom, I need concise steps and minimal explanationsarrow_forwardIn an industrial facility, a counter-flow double-pipe heat exchanger uses superheated steam at a temperature of 155°C to heat feed water at 30°C. The superheated steam experiences a temperature drop of 70°C as it exits the heat exchanger. The water to be heated flows through the heat exchanger tube of negligible thickness at a constant rate of 3.47 kg/s. The convective heat transfer coefficient on the superheated steam and water side is 850 W/m²K and 1250 W/m²K, respectively. To account for the fouling due to chemical impurities that might be present in the feed water, assume a fouling factor of 0.00015 m² K/W for the water side. The specific heat of water is determined at an average temperature of (30+70)°C/2 = 50°C and is taken to be Cp J/kg-K. Water Steam Determine the heat exchanger area required to maintain the exit temperature of the water to a minimum of 70°C. The heat exchanger area required isarrow_forward
- Stress, ksi 160 72 150- 140 80 70 ༄ ྃ ༈ ཎྜ རྦ ༅ ཎྜ ྣཧྨ ➢ 130 120 110 100 90 2.0 2.8 3.6 4.4 5 Wire diameter, mm 6.0 6.8 2 7.6 8.4 Compression and extension springs. ASTM A227 Class II Light service Average service 0.020 0.060 0.100 0.140 0.180 0.220 0.260 0.300 0.340 0.380 0.420 0.460 0.500 Wire diameter, in Torsional stress due to initial tension, ksi 10 ४ 20 Preferred range 100 Stress, MPa 9.2 10.0 10.8 11.6 12.4 1100 1035 965 895 825 760 Severe service 690 620 550 50 150 3456789 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Spring index, C = DJD FIGURE 18-21 Recommended torsional shear stress in an extension spring due to initial tension (Data from Associated Spring, Barnes Group, Inc.) 50 200 485 Stress, MPaarrow_forwardBolted Joint Design Bolted Frames Total Force due to door weight: P = 240 lb Number of Bolts: N = Distance to Bolt C/L: a = 4 N/A Bolt Material - Allowable shear stress of bolt material: T₂ = x Distance from Bolt centroid to bolt: x = y Distance from Bolt centroid to bolt: y = Degrees per Radian- Results y-Load on each bolt: F, = Moment resisted by bolt pattern: M = Radial distance from Bolt centroid to bolt: r = Sum squares of all radial distances: Σr² Force on each bolt to resist moment: F, - Angle for force composition: e= X-Force on each bolt to resist moment: F- y-Force on each bolt to resist moment: Fly Total y-Force on each bolt: Fy = Resultant force on bolt 1: R₁ = Required shear stress area for a bolt: A₂ = ASTM Grade A307 Steel 10,000 0 psi from Table 20-1 3.0 57.296 in degrees lb per bolt lb-in Formula FS-P/N M-Px XB r = (x² + y²)0.5 in² Σ 4r² Mr F₁ = Στ lb degrees lb lb lb Minimum Bolt Diameter: Din = Rounded up Bolt Diameter: D = 55 P. 1.5 in 2 in (3x) 1 in This bracket…arrow_forwardUniversity of Babylon Collage of Engineering/ Al-Musayab Department of Automobiles Final Examination/ Stage: 3rd Notes: Answer 4 questions only 2023-2202 Subject: Theory of vehicles Date: 2023\06\10-Saturday Time: Three Hours Course 2nd Attempt 1st Q1: A Hooke's coupling connects two shafts whose axes are inclined at 30°. The of the driven shaft? Find the maximum value of retardation or acceleration and driving shaft rotates uniformly at 600 rpm. What are the extreme angular velocities state the angle where both will occur. (12.5 Marks) Q2: Four masses, A, B, C, and D), revolve at equal radii and are equally spaced along a shaft. The mass B is 7 kg, and the radius of C and D make angles of 90° and 240°, respectively, with the radius of B. Find the magnitude of the masses A, C, and D and the angular position of A so that the system may be completely balanced. (12.5 Marks) Q3: A cam has straight worked faces that are tangential to a base circle of diameter 90 mm. The follower is a roller…arrow_forward
- Problem 18-26 Added Extension Springs Spring Material ASTM A227 Modulus of Elasticity of the Material in Shear: G 1.150E+07 psi Average Service Max Operating Load: F₁ = 100 lb Max Length between attachment points: L₁ = 60.00 in 20.00 lb 26.00 1.400 Min Operating Load: F₁ = Min Length between attachment points: L₁ = Maximum Outside Diameter = in in Results Note: you select a wire diameter from the "US steel wire gage" column in table 18-2 Formula k = AF/AL k = (F0-F1)/(Lo - L₁) Spring Rate: k = lb/in Assumed Trial Outside Diameter: OD = Assumed Trial Mean: D ma Assumed Design Stress in Spring: Tda in 1.070 in 102,000 psi Assumed Wahl Factor: K = 1.2 Calculated Wire Diameter: Dwa Actual Wire Diameter: Dw Actual outer diameter: OD = Actual inner diameter: ID= Spring Index: C = See Figure 18-8 Dw= [8KF Dm πTd 1/3 in 5' 5' 5' 5' This corresponds to US Steel 9 wire gage ID = Dm - Dw C = Dm/Dw 4C - 1 0.615 K = + 4C - с Wahl Factor: K = 8KFDm 8KFC T = TD πD Stress in Spring at F = Fo: To psi…arrow_forwardCHAIN DRIVE DESIGN Initial Input Data: Application: Garage Door Opener Drive type: AC Motor Driven machine Chain and Sprocket to pull the door up Degrees per Radian: 57.2958 degrees Sprocket Diameter: D = 1.690 in Number of strands: Chain number: 1 40 Service factor: 1.3 Table 7-10 No. of teeth Computed Data: Actual Motor Power Input: 0.000 hp Sprocket Speed (for sprocket attached to gear shaft) Design power: 0.00 rpm 0 hp 11 12 0.06 0.15 0.29 0.56 0.99 1.09 1.61 2.64 TABLE 7-7 Horsepower Ratings-Single Strand Roller Chain No. 40 0.500 inch pitch 10 25 50 100 180 200 300 500 700 900 1000 1: 0.06 0.14 0.27 0.52 0.91 1.00 1.48 2.42 3.34 4.25 4.70 ! 3.64 4.64 5.13 13 0.07 0.16 0.31 0.61 1.07 1.19 1.75 2.86 3.95 5.02 5.56 Design Decisions-Chain Type and Teeth Numbers: 14 Chain number: Use Table 7-7 Chain pitch: p = in 15 Number of Teeth: N = Per Table 7-7 16 0.08 0.20 0.39 0.75 1.32 1.46 2.15 3.52 0.07 0.17 0.34 0.66 1.15 1.28 1.88 3.08 0.08 0.19 0.36 0.70 1.24 1.37 2.02 3.30 4.55 5.80…arrow_forwardInput Data: Torque needed to overcome rolling friction in rollers, slides and other moving parts, except for Motor and Worm Gear the worm gear T₁ = Length of travel of door: Time for door to open or close: LD = 50 lb-in. 90 in t= 12.5 seconds Pitch diameter for chain sprocket: DPC 1.690 in Weight of Door: P = No. of worm threads: Nw = Worm Pitch diameter: Dw Diametral pitch: Pd Normal pressure angle: Degrees per Radian: Number of gear teeth: Calculated Data: Linear velocity of door and chain (in/sec): Linear velocity of door and chain (ft/min): Output Speed of Gear and Sprocket: Upward Force due to Weight of Door: Фо = = NG= 240 lb 2 1.250 in 12 14.5 degrees 57.2958 degrees 28 Vα= in/sec VC= ft/min NG = rpm FD lb Net Upward Force on Door: Fou lb Torque on gear ignoring rolling friction: TG = lb-in. Formula = FDU FD-2 x Fo (note: Fo is the Max Operating load of the extension springs). This is also the initial tension in the chain. TG = FDU X DPC/2 This is the also the torque on the…arrow_forward
- Q5/A: A car with a track of 1.5 m and a wheelbase of 2.9 m has a steering gear mechanism of the Ackermann type. The distance between the front stub axle pivots is 1.3 m. The length of each track arm is 150 mm, and the length of the track rod is 1.2 m. Find the angle turned through by the outer wheel if the angle turned through by the inner wheel is 30°. (6 Marks) Q5/B: Write True on the correct sentences and False on the wrong sentences listed below:- 1- In automobiles, the power is transmitted from the gearbox to the differential through bevel gears. 2- The minimum radius circle drawn to the cam profile is called the base circle. 3- The Proell governor, compared to the Porter governor, has less lift at the same speed. 4- The balancing of rotating and reciprocating parts of an engine is necessary when it runs at a slow speed. (6.5 Marks) ***Best of Luck *** جامعة بابل UNIVERSITY OF BABYLON Examiner: Mohanad R. Hameed Head of Department: Dr. Dhyai H. Jawadarrow_forwardUniversity of Babylon Collage of Engineering/ Al-Musayab Department of Automobiles Mid Examination/ Stage: 3rd Subject: Theory of Vehicles Date: 14 \ 4 \2025 Time: 1.5 Hours 2025-2024 Q1: The arms of a Porter governor are 250 mm long. The upper arms are pivoted on the axis of revolution, but the lower arms are attached to a sleeve at a distance of 50 mm from the axis of rotation. The weight on the sleeve is 600 N and the weight of each ball is 80 N. Determine the equilibrium speed when the radius of rotation of the balls is 150 mm. If the friction is equivalent to a load of 25 N at the sleeve, determine the range of speed for this position. Q2: In a loaded Proell governor shown in Figure below each ball weighs 3 kg and the central sleeve weighs 25 kg. The arms are of 200 mm length and pivoted about axis displaced from the central axis of rotation by 38.5 mm, y=238 mm, x=303.5 mm, CE 85 mm, MD 142.5 mm. Determine the equilibrium speed. Fe mg E M 2 Q3: In a spring loaded Hartnell type…arrow_forwardusing the theorem of three moments, find all the reactions and supports, I need the calculations onlyarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Physics 33 - Fluid Statics (1 of 10) Pressure in a Fluid; Author: Michel van Biezen;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mzjlAla3H1Q;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY