
What is the fundamental concept of Fourier theory?
To discuss: The fundamental concept of the Fourier theory.
Explanation of Solution
According to the Fundamental concept of the Fourier theory, all signals are the summation of the different sinusoidal signal which are of the different amplitude, frequencies and the phase.
The representation of the signal:
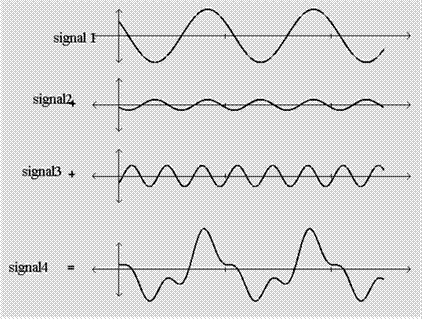
Referring to the above diagram, the signal 4 is the sum of the signal 2 and signal 3.
Whereas the signal 2 and signal 3 are the sinusoidal signal of the different amplitude and the different frequency.
Therefore, the signal 4 is the example of the Fourier theory.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Mastering Engineering with Pearson eText -- Standalone Access Card -- for Electrical Engineering: Principles & Applications
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
Starting Out With Visual Basic (8th Edition)
Java How to Program, Early Objects (11th Edition) (Deitel: How to Program)
Modern Database Management
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
- Please solve it by explaining the steps. I am trying to prepare for my exam tomorrow, so any tips and tricks to solve similar problems are highly appreciated. Plus, this is a past exam I am using to prepare.arrow_forwardPlease solve it by explaining the steps. I am trying to prepare for my exam today, so any tips and tricks to solve similar problems are highly appreciated. Plus, this is a past exam I am using to prepare.arrow_forwardIf C is the circle |z|=4 evaluate f f (z)dz for each of the following functions using residue. 1 f(z) = z(z²+6z+4)arrow_forward
- If C is the circle |z|=4 evaluate ff(z)dz for each of the following functions using residue. f(z) z(z²+6z+4)arrow_forwardDetermine X(w) for the given function shown in Figure (1) by applying the differentiation property of the Fourier Transform. 1 x(t) Figure (1) -2 I -1 1 2arrow_forwardPlease solve it by explaining the steps. I am trying to prepare for my exam tomorrow, so any tips and tricks to solve similar problems are highly appreciated. Plus, this is a past exam I am using to prepare.arrow_forward
- Please solve it by explaining the steps. I am trying to prepare for my exam tomorrow, so any tips and tricks to solve similar problems are highly appreciated. Plus, this is a past exam I am using to prepare.arrow_forwardPlease solve it by explaining the steps. I am trying to prepare for my exam tomorrow, so any tips and tricks to solve similar problems are highly appreciated. Plus, this is a past exam I am using to prepare.arrow_forwardPlease solve it by explaining the steps. I am trying to prepare for my exam tomorrow, so any tips and tricks to solve similar problems are highly appreciated. Plus, this is a past exam I am using to prepare.arrow_forward
- Please solve it by explaining the steps. I am trying to prepare for my exam tomorrow, so any tips and tricks to solve similar problems are highly appreciated. Plus, this is a past exam I am using to prepare.arrow_forwardPlease solve it by explaining the steps. I am trying to prepare for my exam tomorrow, so any tips and tricks to solve similar problems are highly appreciated. Plus, this is a past exam I am using to prepare.arrow_forwardPlease solve it by explaining the steps. I am trying to prepare for my exam tomorrow, so any tips and tricks to solve similar problems are highly appreciated. Plus, this is a past exam I am using to prepare.arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





