
Concept explainers
Account Analysis, Two-Stage Allocation, and Product Costing
Tiger Furnishings’s CFO believes that a two-stage cost allocation system would give managers better cost information. She asks the company’s cost accountant to analyze the accounts and assign
The analysis of overhead accounts by the cost accountant follows:
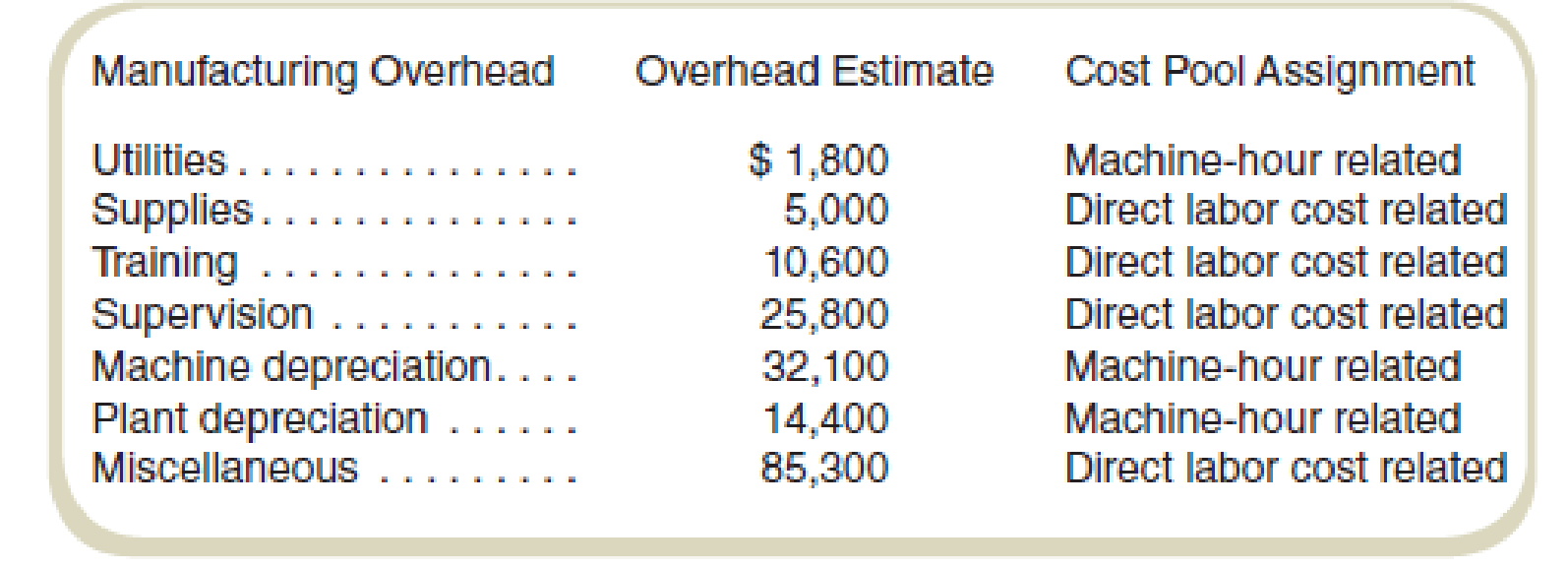
All other information is the same as in Exercise 6-39.
Required
- a. Draw the cost flow diagram that illustrates the two-stage cost allocation of overhead for Tiger Furnishings using the results of the cost accountant’s analysis of accounts.
- b. Compute the product costs per unit assuming that Tiger Furnishings uses direct labor costs and machine-hours to allocate overhead to the products.
a.
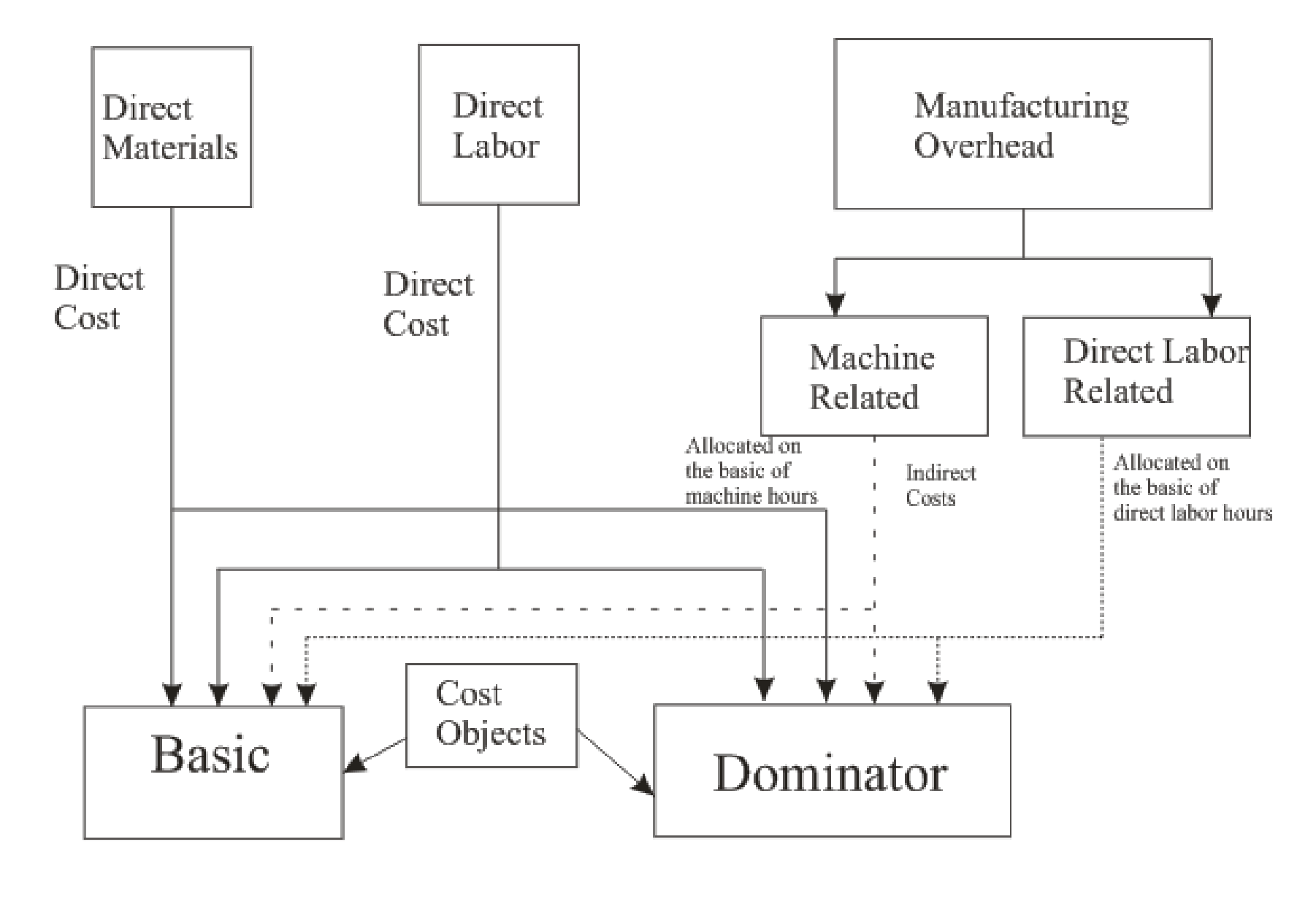
Draw the cost flow diagram that illustrates the two-stage cost allocation of overhead for Company T using the results of the cost accountant’s analysis of accounts.
Explanation of Solution
The cost flow diagram that illustrates the two-stage cost allocation of overhead for Company T using the results of the cost accountant’s analysis of accounts is as follows:
b.
Compute the product costs per unit using direct labor costs and machine-hours to allocate overhead to products.
Answer to Problem 53P
The value of cost per unit for Product Basic is $177 and for Product Dominator is $390.
Explanation of Solution
Cost per unit: The cost per unit is determined by dividing the total of variable and fixed cost with the total number of units.
Compute the cost per unit:
For Product Basic:
For Product Dominator:
Thus, the value of cost per unit for Product Basic is $177 and for Product Dominator is $390.
Working note 1:
For product Basic:
Compute the cost related to machine hours for Product Basic:
Working note 2:
Compute the cost related to direct labor cost for Product Basic:
Working note 3:
Compute the cost related to machine-hour for Product Dominator:
Working note 4:
Compute the cost related to direct-labor for Product Dominator:
Working note 5:
Compute the machine-hours rate for both the products:
Working note 6:
Compute the direct labor costs for both the products:
Working note 7:
Compute the total cost for the Product Basic:
Working note 8:
Compute the total cost of Product Dominator:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
GEN COMBO FUNDAMENTALS OF COST ACCOUNTING; CONNECT 1S ACCESS CARD
- Can you explain the correct methodology to solve this general accounting problem?arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting question with the appropriate accounting analysis techniques?arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting problem using appropriate accounting principles?arrow_forward
- I need help with this general accounting question using the proper accounting approach.arrow_forwardPlease provide the answer to this general accounting question with proper steps.arrow_forwardI am trying to find the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with the correct explanation.arrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning  Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning





