
Predict the organic product(s) of the reaction of 2-butene with each reagent.
- (a) H2O (H2SO4)
- (b) Br2
- (c) Cl2
- (d) Br2 in H2O
- (e) HI
- (f) Cl2 in H2O
- (g) Hg(OAc)2, H2O
- (h) product (g) 1 NaBH4
(a)
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction has to be predicted.
Concept interpretation:
Carbocation: carbon atom bears positive charged species with three bonds is called Carbocation and it plays vital intermediate in organic synthesis. Carbocation migratory aptitude is mainly depends on the stability of the carbocation. This type of carbocation undergoes inter or intra molecule reactions and it form more stable product this type of rearrangement called carbocation rearrangement.
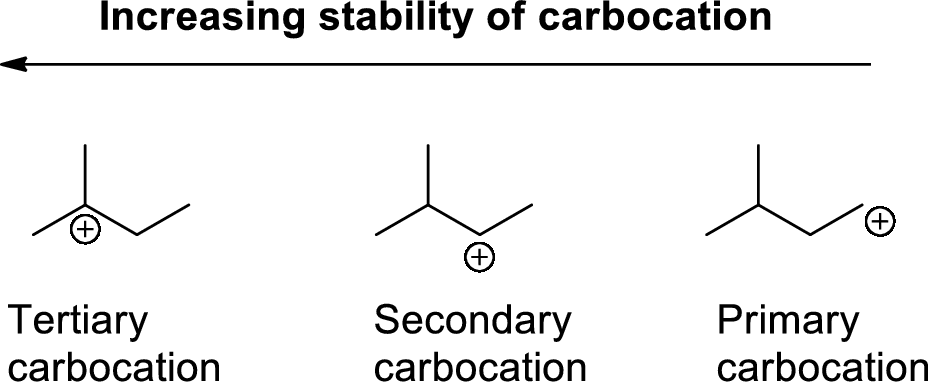
Carbocation’s are classified in to three types as primary, secondary and tertiary depending on the number of carbon atoms which is attached to the ionized carbon.
Tertiary carbocation is more stable than secondary carbocation, secondary carbocation is more stable than the primary carbocation as shown below.
Hydration:
When alkene is undergoes hydration with water in the presence of sulfuric acid which yields the alcohol. In this reaction, the water molecule will behave like a hydrogen halide to the alkene which gives the addition product this reaction is known as a hydration reaction.
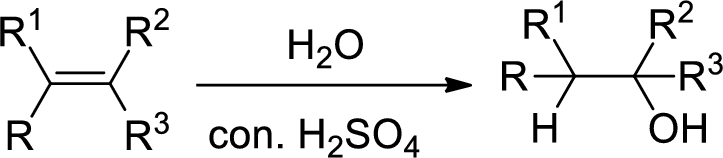
Alkene is reaction with water in the presence of sulfuric acid, first step is proton (
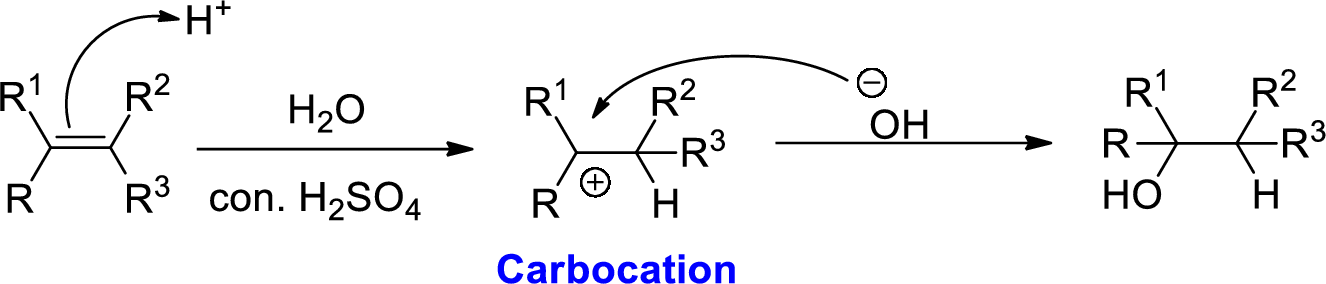
In hydration reaction, sulfuric acid is act as a proton donor, which is the driving force of the reaction. Hydration reaction will not go without acid (sulfuric acid).
Explanation of Solution
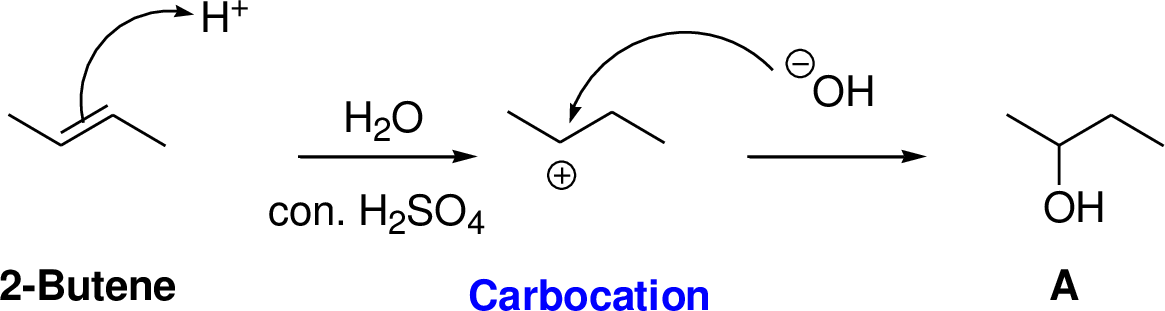
2-Butene reacts with water in the presence of sulfuric acid, first step is proton (
(b)
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction has to be predicted.
Concept interpretation:
Bromination of alkenes:
Alkene undergoes bromination which yields the dibromo compound (vicinal dibromides or 1,2-dibromides).
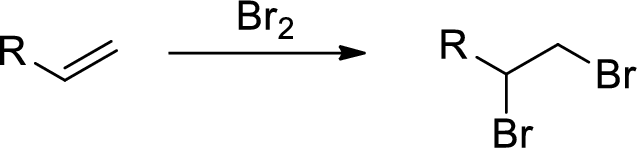
Explanation of Solution
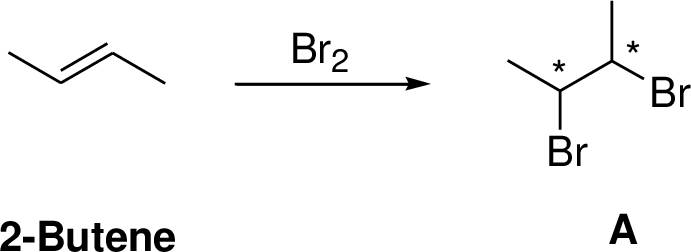
2-Butene undergoes bromination which yields the dibromo compound (B, vicinal dibromides or 1,2-dibromides). The addition product is a chiral molecule, it has two chiral center. Three stereoisomers are possible namely meso compound and stereoisomer.
The reaction is shown below,
(c)
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction has to be predicted.
Concept interpretation:
Chlorination of alkenes:
Alkene undergoes chlorination which yields the dichoro compound (vicinal dichlorides or 1,2-dichlorides).
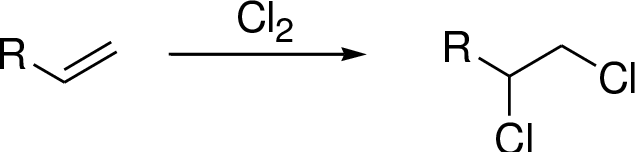
Explanation of Solution
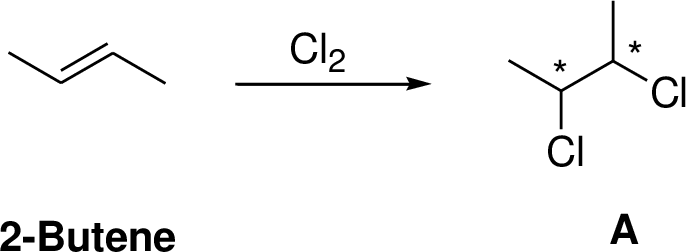
2-Butene undergoes chlorination which yields the dichoro compound (A, vicinal dichlorides or 1,2-dichlorides). The addition product is a chiral molecule, it has two chiral center. Three stereoisomers are possible namely meso compound and stereoisomer.
The reaction is shown below,
(d)
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction has to be predicted.
Concept interpretation:
Alkenes reaction with halogens (bromine, chlorine) in the presence of water which gives three membered ring intermediate, this three membered ring intermediate is highly reactive and it is reaction with hydroxide ion which produces chloro hydrine or bromo hydrine derivative.
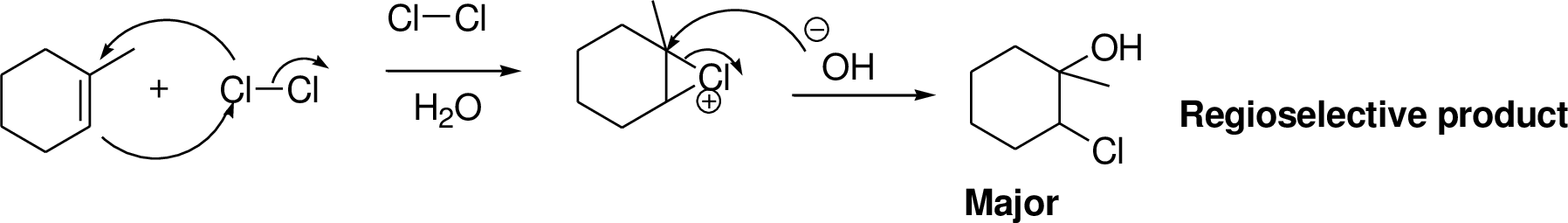
Explanation of Solution
2-Butene reacts with bromine in the presence of water which gives three membered ring intermediate, this three membered ring intermediate is highly reactive and it is reaction with hydroxide ion (from water) which produces bromo hydrine derivative. The reaction is shown below,
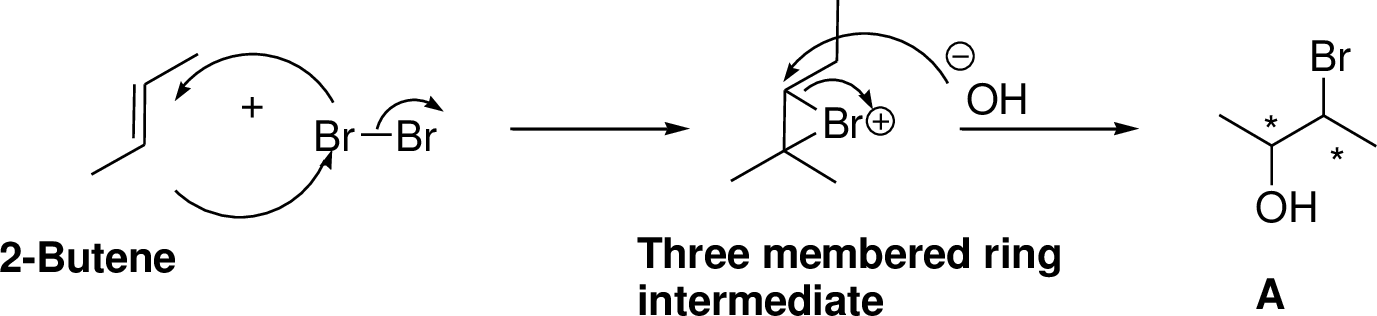
(e)
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction has to be predicted.
Concept interpretation:
Carbocation: carbon atom bears positive charged species with three bonds is called Carbocation and it plays vital intermediate in organic synthesis. Carbocation migratory aptitude is mainly depends on the stability of the carbocation. This type of carbocation undergoes inter or intra molecule reactions and it form more stable product this type of rearrangement called carbocation rearrangement.
Carbocation’s are classified in to three types as primary, secondary and tertiary depending on the number of carbon atoms which is attached to the ionized carbon.
Tertiary carbocation is more stable than secondary carbocation, secondary carbocation is more stable than the primary carbocation as shown below.
