
Concept explainers
Calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold for four Inventory methods (LO6–3)
PROBLEMS: SET A
Sandra’s Purse Boutique has the following transactions related to its top-selling Cued purse for the month of October.
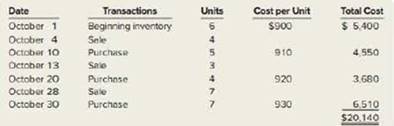
Required:
1 Calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at October 31, using the specific identification method. The October 4 sale consists of purses from beginning inventory, the October 13 sale consists of one purse from beginning inventory and two purses from the October 10 purchase, and the October 28 sale consists of three purses from the October 10 purchase and four purses from the October 20 purchase.
2. Using FIFO, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at October 31.
3. Using LIFO, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at October 31.
4. Using weighted-average cast, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at October 31.
Calculate coding inventory, cost of goods
1.
To Compute: The ending inventory and cost of goods sold using the specific identification method.
Explanation of Solution
Specific identification method:
Specific identification method is a method in which the company records each item of the inventory at its original cost. Under this method, when the goods are sold, the company can easily identify the original costs at which they were purchased for. This method helps in arriving at the accurate cost of goods sold, and ending inventory.
Calculate the units of ending inventory.
| Calculation of Ending Inventory | |||
| Details | Number of Units | Rate Per Unit ($) | Total Cost ($) |
| Beginning balance | 6 | ||
| Less: Sales - October 4 | (4) | ||
| Balance | 2 | ||
| Less: Sales - October 13 | (1) | ||
| Balance | 1 | 900 | 900 |
| Purchases: | |||
| October 10 | 5 | ||
| Less: Sales - October 13 | (2) | ||
| Less: Sales - October 28 | (3) | ||
| Balance | 0 | 910 | 0 |
| Purchases: | |||
| October 20 | 4 | ||
| Less: October 28 | (4) | - | |
| Balance | 0 | 920 | - |
| October 30 | 7 | 930 | 6,510 |
| Ending Inventory | 7,410 | ||
Table (1)
Therefore, the cost of Ending Inventory in specific identification method is $7,410.
Calculate the cost of goods sold:
| Calculation of Cost of Goods Sold | |||
| Details | Number of Units | Rate Per Unit ($) | Total Cost ($) |
| October 1: Beginning balance | 4 | 900 | 3,600 |
| October 1: Beginning balance | 1 | 900 | 900 |
| October 10: Purchase | 2 | 910 | 1,820 |
| October 10: Purchase | 3 | 910 | 2,730 |
| October 20: Purchase | 4 | 920 | 3,680 |
| March 22 Purchase | 4 | 920 | 3,680 |
| Cost of Goods Sold | 14 | 12,730 | |
Table (2)
Therefore, the Cost of Goods Sold in specific identification method is $12,730.
2.
To Compute: The ending inventory and cost of goods sold using the FIFO method.
Explanation of Solution
First-in-First-Out:
In First-in-First-Out method, the costs of the initially purchased items are considered as cost of goods sold, for the items which are sold first. The value of the ending inventory consists of the recent purchased items.
Calculate the total Cost and units of Goods Available for Sales.
| Calculation of Goods Available for Sales | |||
| Details | Number of Units | Rate per unit ($) | Total Cost ($) |
| Beginning balance | 6 | 900 | 5,400 |
| Add: Purchases | |||
| October 10 | 5 | 910 | 4,550 |
| October 20 | 4 | 920 | 3,680 |
| October 30 | 7 | 930 | 6,510 |
| Total Goods available for Sale | 22 | 20,140 | |
Table (3)
Calculate the units of ending inventory.
| Calculation of Ending Inventory (Units) | ||
| Details | Number of Units | Number of Units |
| Beginning balance | 6 | |
| Add: Purchases | ||
| October 10 | 5 | |
| October 20 | 4 | |
| October 30 | 7 | |
| Total Goods available for Sale | 22 | |
| Less: Sales | ||
| October 4 | 4 | |
| October 13 | 3 | |
| October 28 | 7 | |
| Total Sales | (14) | |
| Ending Inventory | 8 | |
Table (4)
Calculate the cost of ending inventory.
