
Nitric acid is a chemical intermediate primarily used in the synthesis of ammonium nitrate, which is used in the manufacture of fertilizers. The acid also is important in the production of other nitrates and in the separation of metals from ores.
Nitric acid may be produced by oxidizing ammonia to nitric oxide over a platinum—rhodium catalyst, then oxidizing the nitric oxide to nitrogen dioxide in a separate unit where it is absorbed in water to form an aqueous solution of nitric acid.
The reaction sequence is as follows:
where, unless otherwise speci?ed, the species are gases. A side reaction in which ammonia is oxidized to form nitrogen and water can lower product yield:
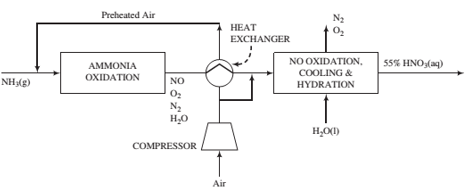
Ammonia vapor produced by vaporizng pure liquid ammonia at 820 kPa absolute is mixed with air, and the combined stream enters the ammonia oxidation unit. Air at 30°C, 1 atm absolute, and 50% relative humidity is compressed and fed to the process. A fraction of the air is sent to the cooling and hydration units, while the remainder is passed through a heat exchanger and mixed with the ammonia. The total oxygen fed to the process is the amount stoichiometrically required to convert all of the ammonia to HNO3, while the fraction sent to the ammonia oxidizer corresponds to the stoichiometric amount required to convert ammonia to NO.
The ammonia reacts completely in the oxidizer, with 97% forming NO and the rest forming N2. Only a negligible amount of NO2is formed in the oxidizer. However, the gas leaving the oxidizer is subjected to a series of cooling and hydration steps in which the NO is completely oxidized to NO2, which in turn combines with water (some of which is present in the gas from the oxidizer and the rest is added) to form a 55 wt% aqueous solution of nitric acid. The product gas from the process may be takento contain only N2and O2.
(a) Taking a basis of 100 kmol of ammonia fed to the process, calculate (i) the volumes (m3) of the ammonia vapor and air fed to the process using the compressibility-factor equation of state; (ii) the amount (kmol) and composition (in mole fractions) of the gas leaving the oxidation unit; (m) the required volume of liquid water(m3) that must be fed to the cooling and hydration units; and (iv) the fraction of the air fed to the ammonia oxidizer.
(b) Scale the results from Part (a) to a new basis of 100 metric tons per hour of 55% nitiic acid solution.
Exploratory Exercises—Research and Discover (c) Nitrogen oxides (collectively referred to as NOx) are a category of pollutants that are formed in many ways, including processes like that described in this problem. List the annual emission rates of the three largest sources of NOxemissions in your home region. What are the effects of exposure to excessive concentrations of NOx?
(d) A platinum—rhodium catalyst is used in ammonia oxidation. Explain the function of the catalyst, describe its structure, and explain the relationship of the structure to the function.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
ELEM.PRIN.OF CHEM.PROCESS-ACCESS
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Degarmo's Materials And Processes In Manufacturing
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (4th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Modern Database Management
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
- 1. (15) John had an loan plan shown in the following discrete cash flow diagram: $4,000 $6,000 GI $2,000 5 7 1 2 3 4 $3,000 $4,000 ? Years a. Please describe this diagram in terms of borrowing and payback. b. How much does John need to pay to totally payoff the loan at the end of year 8 if the interest rate is 8%? c. If John pays the sam amount of money at year 8, how much can John borrow at year 0 without paying back in between with the same interest rate?arrow_forwardA buffer solution is made by mixing 0.1 M acetic acid (HA) and 0.05 M sodium acetate (A⁻). The pKa of acetic acid is 4.76. Due to an experimental error, the actual pH was not recorded, and we need to solve for the concentration of the conjugate base (A⁻) given that the desired pH should be 4.90. Use the Bisection Method to find the concentration of A.arrow_forward1. Liquid heptane is stored in a 100,000-L storage vessel that is vented directly to air. The heptane is stored at 25°C and 1 atm pressure. The liquid is drained from the storage vessel and all that remains in the vessel is the air saturated with heptane vapor. a. Is the vapor in the storage vessel flammable? b. What is the TNT equivalent for the vapor remaining in the vessel? c. If the vapor explodes, what is the overpressure 50 m from the vessel? d. What damage can be expected at 50 m?arrow_forward
