
Concept explainers
Inferring Missing Amounts Based on Income Statement Relationships
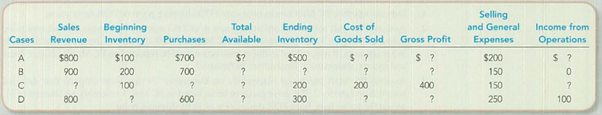
Supply the missing dollar amounts for each of the following independent cases:
Explanation of Solution
Inventory:
It refers to the current assets that a company expects to sell during the normal course of business operations, the goods that are under process to be completed for future sale, or currently used for producing goods to be sold in the market.
Beginning inventory
The balance of stock of goods in hand during the beginning of the accounting period is stated as beginning inventory.
Ending inventory:
The balance of stock of goods in hand during the end of the accounting period is stated as ending inventory.
Cost of goods sold:
Cost of goods sold indicates the costs involved for the inventory sold by the business in a specific period of time.
Following is the table for missing information:
| Case | ||||
| Particulars | (Amount in Dollars) | |||
| A | B | C | D | |
| Sales revenue | $800 | $900 | $600(9) | $800 |
| Less: Cost of Goods sold: | ||||
| Beginning inventory | $100 | $200 | $100 | $150(13) |
| Add: Purchases | $700 | $700 | $300(10) | $600 |
| Total available for sale | $800(1) | $900(5) | $400(11) | $750(14) |
| Less: Ending inventory | $500 | $150(6) | $200 | $300 |
| Total cost of goods sold | $300(2) | $750(7) | $200 | $450(15) |
| Gross profit | $500(3) | $150(8) | $400 | $350(16) |
| Less: Operating expenses | $200 | $150 | $150 | $250 |
| Income from operations | $300(4) | $0 | $250(12) | $100 |
Table (1)
Working notes:
Calculate the total value available for sale of case A.
Calculate the value of total cost of goods sold of case A.
Calculate the value of gross profit of case A.
Calculate the value of income from operations of case A.
Calculate the total value available for sale of case B.
Calculate the value of ending inventory of case B.
Calculate the value of total cost of goods sold of case B.
Calculate the value of gross profit of case B.
Calculate the sales revenue of case C.
Calculate the value of purchases of case C.
Calculate the total value available for sale of case C.
Calculate the value of income from operations of case C.
Calculate the value of beginning inventory of case D.
Calculate the total value available for sale of case D.
Calculate the value of total cost of goods sold of case D.
Calculate the value of gross profit of case D.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Fundamentals Of Financial Accounting
- Need help ! Which of the following errors will not be detected by a trial balance?A. Debiting cash instead of accounts receivableB. Recording revenue twiceC. Failing to record a transactionD. A $100 debit matched with a $100 creditarrow_forwardFinancial Accounting 3.1arrow_forwardWhich of the following errors will not be detected by a trial balance?A. Debiting cash instead of accounts receivableB. Recording revenue twiceC. Failing to record a transactionD. A $100 debit matched with a $100 creditneed helparrow_forward
- General Accounting Question 2.5arrow_forwardI will report your answer to Coursehero using chatgpt they block your account and will not give your payment!!! so don't answer with chatgpt. The accounting cycle begins with:A. Posting to the ledgerB. Journalizing transactionsC. Preparing the financial statementsD. Adjusting entriesarrow_forwardWhich of the following errors will not be detected by a trial balance?A. Debiting cash instead of accounts receivableB. Recording revenue twiceC. Failing to record a transactionD. A $100 debit matched with a $100 creditarrow_forward
- I need help The accounting cycle begins with:A. Posting to the ledgerB. Journalizing transactionsC. Preparing the financial statementsD. Adjusting entriesarrow_forwardHi This Question is Simple I want Answer step by step of this Financial Accountingarrow_forwardNeed help The accounting cycle begins with:A. Posting to the ledgerB. Journalizing transactionsC. Preparing the financial statementsD. Adjusting entriesarrow_forward
 Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning





