
Concept explainers
(a)
The production process without capital input.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
A production function of a firm shows the relationship between the output and two inputs, capital and labor. In this case, the firm follows the Cobb‑Douglas production function.
Here, this production function clearly shows that the firm produces the output using the inputs, capital, and labor at an equal proportion. Therefore, producer cannot build any coffee tables without tools (capital). If did so, the output would be zero.
(b)
The production process without labor input.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
As described in part (a), the firm follows the Cobb‑Douglas production function where the firm uses the inputs, capital, and labor at an equal proportion to produce the given level of output. Therefore, the producer cannot build any coffee tables without labor inputs. If did so, the output would be zero.
(c)
The short run production function.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The production economies state that the short-run is the period of time during which one or more inputs into production cannot be changed, which mean that the short run production function of a firm holds variable inputs as well as fixed inputs. Therefore, the short run production function shows the output as a function of variable input and the fixed input.
In this case, the fixed input, capital, is given as 16. Now substitute the respective value into the given Cobb‑Douglas production function to get the short run production function of the firm.
Therefore, the short run production function is
Fixed inputs: The fixed inputs are inputs that cannot be changed in the short run
Variable inputs: The variable inputs are inputs that can be changed in the short run.
(d)
The graphical representation of the production function.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Short run production function is given below (Derived in subpart (c)).
Substitute the labor of 1 unit in Equation (1) to calculate the output at that particular level.
In the short run, output with one unit of labor is 16 units.
Table 1 shows the output of different levels of labor.
Table 2
| Labor | Output |
| 1 | 16 |
| 4 | 32 |
| 9 | 48 |
| 16 | 64 |
| 25 | 80 |
Figure 1 shows the short-run production function.
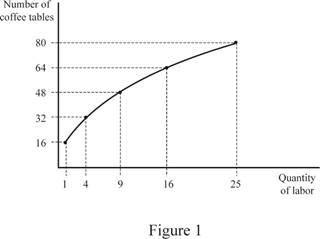
In Figure 1, the vertical axis shows the output and the horizontal axis shows the quantity of labor inputs. The production curve shows the possible level of output with different labor quantities.
(e)
The average and marginal product of labor.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
The marginal product can be calculated using the following equation.
Now substitute the respective in Equation (1) to get the value of marginal product at 4 units of labor inputs.
Therefore, the value of marginal product at 4 units of labor is 5.33.
The average product can be calculated using the following equation.
Now substitute the respective values in Equation (3) to get the value of average product at 4 units of labor inputs.
Therefore, the value of the average product at 4 units of labor is 8.
Table 2 shows the values of total product, marginal product, and average product using Equations (1), (2), and (3).
Table 2
|
Number of workers | Total product | Marginal product | Average product |
| 1 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| 4 | 32 | 5.33 | 8 |
| 9 | 48 | 3.2 | 5.33 |
| 16 | 64 | 2.29 | 4 |
| 25 | 80 | 1.78 | 3.2 |
Marginal product: A marginal product is the additional output that a firm can produce using an additional unit of an input, holding use of the other input constant.
Average product: An average product is the quantity of output produced per unit of input.
(f)
The total product, average product, and marginal product.
(f)
Explanation of Solution
In this case, the capital was fixed at 16 units. If there is a fall of 7 machines, then the capital will be 9
Therefore, the new short run production function is
Table 3 shows the values of total product, marginal product, and average product at each level of new output using equation (1), (2), and (3).
Table 3
|
Number of workers | Total product | Marginal product | Average product |
| 1 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| 4 | 24 | 4 | 6 |
| 9 | 36 | 2.4 | 4 |
| 16 | 48 | 1.71 | 3 |
| 25 | 60 | 1.33 | 2.4 |
Total product: The total product is the total quantity of output produced by a firm at the given time period.
Average product: An average product is the quantity of output produced per unit of input.
Marginal product: A marginal product is the additional output that a firm can produce using an additional unit of an input.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
EBK MICROECONOMICS
- Exercise 4A firm has the following average cost: AC = 200 + 2Q – 36 Q Find the stationary point and determine if it is a maximum or a minimum.b. Find the marginal cost function.arrow_forwardExercise 4A firm has the following average cost: AC = 200 + 2Q – 36 Q Find the stationary point and determine if it is a maximum or a minimum.b. Find the marginal cost function.arrow_forwardExercise 2A firm has the following short-run production function: Q = 30L2 -0.5L3a. Make a table with two columns: Production and Labour b. Add a third column to the table with the marginal product of labour c. Graph the values that you estimated for the production function and the marginal product oflabour Exercise 3A Firm has the following production function: Q= 20L-0.4L2a. Using differential calculus find the unit of labour that maximizes the production. b. Estimate function of Marginal product of labor c. Obtain the Average product of labor. d. Find the point at which the Marginal Product of Labour is equal to the Average Product of Labour.arrow_forward
- Problem 3 You have the following data for the last 12 months' sales for the PRQ Corporation (in thousands of dollars): January 500 July 610 February 520 August 620 March 520 September 580 April 510 October 550 May 530 November 510 June 580 December 480 1. Calculate a 3-month centered moving average. 2. Use this moving average to forecast sales for January of next year. 3. If you were asked to forecast January and February sales for next year, would you be confident of your forecast using the preceding moving averages? Why or why not? expect? Explain.arrow_forwardProblem 5 The MNO Corporation is preparing for its stockholder meeting on May 15, 2013. It sent out proxies to its stockholders on March 15 and asked stockholders who plan to attend the meeting to respond. To plan for a sufficient number of information packages to be distributed at the meeting, as well as for refreshments to be served, the company has asked you to forecast the number of attending stockholders. By April 15, 378 stockholders have expressed their intention to attend. You have available the following data for the last 6 years for total attendance at the stockholder meeting and the number of positive responses as of April 15: Year Positive Responses Attendance 2007 322 520 2008 301 550 2009 398 570 2010 421 600 2011 357 570 2012 452 650 1. What is your attendance forecast for the 2013 stockholder meeting? 2. Are there any other factors that could affect attendance, and thus make your forecast inac- curate?arrow_forwardProblem 4 Office Enterprises (OE) produces a line of metal office file cabinets. The company's economist, having investigated a large number of past data, has established the following equation of demand for these cabinets: Q=10,000+6013-100P+50C Q=Annual number of cabinets sold B = Index of nonresidential construction P = Average price per cabinet charged by OE C=Average price per cabinet charged by OE's closest competitor It is expected that next year's nonresidential construction index will stand at 160, OE's average price will be $40, and the competitor's average price will be $35. 1. Forecast next year's sales. 2. What will be the effect if the competitor lowers its price to 832? If it raises its price to $36? 3. What will happen if OE reacts to the decrease mentioned in part b by lowering its price to $37? 4. If the index forecast was wrong, and it turns out to be only 140 next year, what will be the effect on OE's sales? If not, what does it measure?arrow_forward
- Name: Problem 1: Managerial Economics, Assignment 5 April 20, 2025 If the sales of your company have grown from $500,000 five years ago to $1,050,150 this year, what is the compound growth rate? If you expect your sales to grow at a rate of 10 percent for the next five years, what should they be five years from now?arrow_forward1. In this question, assume all dollar units are real dollars in billions. For example, $100 means $100 billion. Argentina thinks it can find $105 of domestic investment projects with a marginal product of capital (MPK) equal to 10% (each $1 invested in year 0 pays off $0.10 in every later year). Assume a world real interest rate r*is 5%, and initial external wealth W (W in year -1) is 0. a. You find that the formula on the lecture slide: > r*, which means that a country will ΔΟ AK take on investment projects as long as the marginal product of capital (MPK) is at least as high as the real interest rate. Using this formula, answer if Argentina should conduct the project. b. If the projects are not done, GDP = Q = C = $200 in all years. Compute the present value of Q and C. c. If Argentina conducts the projects (investing $105), what is the present value of Q and C? d. If Argentina conducts the projects, what is the present value of C? Is Argentina better off with the investment?arrow_forward2. Consider a world of two countries: Highland (H) and Lowland (L). Each country has an average output of 9 and desires to smooth consumption. All income takes the form of capital income and is fully consumed each period. Initially, there are two states of the world: Pandemic (P) and Flood (F) each occurring with 50% probability. Pandemic affects Highland and lowers the output there to 8, leaving Lowland unaffected with an output of 10. Flood affects Lowland and lowers the output there to 8, leaving Highland unaffected with an output of 10. a. Assume that households in each country own the entire capital stock of their own land. Fill in the numbers on the following table. Pandemic Highland's income Lowland's income Flood Variation about the mean b. Assume that each country owns 50% of the other country's capital. Fill in the numbers on the following table. Pandemic Flood Variation about the mean Highland's income Lowland's income c. Compare your answer to (a) and (b). Does…arrow_forward
- 3. This question explores IS and FX equilibria in a numerical example. a. The consumption function is C = 1.5 + 0.8(Y - T). What is the marginal propensity to consume (MPC)? What is the marginal propensity to save (MPS)? b. The trade balance is TB = 5 [1-()] - (0.2(Y-8). What is the marginal propensity to consume foreign goods (MPCF)? What is the marginal propensity to consume home goods(MPCH)? c. The investment function is I = 3 - 10i. What is investment when the interest rate is equal to 0.10=10%. d. Assume government spending is G. Add up the four components of demand and write down the expression for D. Make sure that you simplify the equation. e. Derive the equation for the good market equilibrium using Y = D.arrow_forward1. A firm has the following demand function: P = 60 – 0.5Q and its total cost is defined by TC= 13+ Qa. Find the maximum revenue b. Find the production to optimize the profit. c. Verify if the marginal revenue and marginal cost are the same at the profit-maximizing productionlevel. Exercise 6From the point of view of the firm, what decision criteria have been found relevant in the analysis ofproduction and profit? Provide two refernces with your answer.arrow_forward5. Some people find options expensive and use more complex structures to reduce the cost. For example, consider buying a call with a strike of $55 and selling a call with a strike of $60. a. What is the cost of establishing this combined position? b. What is the payoff of the combined position if the market price goes to $60? c. What is the payoff of the combined position if the market price goes to $100?arrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





