
Analyze and compare Costco, Wal-Mart, and Nordstrom
The general merchandise retail industry has a number of segments represented by the following companies:
| Company Name | Merchandise Concept |
| Costco Wholesale Corporation (COST) | Membership warehouse |
| Wal-Mart Stores, Inc. (WMT) | Discount general merchandise |
| Nordstrom, Inc. (JWN) | Fashion department store |
For a recent war, the following cost of goods sold and beginning and ending inventories are provided from corporate annual reports (in millions) for these three companies:
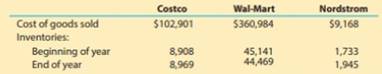
- a. Determine the inventory turnover ratio for all three companies. Round all calculations to one decimal place.
- b. Determine the number of days’ sales in inventory for all three companies. Use 365 days and round all calculations to one decimal place.
- c.
 Interpret these results based on each company’s merchandising concept.
Interpret these results based on each company’s merchandising concept.
(a)
Inventory turnover ratio: Inventory turnover ratio is used to determine the number of times inventory used or sold during the particular accounting period. The formula to calculate the inventory turnover ratio is as follows:
To determine: the inventory turnover for Company C, Company W and Company N
Answer to Problem 6.3MAD
Explanation of Solution
The inventory turnover ratio for Company C is calculated as follows:
Working notes:
The average inventory is calculated as follows:
The inventory turnover ratio for Company W is calculated as follows:
Working notes:
The average inventory is calculated as follows:
The inventory turnover ratio for Company N is calculated as follows:
Working notes:
The average inventory is calculated as follows:
The inventory turnover of Company C is 11.5 Times, the inventory turnover of Company W is 8 Times and the inventory turnover of Company N is 5 Times.
(b)
Days’ sales in inventory: Days’ sales in inventory are used to determine number of days a particular company takes to make sales of the inventory available with them. The formula to calculate the days’ sales in inventory ratio is as follows:
To determine: the Days’ sales in inventory ratio for Company C, Company W and Company N.
Answer to Problem 6.3MAD
Explanation of Solution
The Days’ sale in inventory ratio for Company C is calculated as follows:
The Days’ sale in inventory ratio for Company W is calculated as follows:
The Days’ sale in inventory ratio for Company N is calculated as follows:
The Days’ sales in inventory of Company C is 31.7 days, the Days’ sales in inventory of Company W is 45.6 days, & the Days’ sales in inventory of Company N is 73 days.
(c)
Inventory turnover ratio: Inventory turnover ratio is used to determine the number of times inventory used or sold during the particular accounting period. The formula to calculate the inventory turnover ratio is as follows:
Days’ sales in inventory: Days’ sales in inventory are used to determine number of days a particular company takes to make sales of the inventory available with them. The formula to calculate the days’ sales in inventory ratio is as follows:
To interpret: the above calculated ratios.
Explanation of Solution
The inventory turnover ratio and number of days’ sales in inventory of all the three companies reflect the merchandising approaches of all companies. Company C is a club warehouse and it has approach of holding only items which are quickly sold. Most of the items are sold in bulk at very attractive prices.
In case of company W, it has a traditional discounter approach. Even though it has attractive pricing, the inventory movement is slower than in the case of company C.
In the case of company N, it is a high-end fashioner retailer. It offers a wide collection of specialty and unique goods that are specifically designed for fashion market rather than for general mass market. Therefore, the movement is slower than other two companies yet it has highest margin.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Corporate Financial Accounting
- Which of the following is an intangible asset? A) InventoryB) CopyrightC) EquipmentD) Accounts Receivableno aiarrow_forwardWhich of the following is an intangible asset? A) InventoryB) CopyrightC) EquipmentD) Accounts Receivablearrow_forwardWhat does a ledger account represent? A) A detailed record of all business transactionsB) A summary of trial balancesC) An individual record for each accountD) The final balance of a financial statement Need help!arrow_forward
- What is the primary purpose of accounting? A) To generate tax revenueB) To record, summarize, and report financial transactionsC) To determine the market value of assetsD) To manage payrollarrow_forwardWhat are the three main financial statements in accounting?arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting question with accurate accounting calculations?arrow_forward
 Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning





