
(a)
Interpretation:
The products for the given proton transfer reaction are to be drawn and the favored equilibrium side with numerical factor is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The proton transfer reactions favor the side opposite the stronger acid. Larger the
Answer to Problem 6.41P
The products for the given reaction are:

The equilibrium is favored to product side by a factor of
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
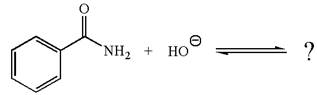
The ion

In the conjugate base formed, the negative charge on nitrogen is delocalized through the electron withdrawing resonance effect of carbonyl group. Thus, amide is a stronger acid than water, and hence, the equilibrium is favored to the product side.
The
The favored equilibrium side with numerical value is determined on the basis of stronger acid and
(b)
Interpretation:
The products for the given proton transfer reaction are to be drawn and the favored equilibrium side with the numerical factor is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The proton transfer reactions favor the side opposite the stronger acid. Larger the
Answer to Problem 6.41P
The products for the given reaction are:
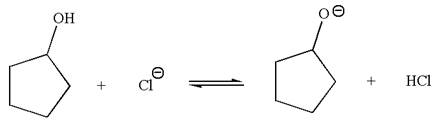
The equilibrium is favored to the reactant side by a factor of
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
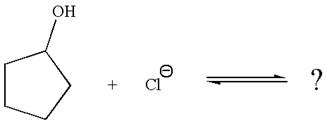
In the given reaction,
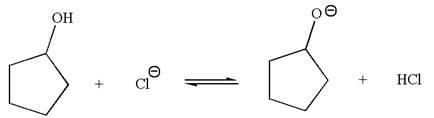
The favored equilibrium side with numerical value is determined on the basis of the stronger acid and
(c)
Interpretation:
The products for the given proton transfer reaction are to be drawn and the favored equilibrium side with numerical factor is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The proton transfer reactions favor the side opposite the stronger acid. Larger the
Answer to Problem 6.41P
The products for the given reaction are:
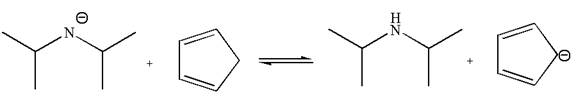
The equilibrium is favored to product side by a factor of
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
In the given reaction, cyclopentadiene acts as an acid and the negatively charge nitrogen abstracts a proton from diisopropylamine to give the following products:
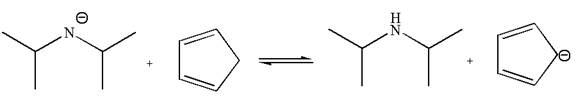
On the product side, the negative charge on carbon is a resonance stabilized by a conjugated double bond; such stabilization of the negative charge is not possible on the reactant side where the negative charge is on nitrogen bonded to two electron donating isopropyl groups. The acid is stronger when its conjugate base is stable, therefore, cyclopentadiene is a stronger acid than
According to Appendix
The favored equilibrium side with numerical value is determined on the basis of stronger acid and
(d)
Interpretation:
The products for the given proton transfer reaction are to be drawn and the favored equilibrium side with numerical factor is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The proton transfer reactions favor the side opposite the stronger acid. Larger the
Answer to Problem 6.41P
The products for the given reaction are:

The equilibrium is favored to the product side by a factor of
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
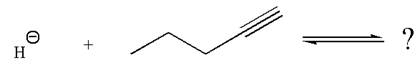
In the given reaction, the hydride ion abstracts the terminal proton of an

As the effective electronegativity of
According to Appendix
The favored equilibrium side with numerical value is determined on the basis of stronger acid and
(e)
Interpretation:
The products for the given proton transfer reaction are to be drawn and the favored equilibrium side with numerical factor is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The proton transfer reactions favor the side opposite the stronger acid. Larger the
Answer to Problem 6.41P
The products for the given reaction are:

The equilibrium is favored to the product side by a factor of
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
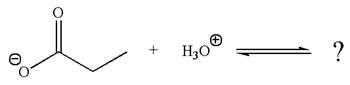
In the given reaction, the propanoate ion abstracts the proton of hydronium ion to give the following products:

According to Appendix
The favored equilibrium side with numerical value is determined on the basis of stronger acid and
(f)
Interpretation:
The products for the given proton transfer reaction are to be drawn and the favored equilibrium side with numerical factor is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The proton transfer reactions favor the side opposite the stronger acid. Larger the
Answer to Problem 6.41P
The products for the given reaction are:

