
Organic Chemistry (9th Edition)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9780321971371
Author: Leroy G. Wade, Jan W. Simek
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6.1, Problem 6.1P
Classify each compound as an
- a. CH3CHCFCH3
- b. (CH3)3CBr
- c. CH3CCl3
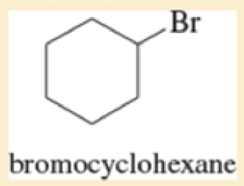
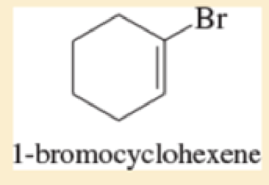
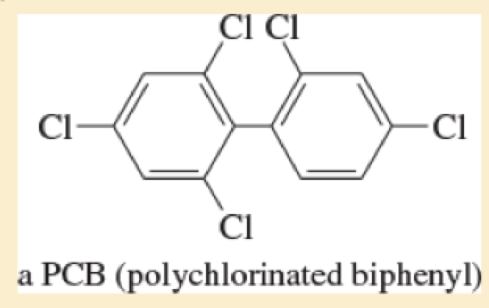
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
How to calculate % of unknown solution using line of best fit y=0.1227x + 0.0292 (y=2.244)
Given a 1,3-dicarbonyl compound, state the (condensed) formula of the compound obtaineda) if I add hydroxylamine (NH2OH) to give an isooxazole.b) if I add thiosemicarbazide (NH2-CO-NH-NH2) to give an isothiazole.
Complete the following acid-base reactions and predict the direction of equilibrium
for each. Justify your prediction by citing pK values for the acid and conjugate acid in
each equilibrium.
(a)
(b) NHs
(c)
O₂N
NH
NH
OH
H₁PO₁
Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic Chemistry (9th Edition)
Ch. 6.1 - Classify each compound as an alkyl halide, a vinyl...Ch. 6.2 - Give the structures of the following compounds. a....Ch. 6.2 - For each of the following compounds, A. give the...Ch. 6.3E - Prob. 6.4PCh. 6.4 - Prob. 6.5PCh. 6.5A - For each pair of compounds, predict which compound...Ch. 6.5B - Prob. 6.7PCh. 6.6B - Prob. 6.8PCh. 6.6B - The light-initiated reaction of...Ch. 6.6B - Show how free-radical halogenation might be used...
Ch. 6.7 - Prob. 6.11PCh. 6.7 - Prob. 6.12PCh. 6.8 - Prob. 6.13PCh. 6.9 - Predict the major products of the following...Ch. 6.9 - Prob. 6.15PCh. 6.10A - Prob. 6.16PCh. 6.11A - When diethyl ether (CH3CH2OCH2CH3) is treated with...Ch. 6.11B - Prob. 6.18PCh. 6.11B - For each pair of compounds, state which compound...Ch. 6.12 - Prob. 6.20PCh. 6.12 - Under appropriate conditions...Ch. 6.13 - Propose an SN1 mechanism for the solvolysis of...Ch. 6.13B - Prob. 6.23PCh. 6.13B - 3-Bromocyclohexene is a secondary halide, and...Ch. 6.15 - Prob. 6.25PCh. 6.15 - Prob. 6.26PCh. 6.16 - For each reaction, give the expected substitution...Ch. 6.16 - Prob. 6.28PCh. 6.16 - Prob. 6.29PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.30SPCh. 6 - Draw the structures of the following compounds. a....Ch. 6 - Give systematic (IUPAC) names for the following...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.33SPCh. 6 - Predict the compound in each pair that will...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.35SPCh. 6 - Give two syntheses for (CH3)2CHOCH2CH3, and...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.37SPCh. 6 - Prob. 6.38SPCh. 6 - Chlorocyclohexane reacts with sodium cyanide...Ch. 6 - Give the substitution products expected from...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.41SPCh. 6 - Prob. 6.42SPCh. 6 - Two of the carbocations in Problem6-42 are prone...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.44SPCh. 6 - Predict the products of the following SN2...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.46SPCh. 6 - Strawberry growers have used large quantities of...Ch. 6 - A solution of pure (S)-2-iodobutane ([]=+15.90) in...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.49SPCh. 6 - Give a mechanism to explain the two products...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.51SPCh. 6 - Because the SN1 reaction goes through a flat...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.53SPCh. 6 - Furfuryl chloride can undergo substitution by both...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.55SPCh. 6 - The following reaction takes place under...Ch. 6 - Propose mechanisms to account for the observed...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.58SPCh. 6 - Prob. 6.59SP
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Why is it necessary to be in a pressurized cabin when flying at 30,000 feet?
