
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The missing lone pairs and curved arrows are to be interpreted for the accomplishment of the given transformation:
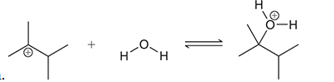
Concept introduction: One or more reactant molecules are changed into product molecules during a
The shifting of electron pairs depends on the electrophile and nucleophilic nature of the bonded atoms.
(b)
Interpretation: The missing lone pairs and curved arrows are to be interpreted for the accomplishment of the given transformation:
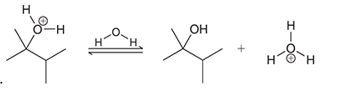
Concept introduction: One or more reactant molecules are changed into product molecules during a chemical reaction. It entails the movement of lone pairs on the connected atoms as well as bonding electrons.
The shifting of electron pairs depended on the electrophile and nucleophilic nature of the bonded atoms.
(c)
Interpretation: The missing lone pairs and curved arrows are to be interpreted for the accomplishment of the given transformation:
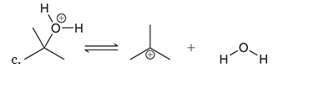
Concept introduction: One or more reactant molecules are changed into product molecules during a chemical reaction. It entails the movement of lone pairs on the connected atoms as well as bonding electrons.
The shifting of electron pairs depended on the electrophile and nucleophilic nature of the bonded atoms.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY WILEYPLUS ACCESS>I<
- What is the reaction mechanism for this?arrow_forwardWhat is the reaction mechanism for this?arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. + Drawing Arrows CH3ONA, CH3OH heat : Br:O Na → H H Br Na + H H H H H :0: .H + Undo Reset Done Q CH3 Drag To Pan +arrow_forward
- What is the reaction mechanism for this?arrow_forward20.19 Predict the structure of the major 1,2-addition product formed by reaction of one mole of Cl₂ with 3-methylenecyclohexene. Also predict the structure of the 1,4-addition product formed under these conditions. 20.20 Which of the two molecules shown do you expect to be the major product formed by 1,2-addition of HCI to cyclopentadiene? Explain. Cyclopentadiene + HC 3-Chlorocyclopentene (racemic) or 4-Chlorocyclopentene (racemic)arrow_forward20.35 Propose structural formulas for compounds A and B and specify the configuration of compound B. EtO₂C 250°C C14H2004 CO₂Et 1. Oso, then NaHSO3 2. HIO4 C14H2006 A Barrow_forward
- 20.21 Predict the major product formed by 1,4-addition of HCI to cyclopentadiene. 20.22 Draw structural formulas for the two constitutional isomers with the molecular for- mula C₂H,Br, formed by adding one mole of Br, to cyclopentadiene.arrow_forwardAdd substituents to draw the conformer below (sighting down the indicated bond), then rotate the back carbon to provide the conformation that will be capable of an E2 elimination. R/S stereochemistry is graded. + I I H CH3 Ph Досн Br OCH 3 Drawing Q H Atoms, Bonds and Rings Charges Tap a node to see suggestions. H H H H H Undo Reset Remove Done Rotatearrow_forward20.17 Predict the structure of the major product formed by 1,2-addition of HBr to 3-methylenecyclohexene. 3-Methylenecyclohexene 20.18 Predict the major product formed by 1,4-addition of HBr to 3-methylenecyclohexene.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

