
Concept explainers
1.
Calculate the equivalent units of transferred-in, direct materials and conversion using weighted average method.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Equivalents units for production: Equivalents units are a measure of the work done during an accounting period. It includes the beginning and closing inventory of work in process and they also provide information relating to work on units that are completely processed during the period
Calculate the equivalent units of transferred-in, direct materials and conversion using weighted average method.
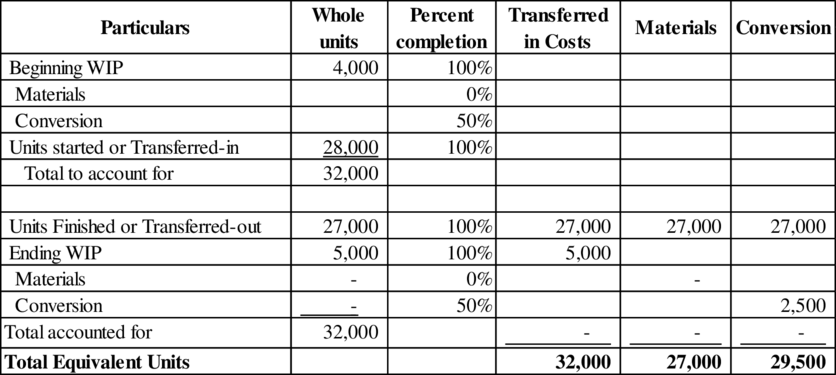
(Table 1)
2.
Compute the unit cost of transferred-in, direct materials and conversion department.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Compute the unit cost of transferred-in, direct materials and conversion department.
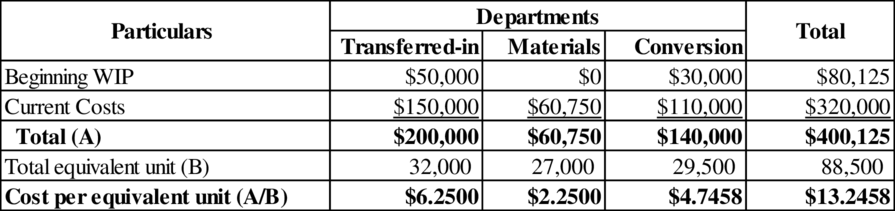
(Table 2)
3.
Determine the amount goods completed and transferred out during July.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Compute the amount goods completed and transferred out during July.
Therefore, the amount goods completed and transferred out during July is $357,750.
4.
Calculate the cost of work in process for the month of July.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the cost of work in process of transferred-in for the month of July.
Calculate the cost of work in process of conversion for the month of July.
Therefore, the cost of work in process for the month July is
5.
Prepare
5.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare journal entry to record the materials.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
|
Work in process inventory | 60,750 | ||
| Materials inventory | 60,750 | ||
| (To record the direct materials) |
(Table 3)
- Work in process inventory is an asset and there is an increase in the value of an asset. Hence, debit the work in process inventory $60,750.
- Materials inventory is an asset and there is a decrease in the value of an asset. Hence, credit the materials inventory by $60,750.
Prepare journal entry to record the labor assuming that labor is 50% of conversion cost.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
|
Work in process inventory (1) | 55,000 | ||
| Accrued payroll | 55,000 | ||
| (To record the direct materials) |
(Table 4)
- Work in process inventory is an asset and there is an increase in the value of an asset. Hence, debit the work in process inventory $55,000
- Accrued payroll is an expense and there is an increase in the value of equity. Hence, credit accrued payroll by $55,000.
Prepare journal entry to record the
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Work in process inventory | 55,000 | ||
| Factory overhead | 55,000 | ||
| (To record |
(Table 5)
- Work in process inventory is an asset and there is an increase in the value of an asset. Hence, debit the work in process inventory account with $55,000.
- Factory overhead (Expense) is a component of
stockholder’s equity and there is a decrease value of expense. Hence, credit the factory overhead account by $55,000.
Prepare journal entry to record the finished product.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Finished goods inventory | 357,750 | ||
| Work in process inventory | 357,750 | ||
| (To transfer cost of jobs completed to finished goods inventory) |
(Table 6)
- Finished goods inventory is an asset and there is an increase in the value of an asset. Hence, debit the finished goods inventory account with $357,750.
- Work in process inventory is an asset and there is a decrease in the value of an asset. Hence, credit the work in process inventory account with $357,750.
Working notes:
Calculate the amount of labor cost.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Cost Management: A Strategic Emphasis
- Solve with explanation and accounting questionarrow_forwardPlease provide the correct answer to this general accounting problem using valid calculations.arrow_forwardHonda Corporation had beginning raw materials inventory of $34,500. During the period, the company purchased $128,000 of raw materials on account. If the ending balance in raw materials was $22,700, the amount of raw materials transferred to work in process inventory is?arrow_forward
- Calculate the gross profit for salvatore companyarrow_forwardAt the beginning of the recent period there were 1,250 units of product in a department, one-half completed. These units were finished and an additional 4,850 units were started and completed during the period. 1,100 units were still in process at the end of the period, one-third completed. Using the weighted-average valuation method the equivalent units produced by the department were ____Units. (Round your answer to nearest unit)arrow_forwardI am looking for the correct answer to this general accounting problem using valid accounting standards.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