The equilibrium is favored to the product side. Benzene is the weaker acid by a factor of
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
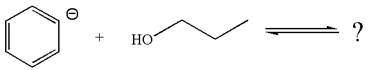
In the given reaction, the

As the oxygen atom is more electronegative than carbon, the negative charge on oxygen is more stable as compared to carbon. Thus, an anion on the right side, having negative charge on oxygen, is more stable than the anion on the left side where the negative charge is on carbon. Therefore, propanol is more acidic than benzene, and hence, the reaction is favored to the product side.
According to Appendix
The favored equilibrium side with numerical value is determined on the basis of stronger acid and the
(g)
Interpretation:
The products for the given proton transfer reaction are to be drawn and the favored equilibrium side with numerical factor is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The proton transfer reactions favor the side opposite the stronger acid. Larger the
Answer to Problem 6.41P
The products for the given reaction are:

The equilibrium is favored to the product side. Benzene is the weaker acid by a factor of
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
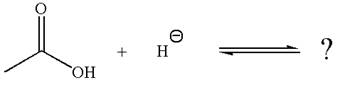
In the given reaction, the hydride ion abstracts the proton from carboxylic acid and gives the following products:

The conjugate base formed with a negative charge on the oxygen atom is better stabilized by the resonance effect. This makes the carboxylic acid the stronger acid, and the equilibrium is favored to the product side.
According to Appendix
The favored equilibrium side with numerical value is determined on the basis of stronger acid and the
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY PRINCIPLES & MECHANISM
- draw the enolate anion and the carbonyl that would be needed to make this product through an aldol addition reaction.arrow_forwardDraw the Michael Adduct and the final product of the Robinson annulation reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts.arrow_forwardDraw the Michael adduct and final product of the Robinson annulation reaction. Ignore inorganic byproductsarrow_forward
- Post Lab Questions. 1) Draw the mechanism of your Diels-Alder cycloaddition. 2) Only one isomer of product is formed in the Diels-Alder cycloaddition. Why? 3) Imagine that you used isoprene as diene - in that case you don't have to worry about assigning endo vs exo. Draw the "endo" and "exo" products of the Diels-Alder reaction between isoprene and maleic anhydride, and explain why the distinction is irrelevant here. 4) This does not hold for other dienes. Draw the exo and endo products of the reaction of cyclohexadiene with maleic anhydride. Make sure you label your answers properly as endo or exo. 100 °C Xylenes ??? 5) Calculate the process mass intensity for your specific reaction (make sure to use your actual amounts of reagent).arrow_forwardIndicate the product(s) A, B C and D that are formed in the reaction: H + NH-NH-CH [A+B] [C+D] hydrazonesarrow_forwardHow can you prepare a 6 mL solution of 6% H2O2, if we have a bottle of 30% H2O2?arrow_forward
- How many mL of H2O2 from the 30% bottle must be collected to prepare 6 mL of 6% H2O2.arrow_forwardIndicate the product(s) B and C that are formed in the reaction: HN' OCH HC1 B + mayoritario C minoritario OCH3arrow_forwardIndicate the product(s) that are formed in the reaction: NH-NH, OCH3 -H₂O OCH3arrow_forward
- 21.38 Arrange the molecules in each set in order of increasing acidity (from least acidic to most acidic). OH OH SH NH2 8 NH3 OH (b) OH OH OH (c) & & & CH3 NO2 21.39 Explain the trends in the acidity of phenol and the monofluoro derivatives of phenol. OH OH OH OH PK 10.0 PK 8.81 PK 9.28 PK 9.81arrow_forwardidentify which spectrum is for acetaminophen and which is for phenacetinarrow_forwardThe Concept of Aromaticity 21.15 State the number of 2p orbital electrons in each molecule or ion. (a) (b) (e) (f) (c) (d) (h) (i) DA (k) 21.16 Which of the molecules and ions given in Problem 21.15 are aromatic according to the Hückel criteria? Which, if planar, would be antiaromatic? 21.17 Which of the following structures are considered aromatic according to the Hückel criteria? ---0-0 (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (h) H -H .8.0- 21.18 Which of the molecules and ions from Problem 21.17 have electrons donated by a heteroatom?arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