The ending inventory is 8 units.
| Calculation of Cost of Ending Inventory | |||
| Details | Number of Units | Rate per Unit ($) | Total Cost ($) |
| October 20 | 1 | 920 | 920 |
| October 30 | 7 | 930 | 6,510 |
| Ending Inventory | 8 | 7,430 | |
Table (5)
In FIFO method the ending inventory comprises of the inventory purchased last, because the inventory purchased first were sold first.
Therefore, the cost of Ending Inventory in the FIFO is $7,430.
Cost of Goods Sold.
14 units are sold.
| Calculation of Cost of Goods Sold | |||
| Details | Number of Units | Rate per Unit ($) | Total Cost ($) |
| Beginning Inventory | 6 | 900 | 5,400 |
| March 9 Purchase | 5 | 910 | 4,550 |
| March 22 Purchase | 3 | 920 | 2,760 |
| Cost of Goods Sold | 14 | 12,710 | |
Table (6)
As it is FIFO method the earlier purchased items will sell first.
Therefore, the Cost of Goods Sold in the FIFO Method is $12,710
3.
To Compute: The ending inventory and cost of goods sold using the LIFO method.
Explanation of Solution
Last-in-Last-Out:
In Last-in-First-Out method, the costs of last purchased items are considered as the cost of goods sold, for the items which are sold first. The value of the closing stock consists of the initial purchased items.
Ending Inventory:
Calculate the cost of ending inventory.
| Calculation of Cost of Ending Inventory | |||
| Details | Number of Units | Rate per Unit ($) | Total Cost ($) |
| Beginning Inventory | 6 | 900 | 5,400 |
| Ending Inventory | 6 | 900 | 5,400 |
Table (7)
- The ending inventory is 8 units (Refer to Table 4).
- In LIFO method, the ending inventory comprises of the inventory purchased first, because the inventory purchased last were sold first.
- Therefore, the ending inventory of 8 units is from the beginning inventory.
Therefore, the cost of Ending Inventory in the LIFO method is $5,400.
Cost of Goods Sold:
| Details | Number of Units | Rate per unit ($) | Total Cost ($) |
| October10 Purchase | 3 | 910 | 2,730 |
| October20 Purchase | 4 | 920 | 3,680 |
| October30 Purchase | 7 | 930 | 6,510 |
| Cost of Goods Sold |
14 | 2,760 |
12,920 |
Table (8)
- 8 units are sold (Refer to Table 4).
- As it is LIFO method the recent purchased items will sell first.
- Hence, the cost of goods sold will be the recent purchased items.
Therefore, the Cost of Goods Sold in the LIFO Method is $12,920.
4.
To Compute: The ending inventory and cost of goods sold using the Weighted-average method.
Explanation of Solution
Weighted-average cost method:
Under Weighted average cost method, the company calculates a new average cost after every purchase is made. It is determined by dividing the cost of goods available for sale by the units on hand.
Calculate the Weighted-average cost.
Total cost of goods available for sale = $20,140 (Refer to table - 3)
Total units of goods available for sale = 22 units (Refer to table - 3)
Calculate the amount of Ending Inventory.
Weighted- average cost per unit = $915.45 (1)
Number of units in ending inventory = 22 units (Refer to table - 4)
Therefore, the cost of Ending Inventory in the Weighted-average-cost Method is $7,323.6.
Calculate the Cost of Goods Sold.
Weighted- average cost per unit= $915.45 (1)
Units sold = 14 units
Therefore, the Cost of goods sold in the Weighted-average-cost Method is $12,816.30.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Financial Accounting
- I need help with this general accounting question using standard accounting techniques.arrow_forwardCan you help me solve this general accounting problem using the correct accounting process?arrow_forwardCan you help me solve this general accounting question using the correct accounting procedures?arrow_forward
- Can you help me solve this general accounting problem using the correct accounting process?arrow_forwardI am searching for the correct answer to this general accounting problem with proper accounting rules.arrow_forwardI need help with this general accounting question using the proper accounting approach.arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning