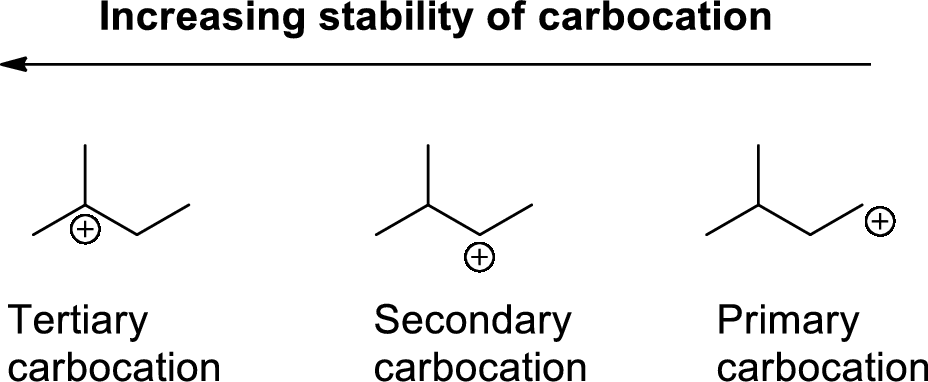
Markovnikov’s rule: unsymmetrical alkene reacts with hydrogen halide, halide ions goes to the more substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond which provides alkyl halides.
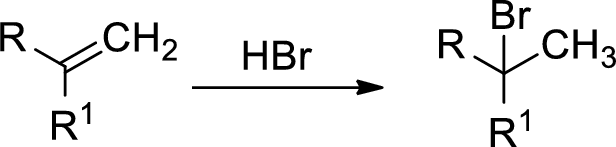
Explanation of Solution
The 2-butene reacts with hydrogen iodide forms carbocation intermediate, then iodine ion reacts with carbocation yields addition product B. Tertiary carbocation is more stable than secondary carbocation, secondary carbocation is more stable than the primary carbocation.
The addition product is a chiral molecule, it has one chiral center. The reaction is shown below,
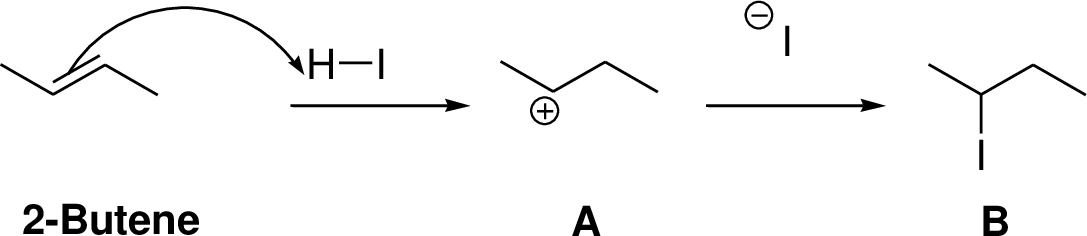
(f)
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction has to be predicted.
Concept interpretation:
Alkenes reaction with halogens (bromine, chlorine) in the presence of water which gives three membered ring intermediate, this three membered ring intermediate is highly reactive and it is reaction with hydroxide ion which produces chloro hydrine or bromo hydrine derivative.
Explanation of Solution
2-Butene reacts with chlorine in the presence of water which gives three membered ring intermediate, this three membered ring intermediate is highly reactive and it is reaction with hydroxide ion (from water) which produces chloro hydrine derivative. The reaction is shown below,
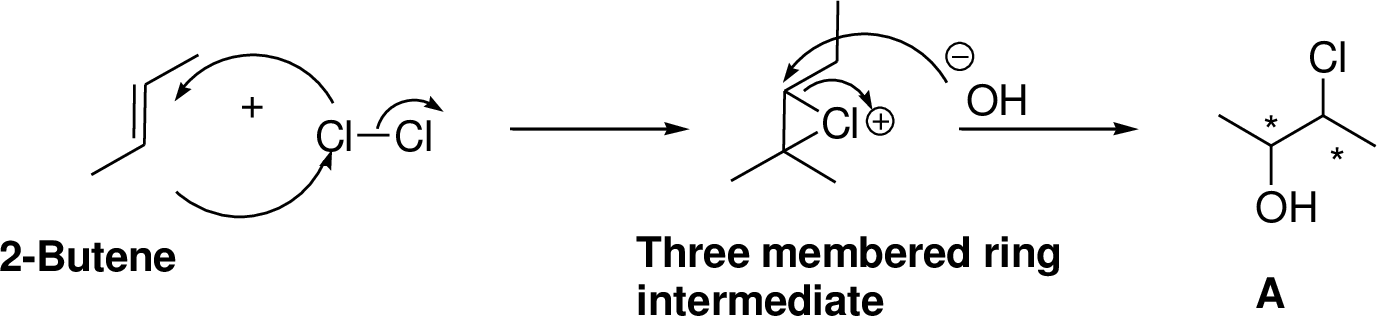
(g)
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction has to be predicted.
Concept interpretation:
Oxymercuration:
Alkenes reaction with mercuric acetate in the presence of water, the
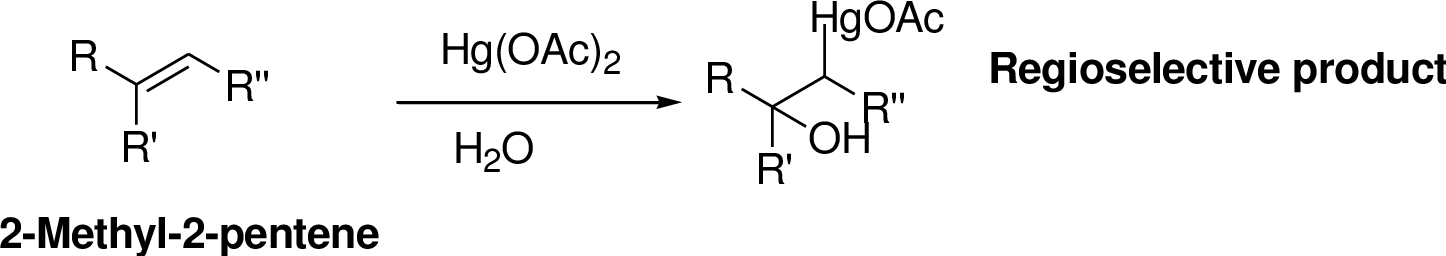
Explanation of Solution
2-Butene reacts reaction with mercuric acetate in the presence of water, the
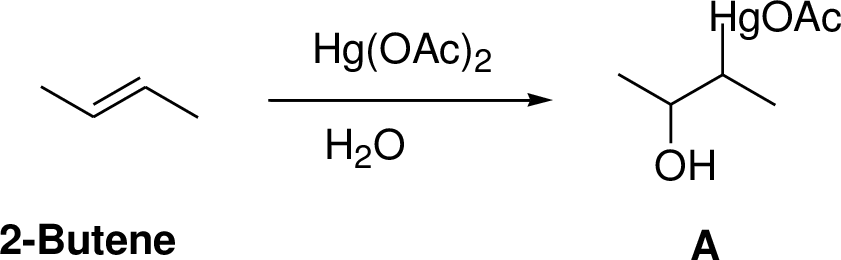
(h)
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction has to be predicted.
Concept interpretation:
Oxymercuration:
Alkenes reaction with mercuric acetate in the presence of water, the
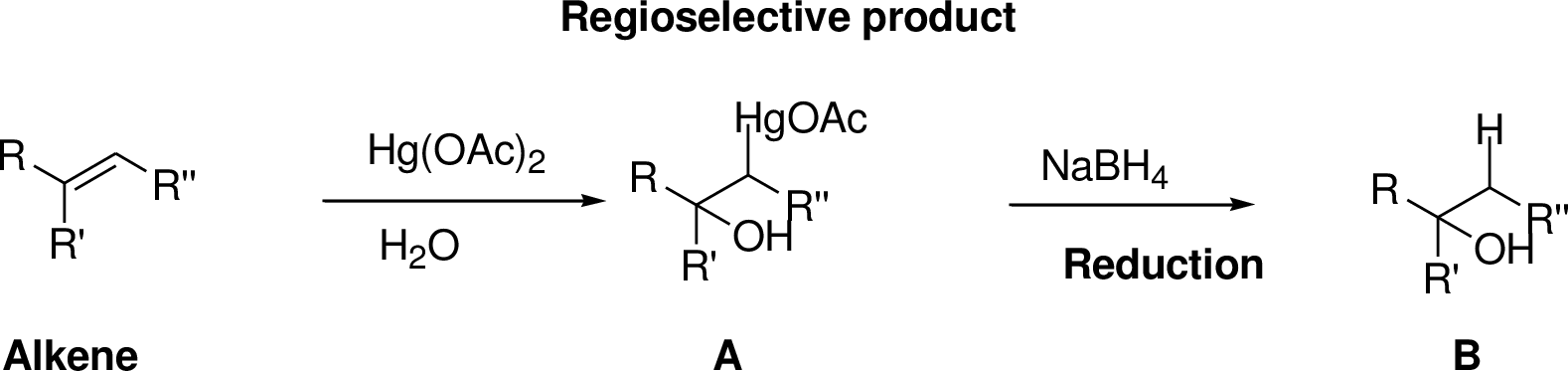
Explanation of Solution
2-Butene reacts reaction with mercuric acetate in the presence of water, the
The reaction is shown below,
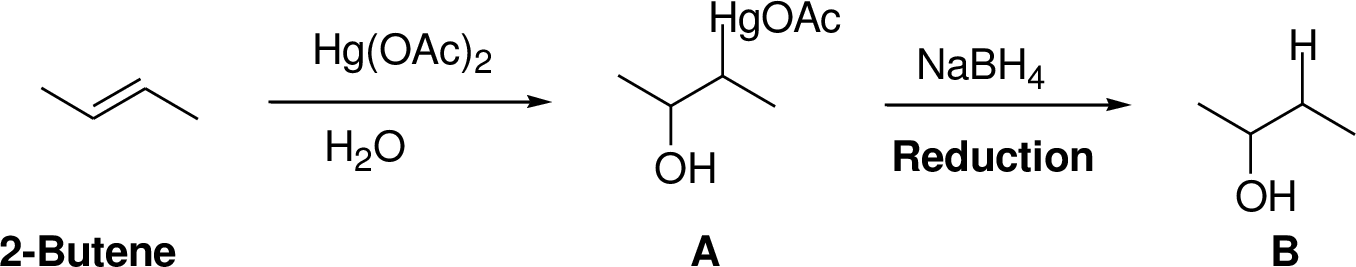
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Loose-leaf Version
- H H:O::::H H H HH H::O:D:D:H HH HH H:O:D:D:H .. HH H:O:D:D:H H H Select the correct Lewis dot structure for the following compound: CH3CH2OHarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point. ннннн -С-С-Н . н-с- ННННН H ΗΤΗ НННН TTTĪ н-с-с-с-с-о-н НННН НН C' Н н-с-с-с-с-н НН || Ш НННН H-C-C-C-C-N-H ННННН IVarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing dipole moment. |>||>||| ||>|||>| |>|||>|| |||>||>| O ||>>||| H F H F H c=c || H c=c F F IIIarrow_forward
- choose the description that best describes the geometry for the following charged species ch3-arrow_forwardWhy isn't the ketone in this compound converted to an acetal or hemiacetal by the alcohol and acid?arrow_forwardWhat is the approximate bond angle around the nitrogen atom? HNH H Harrow_forward
- OH 1. NaOCH2CH3 Q 2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv) H3O+ Select to Draw 1. NaOCH2 CH3 2. CH3Br (1 equiv) heat Select to Edit Select to Drawarrow_forwardComplete and balance the following half-reaction in acidic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. S₂O₃²⁻(aq) → S₄O₆²⁻(aq)arrow_forwardQ Select to Edit NH3 (CH3)2CHCI (1 equiv) AICI 3 Select to Draw cat. H2SO4 SO3 (1 equiv) HO SOCl2 pyridine Select to Edit >arrow_forward
- Complete and balance the following half-reaction in basic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. Zn(s) → Zn(OH)₄²⁻(aq)arrow_forwardb. ὋΗ CH3CH2OH H2SO4arrow_forwardFor the reaction A (g) → 3 B (g), Kp = 0.379 at 298 K. What is the value of ∆G for this reaction at 298 K when the partial pressures of A and B are 5.70 atm and 0.250 atm?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