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Identify each of the following reproductive barriers as prezygotic or postzygotic. a. One lilac species lives o...
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Label each statement about the polynucleotide ATGGCG as true or false. The polynucleotide has six nucleotides. ...
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
Give the IUPAC name for each compound.
Organic Chemistry
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 23.34 Show how to convert each starting material into isobutylamine in good yield. ཅ ནད ཀྱི (b) Br OEt (c) (d) (e) (f) Harrow_forwardPlease help me Please use https://app.molview.com/ to draw this. I tried, but I couldn't figure out how to do it.arrow_forwardPropose a synthesis of 1-butanamine from the following: (a) a chloroalkane of three carbons (b) a chloroalkane of four carbonsarrow_forward
- Select the stronger base from each pair of compounds. (a) H₂CNH₂ or EtzN (b) CI or NH2 NH2 (c) .Q or EtzN (d) or (e) N or (f) H or Harrow_forward4. Provide a clear arrow-pushing mechanism for each of the following reactions. Do not skip proton transfers, do not combine steps, and make sure your arrows are clear enough to be interpreted without ambiguity. a. 2. 1. LDA 3. H3O+ HOarrow_forwardb. H3C CH3 H3O+ ✓ H OHarrow_forward
- 2. Provide reagents/conditions to accomplish the following syntheses. More than one step is required in some cases. a. CH3arrow_forwardIdentify and provide an explanation that distinguishes a qualitative and quantitative chemical analysis. Provide examples.arrow_forwardIdentify and provide an explanation of the operational principles behind a Atomic Absorption Spectrometer (AAS). List the steps involved.arrow_forward
- Instructions: Complete the questions in the space provided. Show all your work 1. You are trying to determine the rate law expression for a reaction that you are completing at 25°C. You measure the initial reaction rate and the starting concentrations of the reactions for 4 trials. BrO³¯ (aq) + 5Br¯ (aq) + 6H* (aq) → 3Br₂ (l) + 3H2O (l) Initial rate Trial [BrO3] [H*] [Br] (mol/L) (mol/L) | (mol/L) (mol/L.s) 1 0.10 0.10 0.10 8.0 2 0.20 0.10 0.10 16 3 0.10 0.20 0.10 16 4 0.10 0.10 0.20 32 a. Based on the above data what is the rate law expression? b. Solve for the value of k (make sure to include proper units) 2. The proposed reaction mechanism is as follows: i. ii. BrО¸¯ (aq) + H+ (aq) → HBrO3 (aq) HBrO³ (aq) + H* (aq) → H₂BrO3* (aq) iii. H₂BrO³* (aq) + Br¯ (aq) → Br₂O₂ (aq) + H2O (l) [Fast] [Medium] [Slow] iv. Br₂O₂ (aq) + 4H*(aq) + 4Br(aq) → 3Br₂ (l) + H2O (l) [Fast] Evaluate the validity of this proposed reaction. Justify your answer.arrow_forwardе. Д CH3 D*, D20arrow_forwardC. NaOMe, Br Brarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Chapter 4 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Lesson 2; Author: Linda Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AL_CM_Btef4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Chapter 4 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Lesson 1; Author: Linda Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PPIa6EHJMJw;License: Standard Youtube License