Engineering Mechanics: Statics & Dynamics (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133915426
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 6.3, Problem 1PP
In each case, calculate the support reactions and then draw the free-body diagrams of joints A, B, and C of the truss.
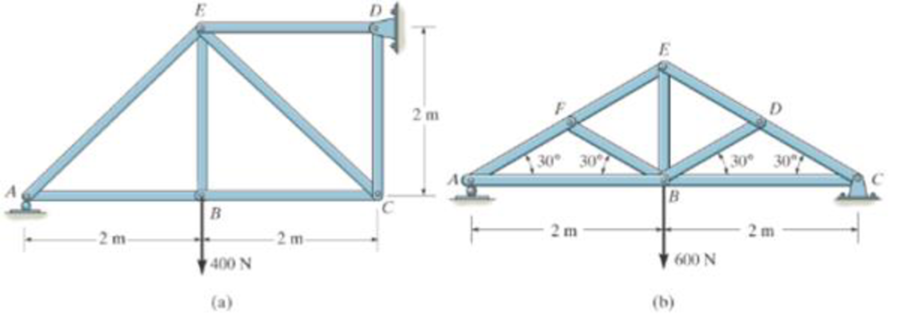
Prob. P6-1
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule08:29
Students have asked these similar questions
(read image) (answer given)
11-5. Compute all the dimensional changes for the steel bar
when subjected to the loads shown. The proportional limit of the
steel is 230 MPa.
265 kN
100 mm
600 kN
25 mm thickness
X
Z
600 kN
450 mm
E=207×103 MPa; μ= 0.25
265 kN
T₁
F
Rd = 0.2 m
md =
2 kg
T₂
Tz1
Rc = 0.4 m
mc = 5 kg
m = 3 kg
Chapter 6 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Statics & Dynamics (14th Edition)
Ch. 6.3 - In each case, calculate the support reactions and...Ch. 6.3 - Identify the zero-force members in each truss....Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss....Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss....Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss....Ch. 6.3 - Determine the greatest load P that can be applied...Ch. 6.3 - Identify the zero-force members in the truss....Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss....Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...
Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss....Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Prob. 5PCh. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss,...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Prob. 9PCh. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the Pratt...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss in...Ch. 6.3 - Members AB and BC can each support a maximum...Ch. 6.3 - Members AB and BC can each support a maximum...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss....Ch. 6.3 - If the maximum force that any member can support...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Prob. 20PCh. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the double...Ch. 6.3 - Prob. 23PCh. 6.3 - The maximum allowable tensile force in the members...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss in...Ch. 6.3 - The maximum allowable tensile force in the members...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members BC, CF, and FE....Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members LK, KC, and CD of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members KJ, KD, and CD of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members EF, CF, and BC of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members GF, GD, and CD of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members DC, HI, and JI of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members DC, HC, and HI of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members ED, EH, and GH of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members HG, HE and DE of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members CD, HI, and CH of...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 31PCh. 6.4 - Prob. 32PCh. 6.4 - Prob. 33PCh. 6.4 - Prob. 34PCh. 6.4 - Determine the force in members EF, CF, and BC, and...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members AF, BF, and BC, and...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 39PCh. 6.4 - Determine the force in members CD, CF, and CG and...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force developed in members FE, EB,...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members BC, HC, and HG....Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members CD, CJ, GJ, and CG...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members BE, EF, and CB, and...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 45PCh. 6.4 - Determine the force in members BC, CH, GH, and CG...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members CD, CJ, and KJ and...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 48PCh. 6.4 - Determine the force in members HI, FI, and EF of...Ch. 6.6 - In each case, identify any two-force members, and...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force P needed to hold the 60-lb...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - If a 100-N force is applied to the handles of the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the normal force that the 100-lb plate A...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force P needed to lift the load....Ch. 6.6 - Prob. 19FPCh. 6.6 - Prob. 20FPCh. 6.6 - Determine the components of reaction at A and C....Ch. 6.6 - Determine the components of reaction at C. Prob....Ch. 6.6 - Determine the components of reaction at E. Prob....Ch. 6.6 - Determine the components of reaction at D and the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force P required to hold the 100-lb...Ch. 6.6 - In each case, determine the force P required to...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force P required to hold the 50-kg...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force P required to hold the 150-kg...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force that the smooth rotor C exerts...Ch. 6.6 - The bridge frame consists of three segments which...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the reactions at supports A and B. Prob....Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the reactions at the supports A, C, and...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the resultant force at pins A, B, and C...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the reactions at the supports at A, E,...Ch. 6.6 - The wall crane supports a load of 700 lb....Ch. 6.6 - The wall crane supports a load of 700 lb....Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - The two-member structure is connected at C by a...Ch. 6.6 - The compound beam is pin supported at B and...Ch. 6.6 - When a force of 2 lb is applied to the handles of...Ch. 6.6 - The toggle clamp is subjected to a force F at the...Ch. 6.6 - The hoist supports the 125-kg engine. Determine...Ch. 6.6 - A 5-lb force is applied to the handles of the vise...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force in members FD and DB of the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force that the smooth 20-kg cylinder...Ch. 6.6 - Prob. 85PCh. 6.6 - The pumping unit is used to recover oil. When the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force that the jaws J of the metal...Ch. 6.6 - Prob. 88PCh. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - The pipe cutter is clamped around the pipe P. If...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force created in tire hydraulic...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - The constant moment of 50 N m is applied to the...Ch. 6.6 - Five coins are stacked in the smooth plastic...Ch. 6.6 - The nail cutter consists of the handle and the two...Ch. 6.6 - A man having a weight of 175 lb attempts to hold...Ch. 6.6 - Prob. 97PCh. 6.6 - The two member frame is pin connected at E. The...Ch. 6.6 - If the 300 kg drum has a center of mass at point...Ch. 6.6 - Operation of exhaust and intake valves in an...Ch. 6.6 - If a clamping force of 300 N is required at A,...Ch. 6.6 - If a force of F = 350 N is applied to the handle...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - The hydraulic crane is used to lift the 1400-lb...Ch. 6.6 - Determine force P on the cable if the spring is...Ch. 6.6 - Prob. 106PCh. 6.6 - If a force of F = 50 lb is applied to the pads at...Ch. 6.6 - The skid-steer loader has a mass of 1.18 Mg, and...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force P on the cable if the spring...Ch. 6.6 - The spring has an unstretched length of 0.3 m....Ch. 6.6 - The spring has an unstretched length of 0.3 m....Ch. 6.6 - The piston C moves vertically between the two...Ch. 6.6 - Prob. 113PCh. 6.6 - The platform scale consists of a combination of...Ch. 6.6 - The three pin-connected members shown in the top...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force in member GJ and GC of the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force in members GF, FB, and BC of...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the resultant forces at pins B and C on...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
F43. Determine the moment of the force about point O.