- 2. You have decided to use a vacuum purging technique to purge oxygen from a reactor vessel to reduce the concentration to 2.0% (mol). The reactor is 18 ft diameter and 40 ft tall. The temperature is 80°F. Assume that the vacuum purge goes from atmospheric pressure to 10.0 psia. How many purge cycles are required and how many total moles of nitrogen must be used? Assume the purge is done with pure nitrogen. 3. If the purging described in problem 2 takes place using nitrogen that has 1% (mol) oxygen in it, how many vacuum purge cycles are required? How many total moles of the inert gas must be used? 4. If the purging described in problem 2 is done by way of a "sweep-through" purge instead of a vacuum purge, for how long (in minutes) must the inert gas flow through the vessel if there is a 20 psig supply of pure nitrogen available at 150 CFM (ft³/min)? How much nitrogen must be used (lbm)?arrow_forward5. Look at Figure 7-14. Determine the voltage developed between the steel nozzle and the grounded vessel, and how much energy is stored in the nozzle. Explain the potential hazards for cases A and B from the following table: Case A Case B Hose length (ft) 75 75 Hose diameter (in) 2.0 2.0 Flow rate (gpm) 30 30 Liquid conductivity (mho/cm) 2x10-8 1x10-14 Dielectric constant 2.3 25 Density (g/cm³) 0.8 0.9 6. In Problem 5, case B, what would be the most effective way to reduce the potential hazards in this situation?arrow_forward2. You have decided to use a vacuum purging technique to purge oxygen from a reactor vessel to reduce the concentration to 2.0% (mol). The reactor is 18 ft diameter and 40 ft tall. The temperature is 80°F. Assume that the vacuum purge goes from atmospheric pressure to 10.0 psia. How many purge cycles are required and how many total moles of nitrogen must be used? Assume the purge is done with pure nitrogen.arrow_forward
- An 8-foot ion exchange bed needs to be backwashed with water to remove impurities. The particles have a density of 1.24 g/cm³ and an average size of 1.1 mm. Calculate: a. The minimum fluidization velocity using water at 30°C? b. The velocity required to expand the bed by 30%? Assumptions: The ion exchange bed particles are spherical (sphericity = 1.1), and the minimum fluidization porosity (ɛM) is 0.3. Notes: At 30°C, the viscosity (μ) of water is 0.797 cP, and the density (ρ) is 0.995 g/cm³.arrow_forwardfluidized bed reactor uses a solid catalyst with a particle diameter of 0.25 mm, a bulk density of 1.50 g/mL, and a sphericity of 0.90. Under packed bed conditions, the porosity is 0.35, and the bed height is 2 m. The gas enters from the bottom of the reactor at a temperature of 600°C, with a viscosity of 0.025 cP and a density of 0.22 lb/ft³. At minimum fluidization, the porosity reaches 0.45. Calculate: a. The minimum superficial velocity (VM) of the gas entering the fluidized column. b. The bed height if V = 2 VM c. The pressure drop under conditions where V =2.5 VMarrow_forwardA fluidized bed reactor uses a solid catalyst with a particle diameter of 0.25 mm, a bulk density of 1.50 g/mL, and a sphericity of 0.90. Under packed bed conditions, the porosity is 0.35, and the bed height is 2 m. The gas enters from the bottom of the reactor at a temperature of 600°C, with a viscosity of 0.025 cP and a density of 0.22 lb/ft³. At minimum fluidization, the porosity reaches 0.45. Calculate: a. The minimum superficial velocity (VM) of the gas entering the fluidized column. b. The bed height if V = 2 VM c. The pressure drop under conditions where V =2.5 VMarrow_forward
- Please answer 5.8arrow_forwardPlease answer 5.6arrow_forwardYou have been tasked with figuring out how to suppress changes in the supply flow rate to a reactorfor which it is desired to keep the inlet flow rate as constant as possible. You are considering designing a surgetank to place upstream of the reactor and then installing a pump on the line between that surge tank and thereactor. A surge tank is one with a weir inside it, which is a partial wall separating the tank volume into twoconnected sections allowing for flow under the weir between the two sections. The variable inlet mass flow,wi(t) flows into volume 1 and then flows due to hydrostatic pressure at a mass flow rate of w1(t) into volume 2.The weir causes a flow resistance, R1, such that w1 = (h1-h2)/R1. Fluid is then pumped out of volume 2 at thedesired constant mass flow rate of w2. Make a summary table of the three transfer functions written in standard form and their keyparameters (gains, time constants) in terms of the physical system parameters (A1, A2, , A, R…). Checkif/how…arrow_forward
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The