INTERNATIONAL EDITION---Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 14th edition (SI unit)
Write Java statements that create a yes-or-no dialog box to answer the question. Are you in college?
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
What is the difference between overriding a superclass method and overloading a superclass method?
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
3.3 It is known that a vertical force of 200 lb is required to remove the nail at C from the board. As the nail...
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics
What is the importance of modeling in engineering? How are the mathematical models for engineering processes pr...
HEAT+MASS TRANSFER:FUND.+APPL.
Compare and contrast the break and continue statements.
Java How to Program, Early Objects (11th Edition) (Deitel: How to Program)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2. Find a basis of solutions by the Frobenius method. Try to identify the series as expansions of known functions. (x + 2)²y" + (x + 2)y' - y = 0 ; Hint: Let: z = x+2arrow_forward1. Find a power series solution in powers of x. y" - y' + x²y = 0arrow_forward3. Find a basis of solutions by the Frobenius method. Try to identify the series as expansions of known functions. 8x2y" +10xy' + (x 1)y = 0 -arrow_forward
- Hello I was going over the solution for this probem and I'm a bit confused on the last part. Can you please explain to me 1^4 was used for the Co of the tubular cross section? Thank you!arrow_forwardBlood (HD = 0.45 in large diameter tubes) is forced through hollow fiber tubes that are 20 µm in diameter.Equating the volumetric flowrate expressions from (1) assuming marginal zone theory and (2) using an apparentviscosity for the blood, estimate the marginal zone thickness at this diameter. The viscosity of plasma is 1.2 cParrow_forwardQ2: Find the shear load on bolt A for the connection shown in Figure 2. Dimensions are in mm Fig. 2 24 0-0 0-0 A 180kN (10 Markarrow_forward
- determine the direction and magnitude of angular velocity ω3 of link CD in the four-bar linkage using the relative velocity graphical methodarrow_forwardFour-bar linkage mechanism, AB=40mm, BC=60mm, CD=70mm, AD=80mm, =60°, w1=10rad/s. Determine the direction and magnitude of w3 using relative motion graphical method. A B 2 3 77777 477777arrow_forwardFour-bar linkage mechanism, AB=40mm, BC=60mm, CD=70mm, AD=80mm, =60°, w1=10rad/s. Determine the direction and magnitude of w3 using relative motion graphical method. A B 2 3 77777 477777arrow_forward
- The evaporator of a vapor compression refrigeration cycle utilizing R-123 as the refrigerant isbeing used to chill water. The evaporator is a shell and tube heat exchanger with the water flowingthrough the tubes. The water enters the heat exchanger at a temperature of 54°F. The approachtemperature difference of the evaporator is 3°R. The evaporating pressure of the refrigeration cycleis 4.8 psia and the condensing pressure is 75 psia. The refrigerant is flowing through the cycle witha flow rate of 18,000 lbm/hr. The R-123 leaves the evaporator as a saturated vapor and leaves thecondenser as a saturated liquid. Determine the following:a. The outlet temperature of the chilled waterb. The volumetric flow rate of the chilled water (gpm)c. The UA product of the evaporator (Btu/h-°F)d. The heat transfer rate between the refrigerant and the water (tons)arrow_forward(Read image) (Answer given)arrow_forwardProblem (17): water flowing in an open channel of a rectangular cross-section with width (b) transitions from a mild slope to a steep slope (i.e., from subcritical to supercritical flow) with normal water depths of (y₁) and (y2), respectively. Given the values of y₁ [m], y₂ [m], and b [m], calculate the discharge in the channel (Q) in [Lit/s]. Givens: y1 = 4.112 m y2 = 0.387 m b = 0.942 m Answers: ( 1 ) 1880.186 lit/s ( 2 ) 4042.945 lit/s ( 3 ) 2553.11 lit/s ( 4 ) 3130.448 lit/sarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Physics 33 - Fluid Statics (1 of 10) Pressure in a Fluid; Author: Michel van Biezen;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mzjlAla3H1Q;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY